SEO Best Practices
What Are SEO Best Practices?
SEO best practices are a set of tasks that aim to improve a website’s search engine ranking. These practices include on-site optimization, keyword research, and backlink building. By implementing these practices, website owners can increase their website’s visibility and attract more organic traffic.
Put another way:
There are a million things you can do to get higher Google rankings (including advanced SEO strategies and techniques).
But it’s important to get the basics of SEO first.
In other words: you want to make sure that your site follows current SEO best practices. That’s the foundation.
Then, once you get your foundation in place, dive into new and advanced approaches.
With that, here are the 10 most important SEO fundamentals you need to know:
- Add Your Main Keyword Early On In Your Content
- Write Unique Titles, Descriptions and Content
- Optimize Your Title Tag for SEO
- Improve Your Site’s User Experience
- Optimize Your Site’s Loading Speed
- Track Your Results With The Google Search Console
- Optimize Images for SEO
- Use Internal Linking
- Publish Amazing Content
- Build Backlinks To Your Website
1. Add Your Main Keyword Early On In Your Content
It’s no secret that you want to use your keyword a handful of times on your page.
But you may not know that the location of your keyword also makes a difference.
Specifically, you want to mention your main keyword at least once at the top of your page.
Why does this matter?
Google puts more weight on terms that appear at the top of a webpage.

For example, this page on my site is optimized around “mobile seo”.
So I mentioned that term once in the first 25 words of my content.

Simple.
2. Write Unique Titles, Descriptions and Content
Avoiding duplicate content is one of the most important SEO best practices to keep in mind.
In fact, Google has stated that you should avoid “duplicate or near-duplicate versions of your content across your site.”

And this rule applies to every piece of content on your website, including:
- Title tags
- Meta description tags
- Ecommerce product pages
- Landing pages
- Image alt text
- Category pages
Basically: if you publish a page on your site, the content on that page has to be 100% unique.
If you run a small blog with a homepage and a bunch of blog posts, this rule is pretty easy to follow.
But if you’re an eCommerce site owner with thousands of products, writing unique content for each page can be tricky.
Tricky… but worth it.
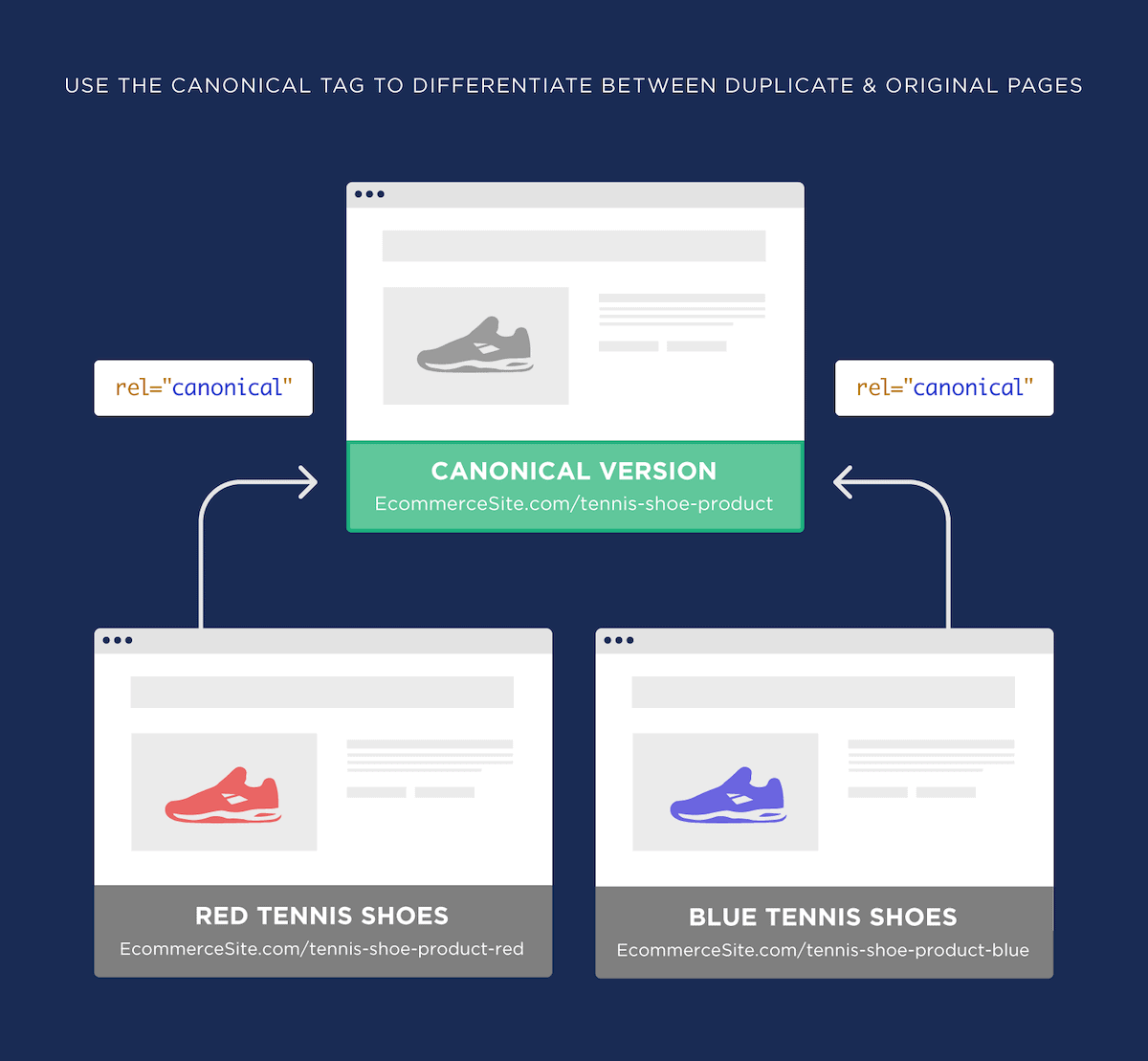
If you’re having trouble writing content for each page, consider combining pages that have similar content together. Or use the canonical tag.
3. Optimize Your Title Tag for SEO
When it comes to on-page SEO, your title tag is KEY.
Google has even said that: “it’s important to use high-quality titles on your web pages.”.

Here’s how to get the most out of your page’s title tag:
Front-load Your Main Keyword: “Front-load” simply means that you start your title tag with your target keyword.
Why is this important?
Well, search engines pay close attention to the terms that you use in your title tag. This is why you want your keyword in your page title.
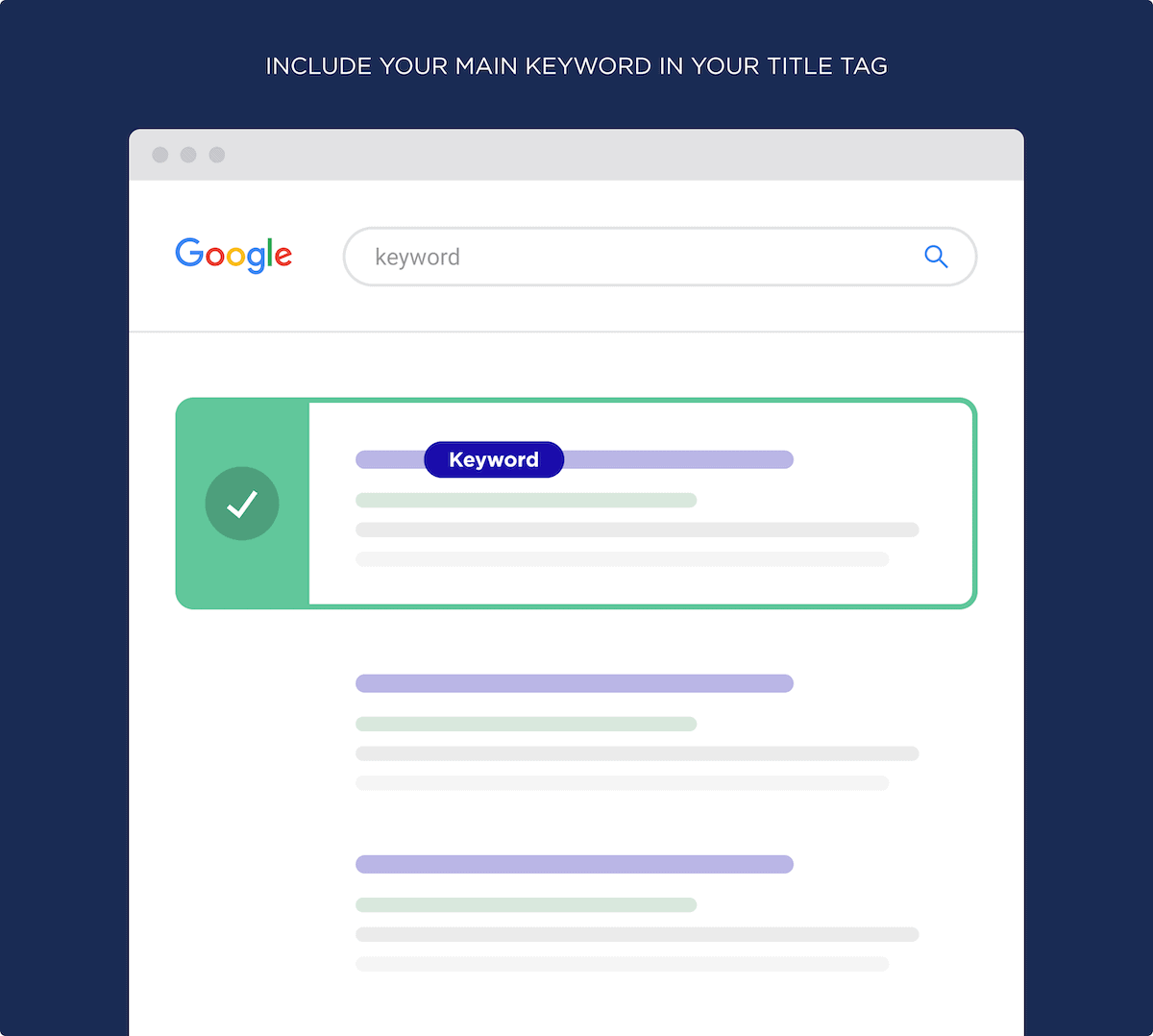
But what you may not know is that Google also puts more emphasis on words and phrases that show up early in your title tag.
So if it makes sense, start your title off with the keyword that you want to rank for.
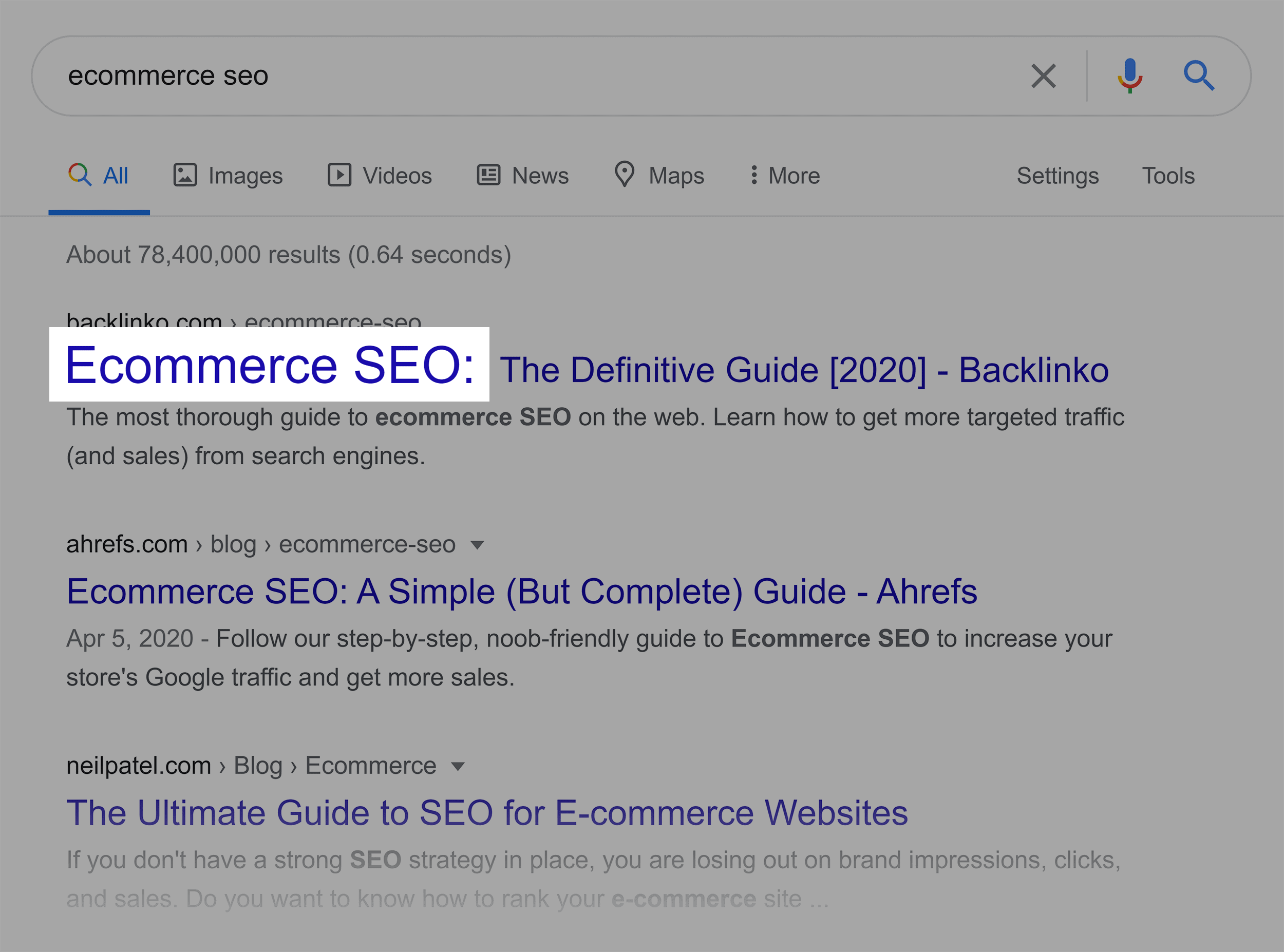
For example, I currently rank #1 for the super competitive term “eCommerce SEO”.
And my title tag starts off with that exact phrase.
Sometimes it’s not possible to use your keyword that early on because it will make your title tag look weird. Yes, search engine optimization is important. But your title tags need to be useful for users too.
(More on that later)
If you’re not able to start your title tag off with a keyword, no biggie. Just include your keyword as early on as you can.
For example, this page is optimized around the keyword “SEO strategy”.
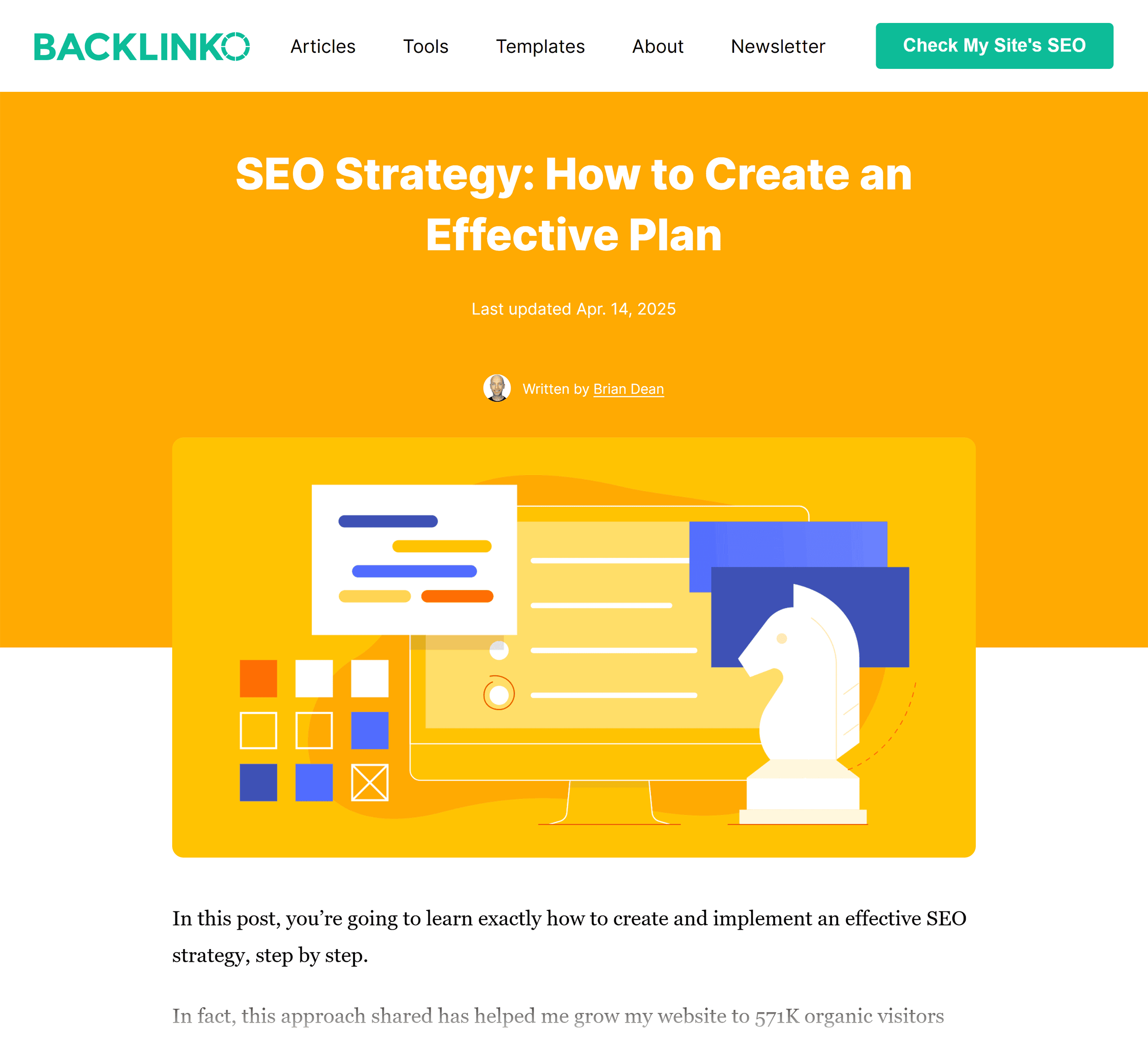
I couldn’t figure out a way to include the keyword “SEO strategy” really early in my title. So I just used my keyword as early as I could.

It’s not right in the beginning. But it’s early enough so that Google can see that my page is clearly about “SEO strategy”.
Use One Keyword Per Title: Google has been really clear on this.
They don’t want you to stuff your title with a bunch of different keywords.
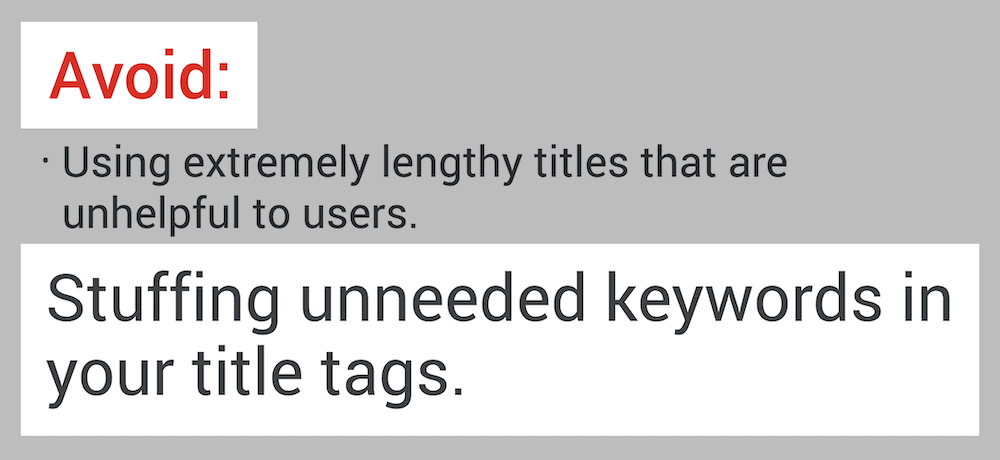
(Also known as “keyword stuffing”)
Instead, you want to use one main keyword in your title. And if your page is high-quality, you’ll naturally rank for that keyword… and lots of others.
For example, this page on my site was, at one time, optimized around the term: “keyword research”.
And, as you can see, I use that term in my title tag.
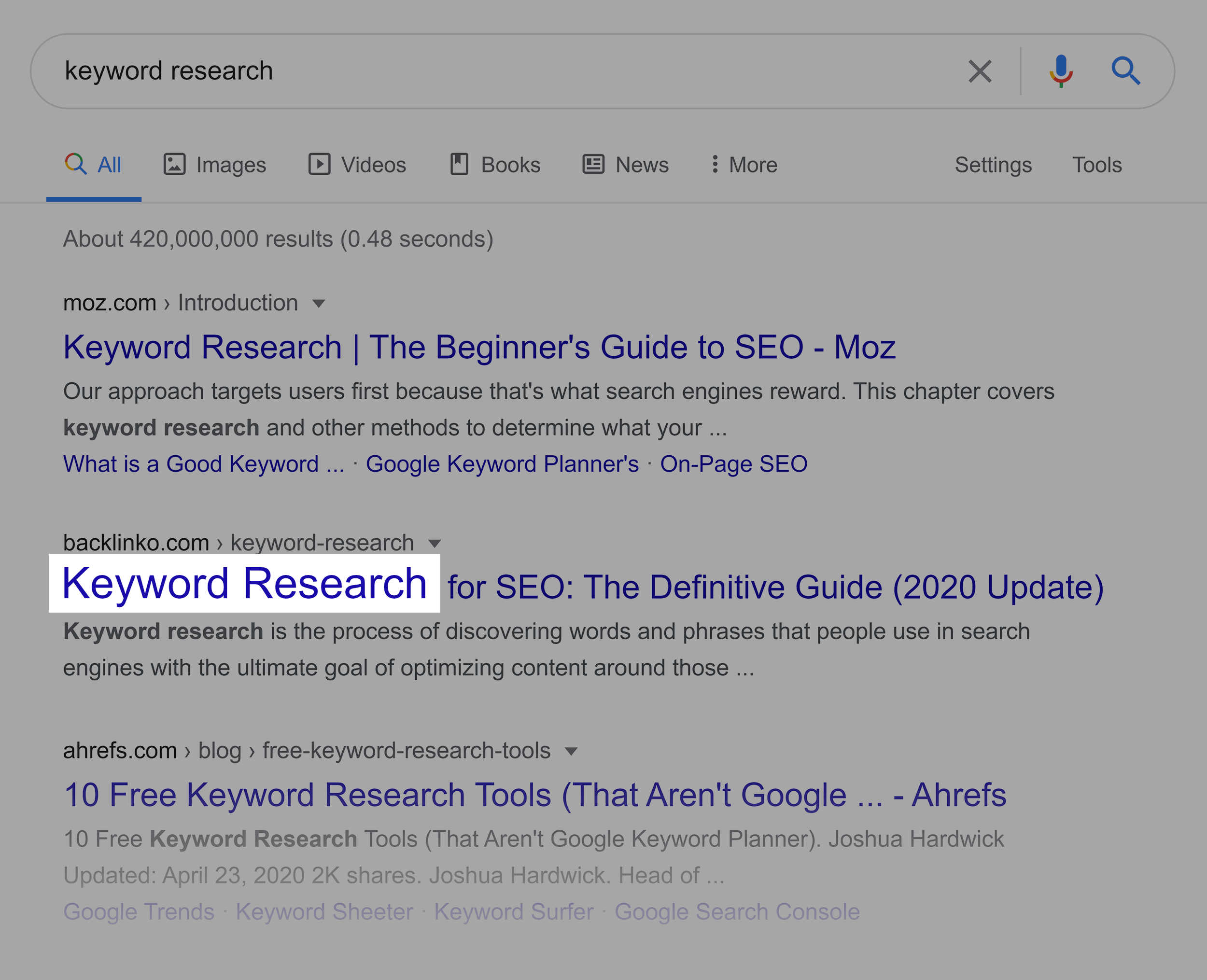
The other words and phrases in my title are just to highlight what my page is actually about.
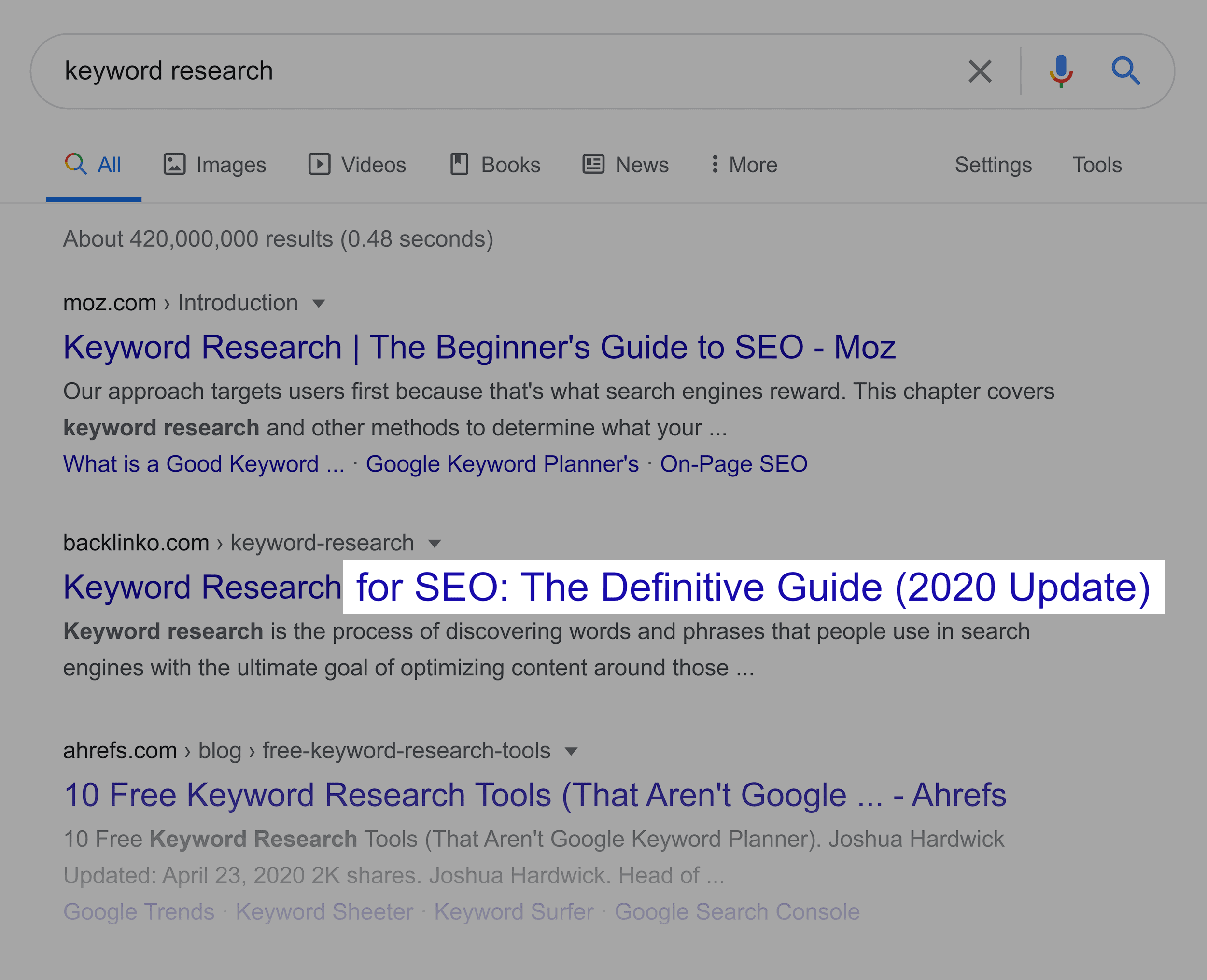
And because my page contains high-quality content, it ranks in the top 5 for my main keyword.
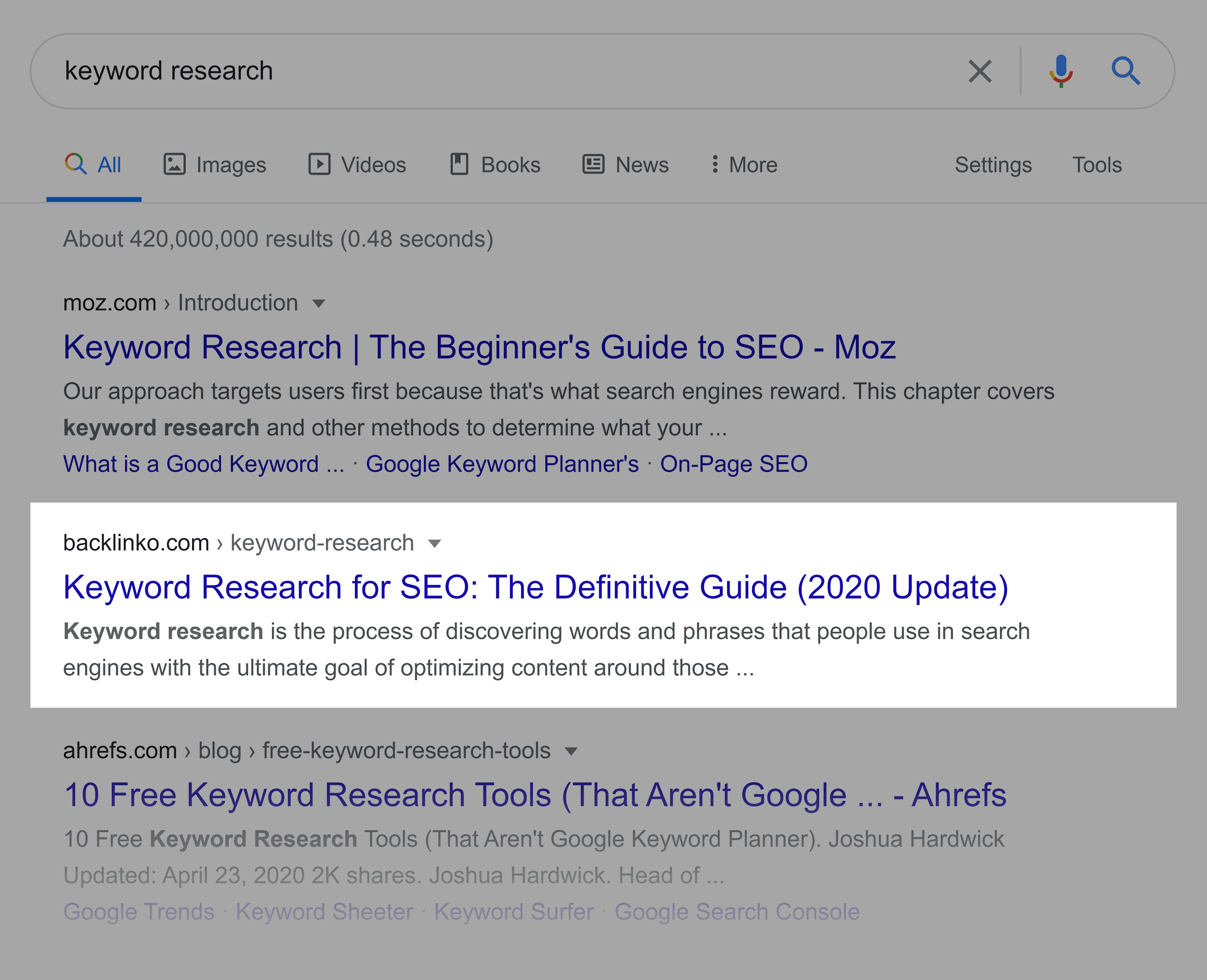
And, according to Semrush, this page also ranks for 5.9k different keywords.
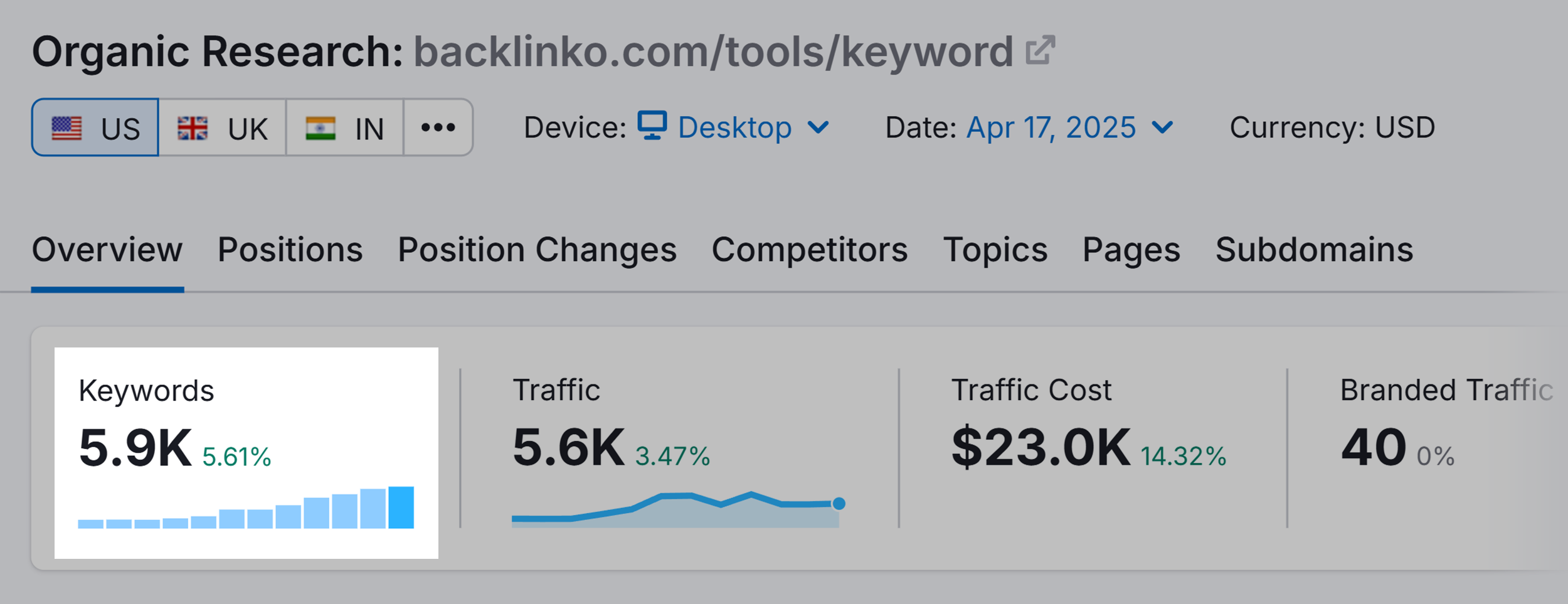
Did I optimize my page around 5.9k keywords? Nope!
Instead, I optimized my page (and title) around ONE important keyword. And Google largely took care of the rest.
Write Compelling, Shareable Titles: Your title tags should make people want to click on your page to learn more.
Why?
When lots of people click on your result in Google, you can find yourself with higher rankings for that term.
This is why, once my SEO stuff is taken care of, I then start optimizing my title for clicks and shares.
In other words:
I try to write title tags that are interesting, compelling and push people to share.
For example, this list of content marketing tools has an eye-catching title.
4. Improve Your Site’s User Experience
Improving your site’s user experience (UX) can, directly and indirectly, help with your SEO.
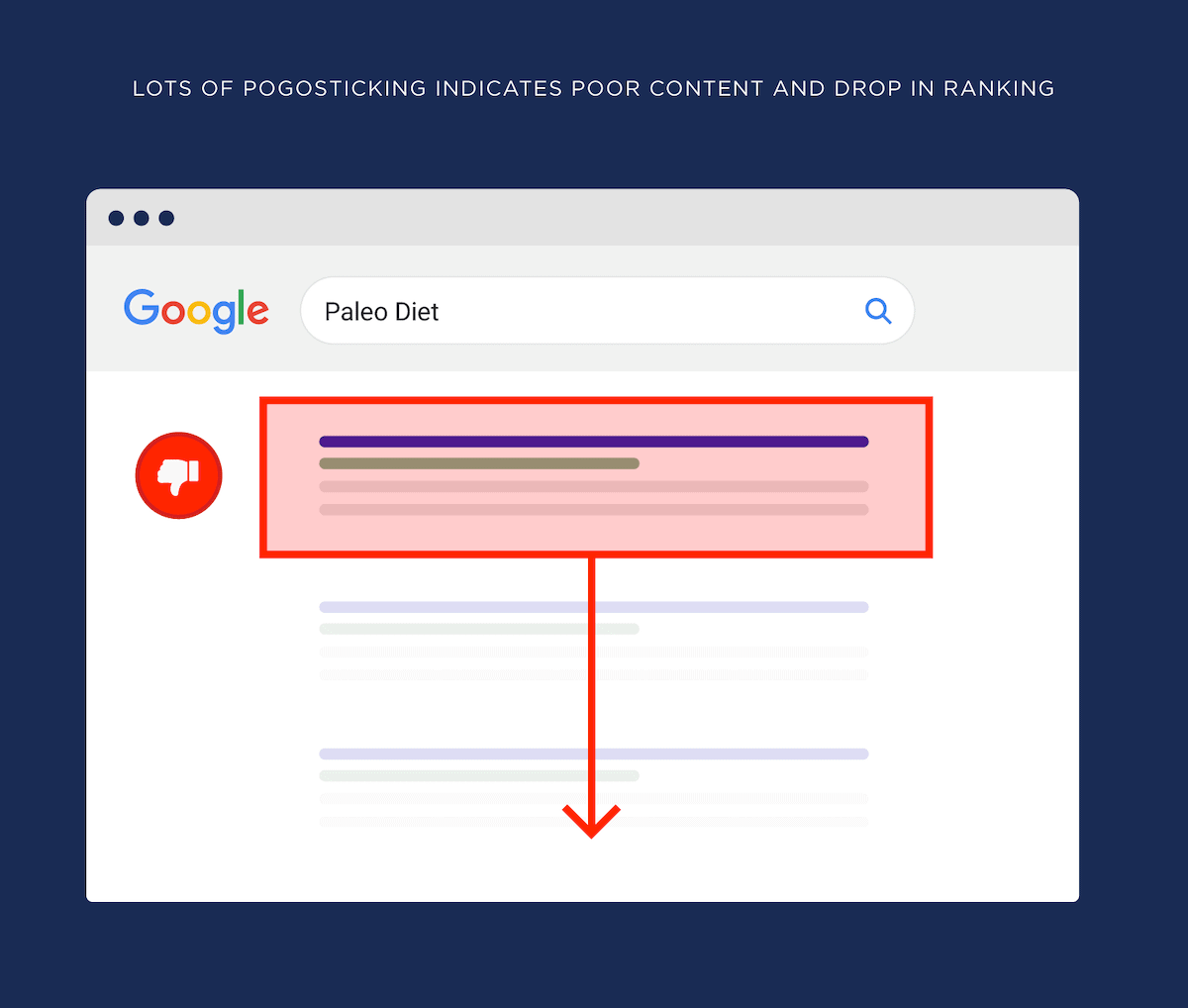
UX can directly help with SEO because Google knows when people start “Pogo sticking” after landing on your site from the search results.
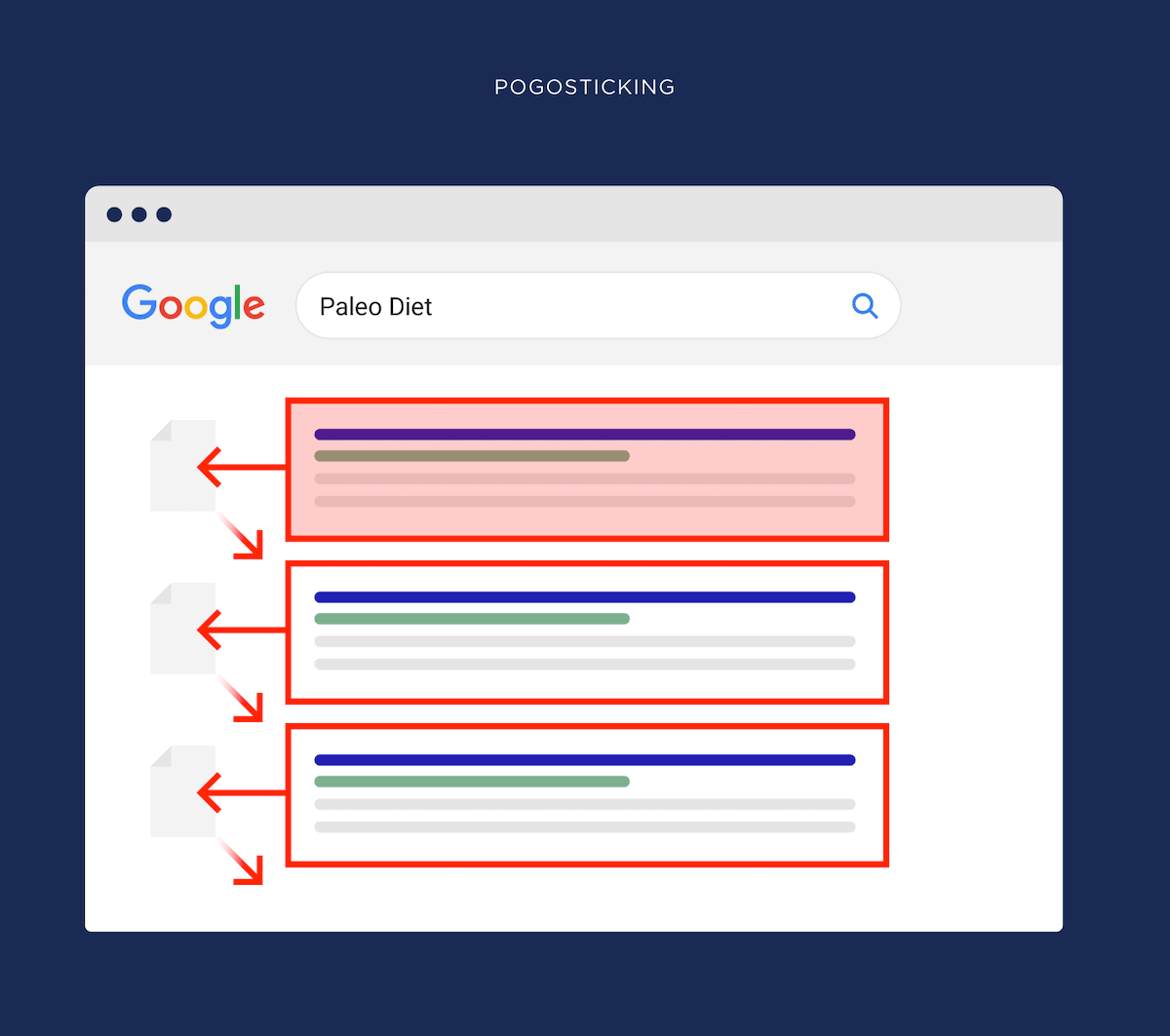
If enough people bounce from your site to the search engine results, this tells Google that your result didn’t give that searcher what they were looking for.
And your search engine rankings can start to dip.
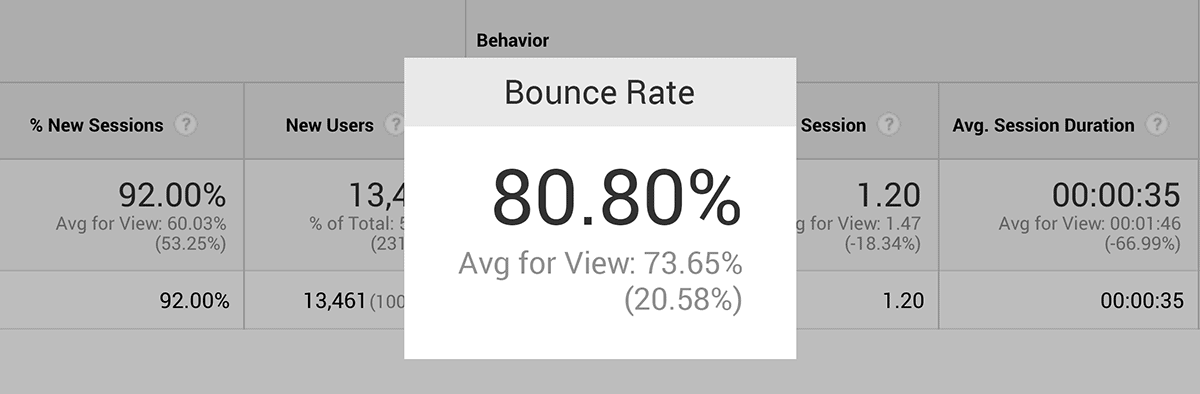
You can get a proxy measurement of Pogo sticking from Google Analytics. If your page has a really high bounce rate, this might be a sign that users aren’t finding what they’re looking for.
UX can indirectly help with SEO because people are more likely to share and link to user-friendly site.
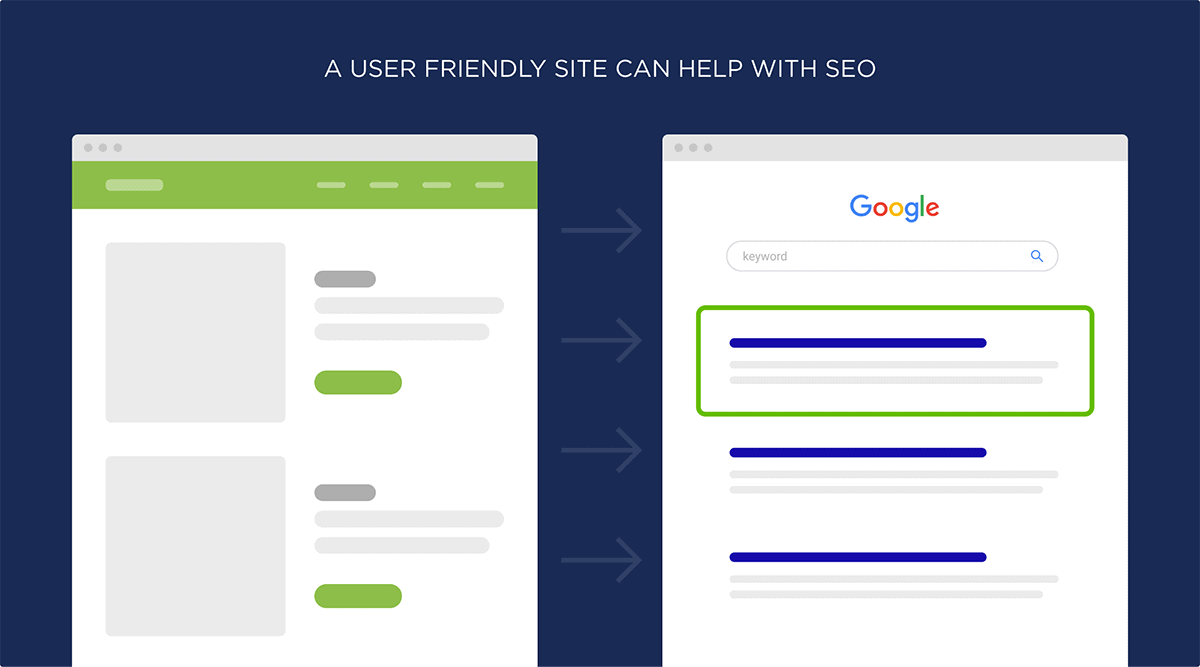
So if your site is hard to use, uses intrusive popups and ads, and has a bunch of broken links… people aren’t going to link to it.
(Even if you have great content.)
So yeah, UX is something that every site owner should pay attention to anyway. It just so happens that great UX can give your SEO a boost too.
5. Optimize Your Site’s Loading Speed
Google usually doesn’t talk publicly about the ranking factors in their algorithm.
So when they talk a lot about a specific ranking signal, you KNOW it’s a big deal.
Site loading speed is one of those rare ranking factors.
This is why I highly recommend making your site load as quickly as possible.
(Especially on mobile devices.)
Your first step is to benchmark your site’s current loading speed. That way, you know where you’re at before you start making changes.
I recommend the super-helpful PageSpeed Insights tool.
After all, the recommendations you get from this tool come from Google themselves.
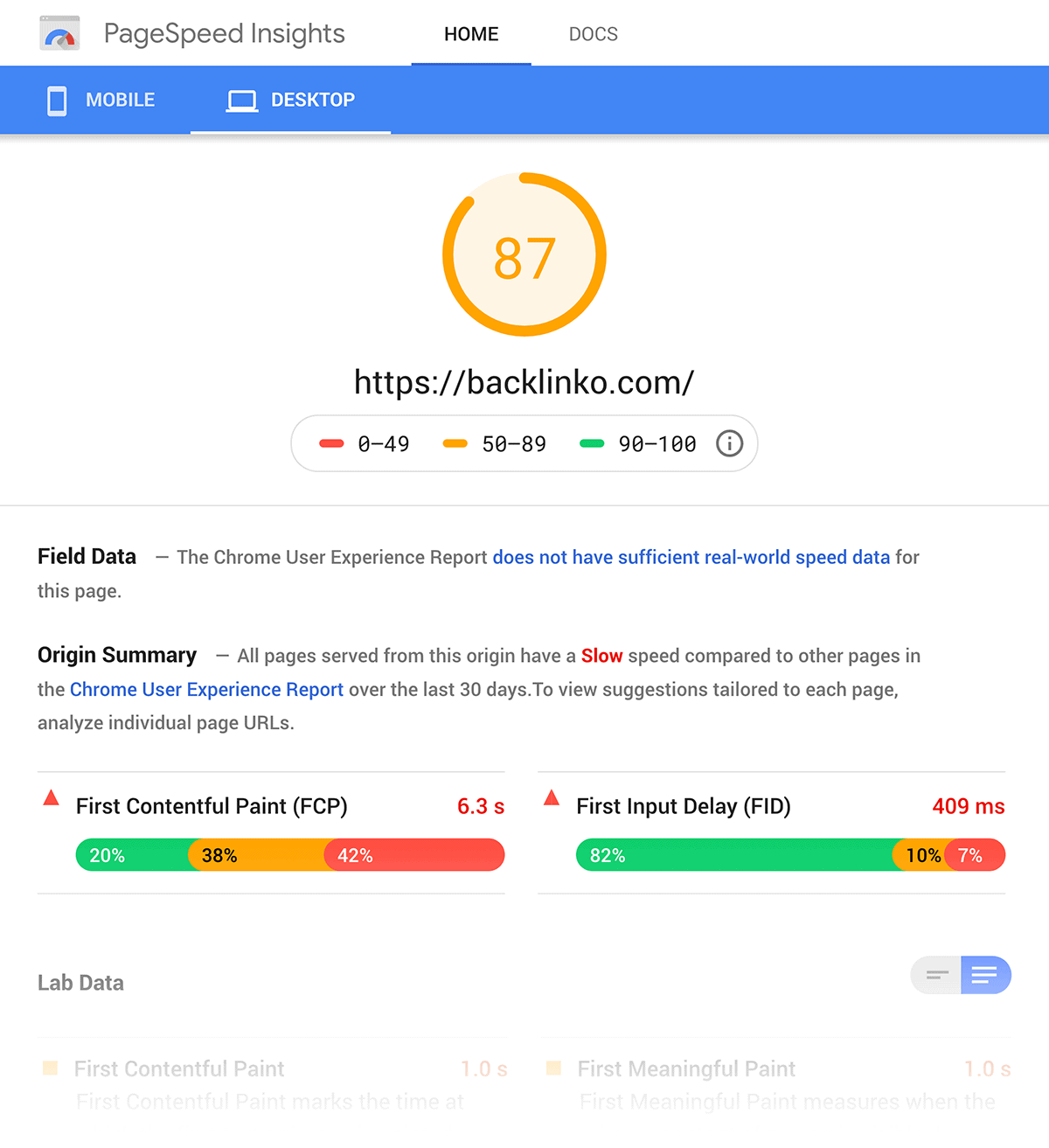
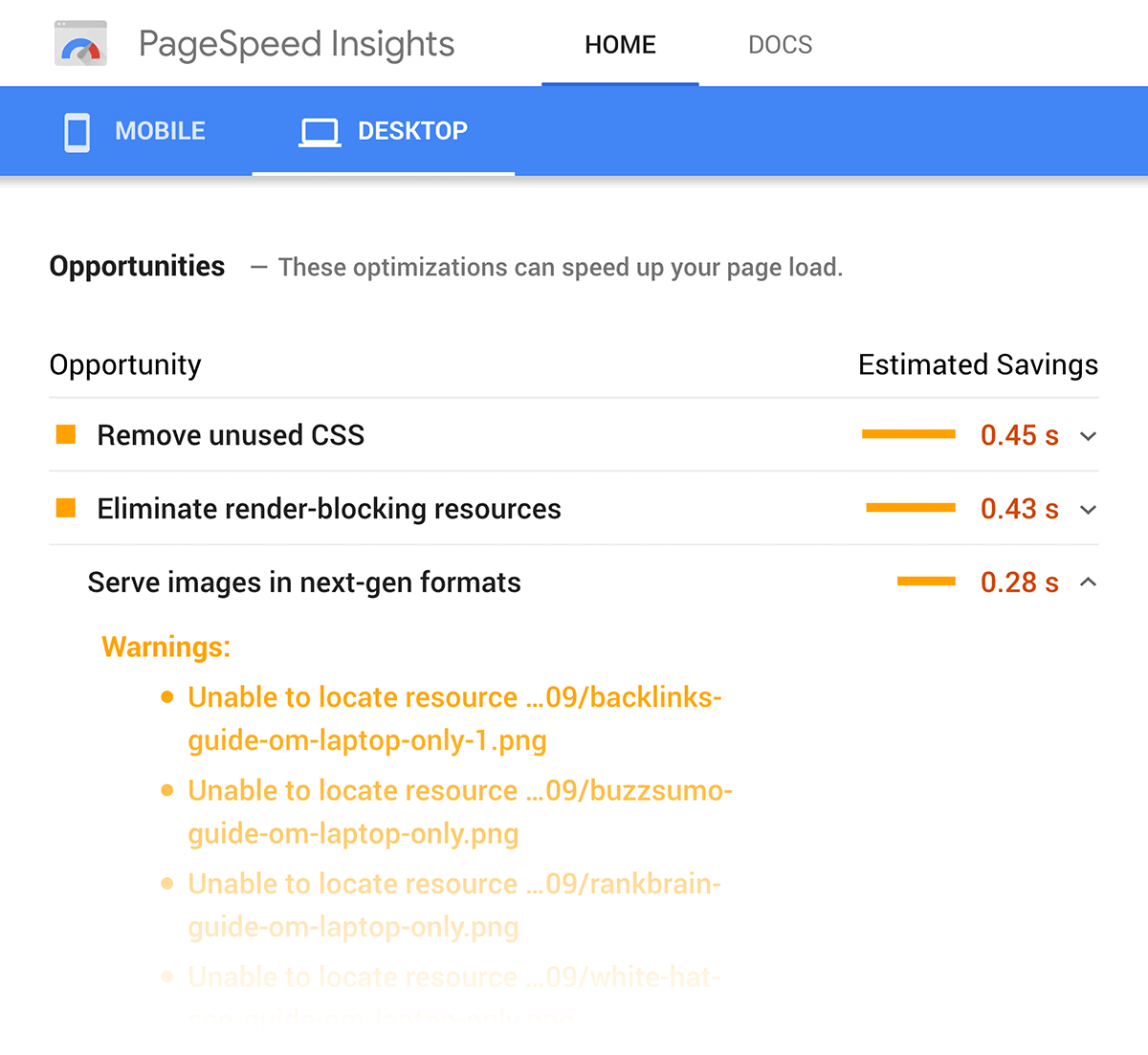
Plus, it doesn’t just tell you if your page is fast or slow. The tool gives you a detailed report that includes ways you can improve.
If you want to dig deeper with page speed stuff, check out Web Page Test.
It’s a free tool that tends to give a more accurate feel of how your site loads to actual users.
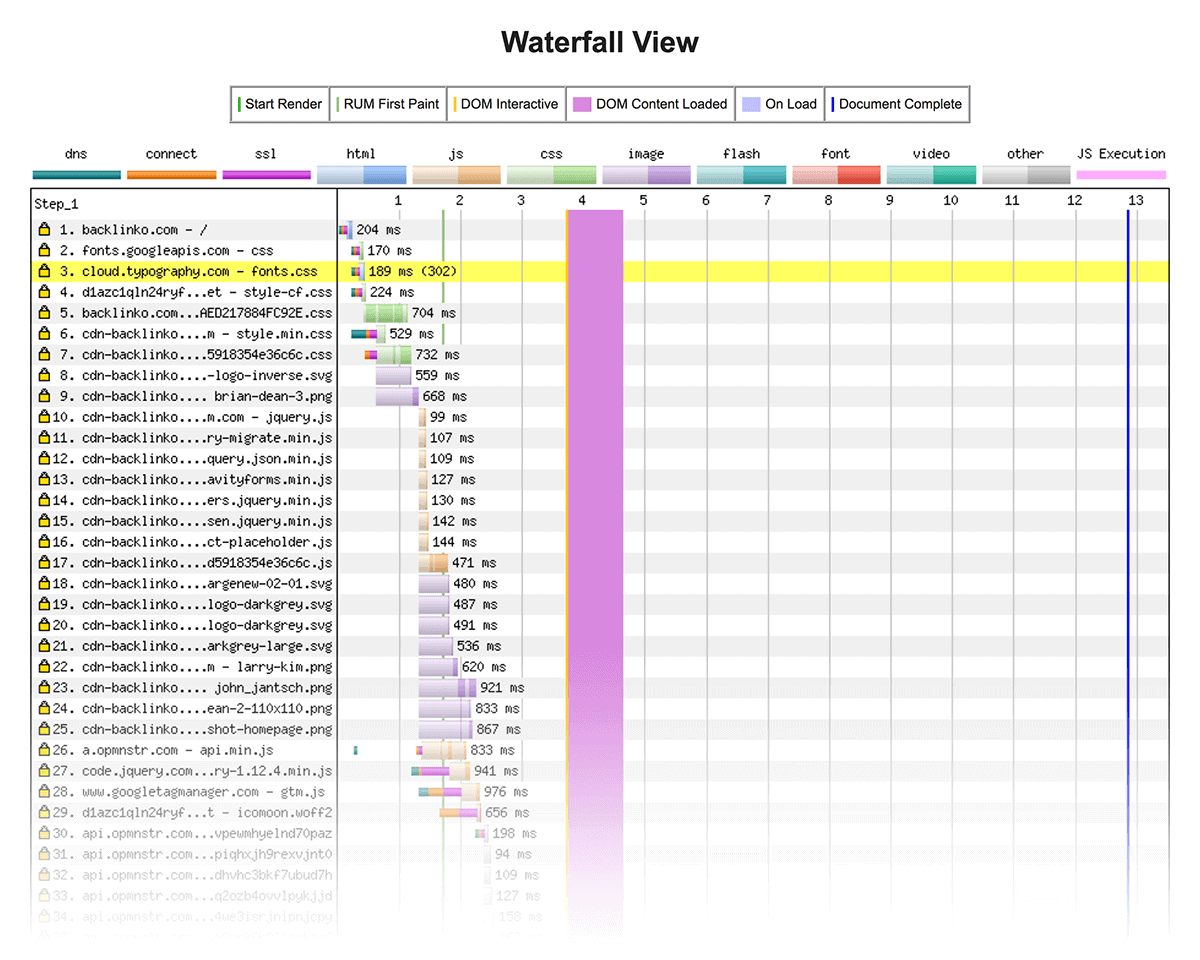
Either way, here are a few ways you can improve your site’s loading speed.
- Compress Images: This is a big one. Images tend to make up the bulk of a page’s size (in terms of KB). Which is why I recommend using a tool like Kraken.io to shrink your image sizes.
- Use Lightweight Themes: Bulky WordPress themes can slow things down. So if your theme isn’t optimized for speed, consider switching to one that is.
- Use Lazy Loading: Lazy loading images can boost your site’s loading speed by 50% or more. The downside is that images show up as users scroll down the page, which isn’t great for UX. So it’s a tradeoff.
- Use a CDN: CDNs serve images and other media on your site on servers that are close to your users.
6. Track Your Results With The Google Search Console
If you don’t have the Google Search Console setup, you’re flying blind with your SEO.
The Search Console is like a live dashboard that lets you know how your site is doing in the SERPs (Search Engine Results Pages).
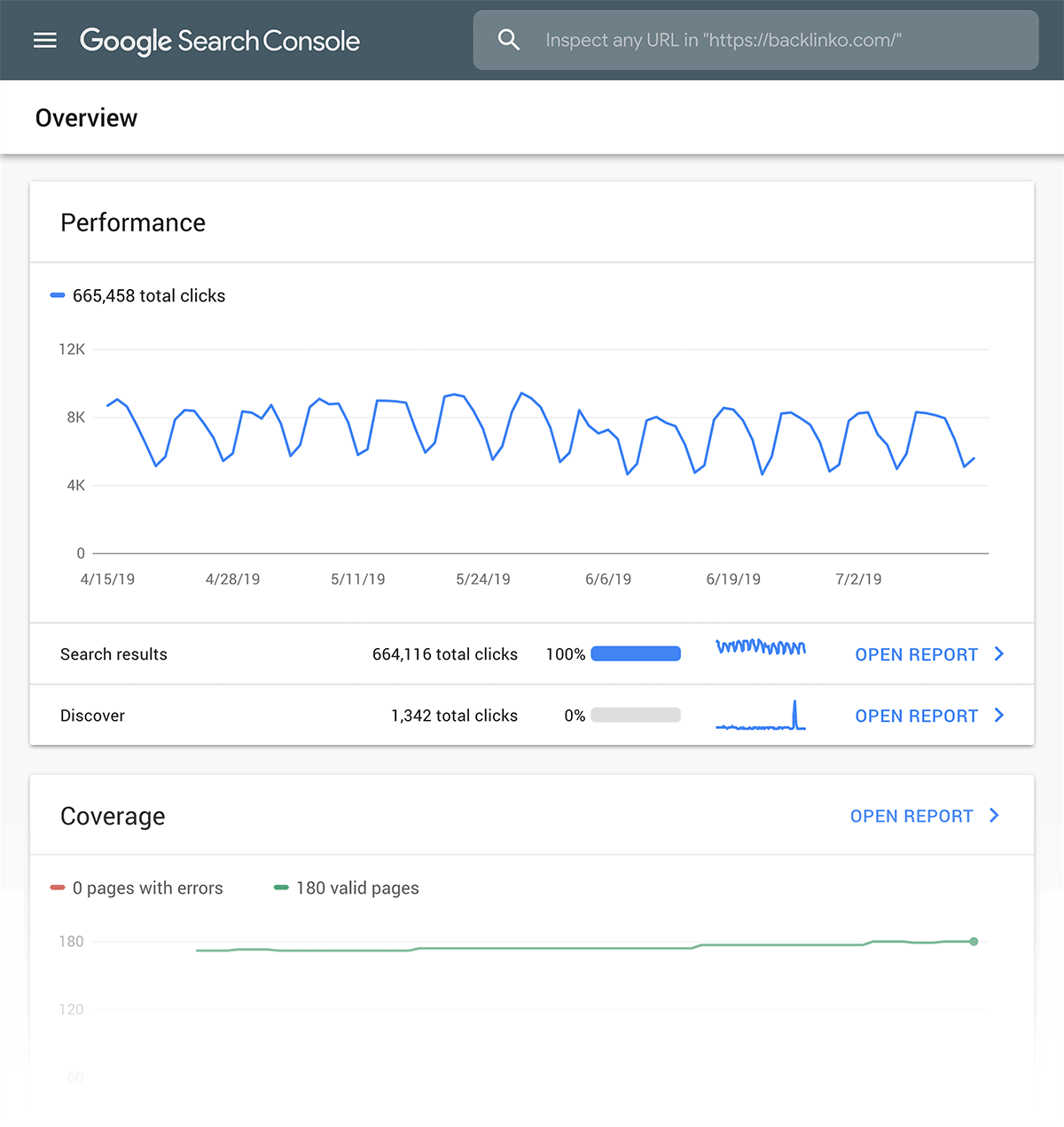
There are a lot of cool features and tools in the Search Console.
But you probably won’t need most of them.
Instead, I recommend checking these 3 reports on a regular basis.
Performance: This data lets you know how many people see and click on your site in Google search.
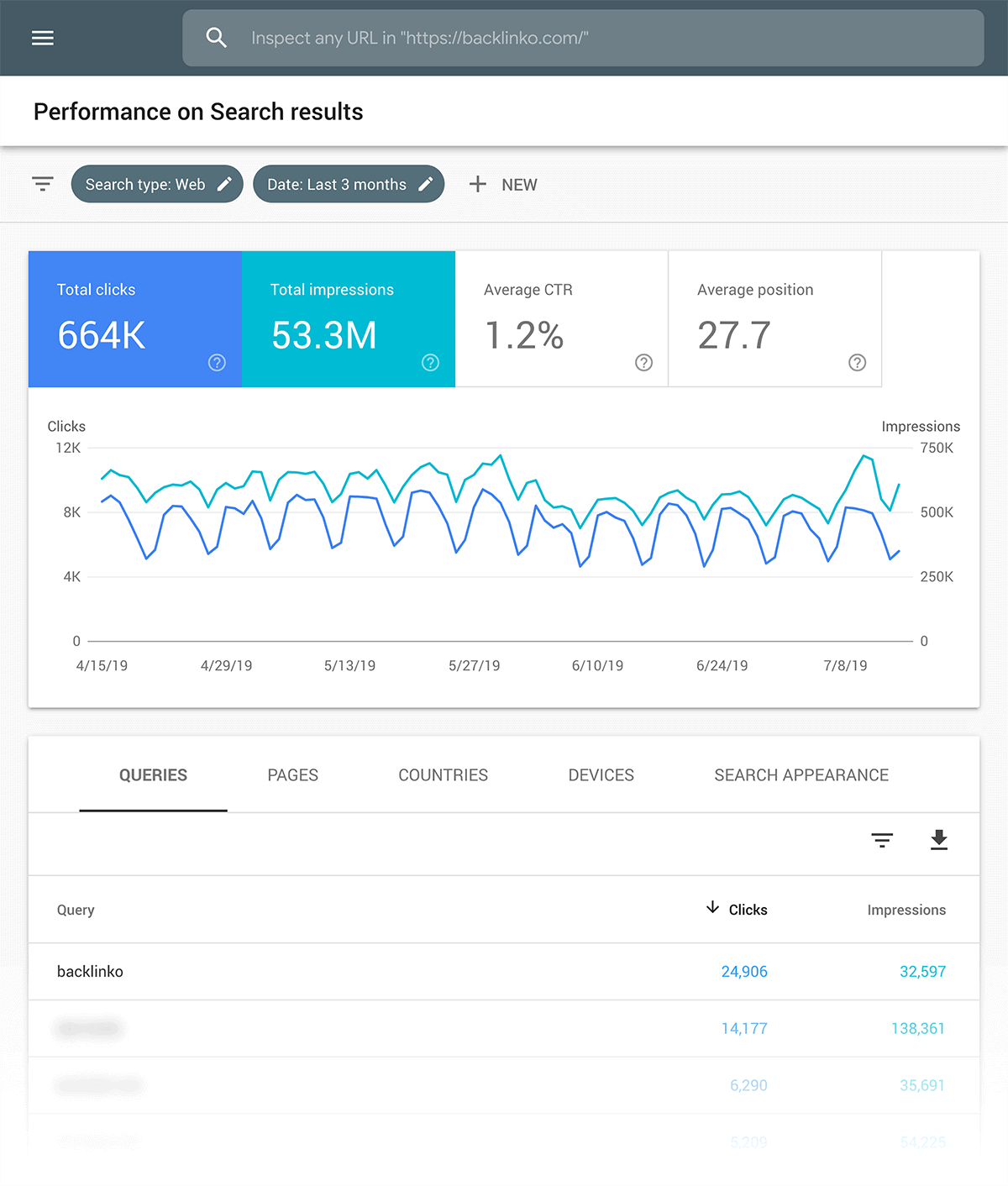
You can also see the exact keywords that people use to find your content… and where you tend to rank.
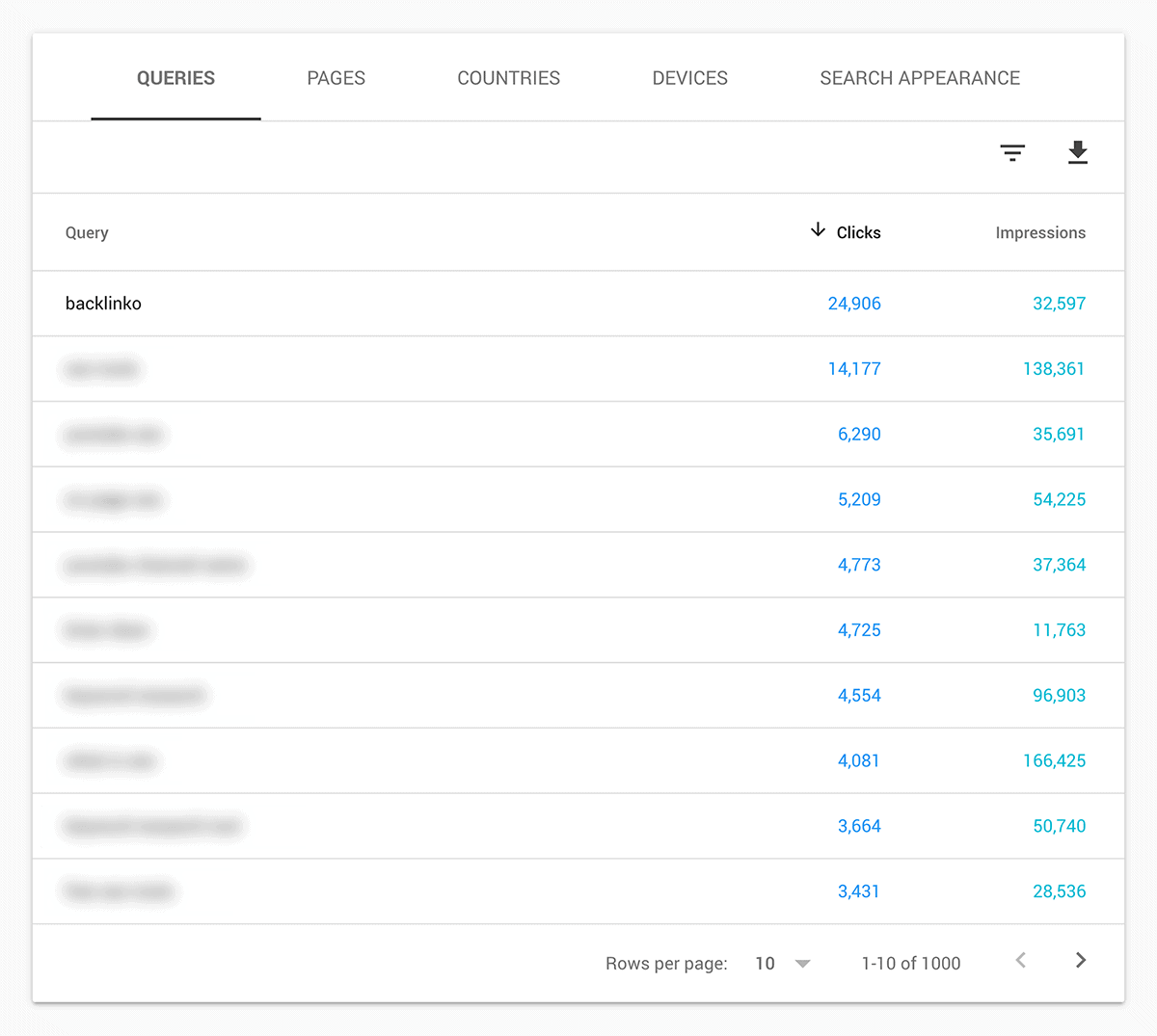
This is all super valuable on its own. But the real value is tracking your impressions and clicks over time. If they’re moving on’ up, it’s clear that these SEO best practices are working.
If not, it may be time to try a different approach.
Coverage: The coverage report lets you know which pages from your site Google has indexed.
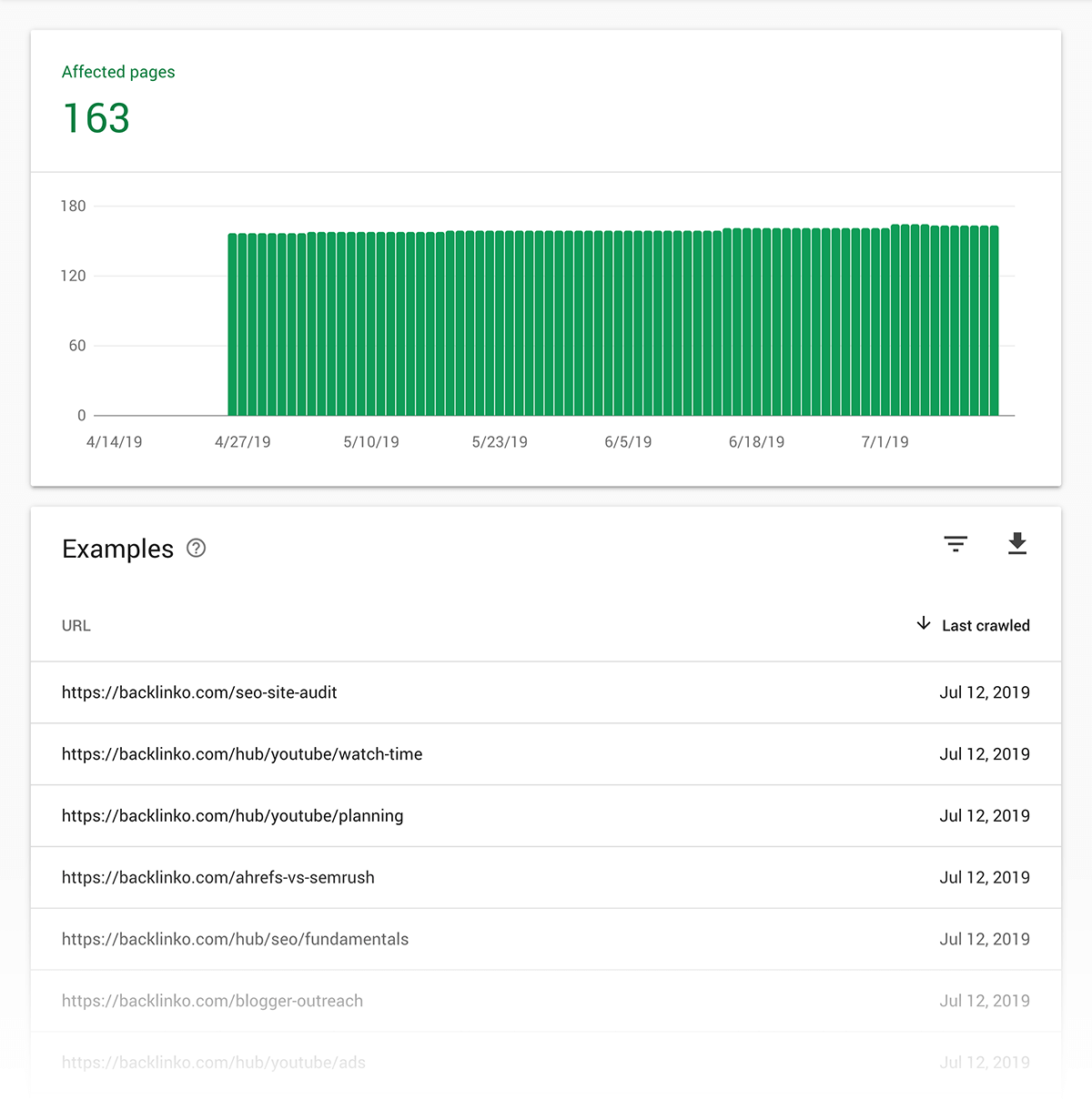
It will also let you know if it’s having trouble fully-crawling any of your pages.
If you see “errors” and “warnings” here, I recommend fixing these ASAP.
After all, if Google can’t index your page, it won’t rank for anything. Fortunately, Google doesn’t just tell you: “We can’t index this page”. They usually let you know what’s causing the issue.
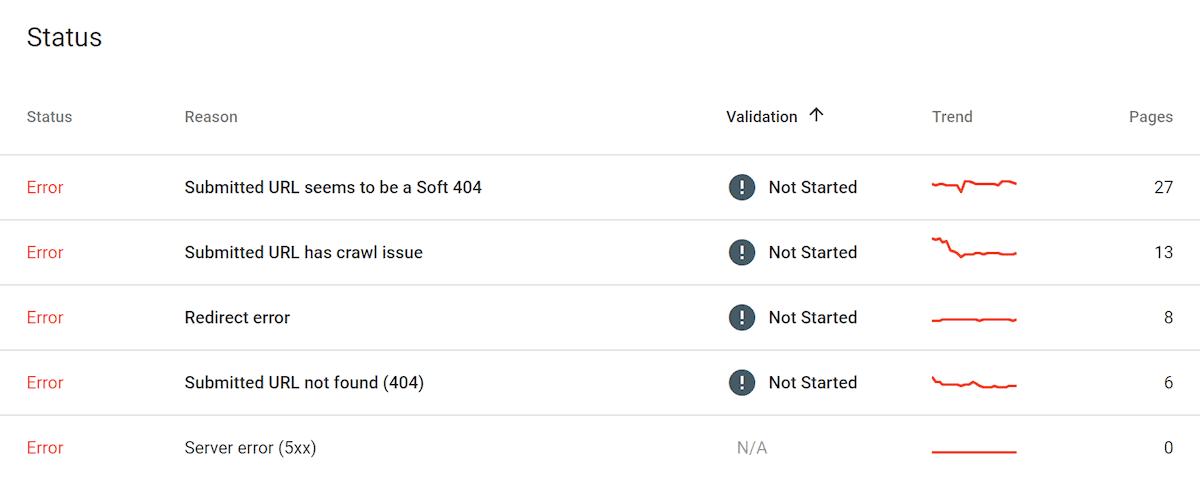
Enhancements: The main thing to pay attention to in this report is “Mobile Usability”.
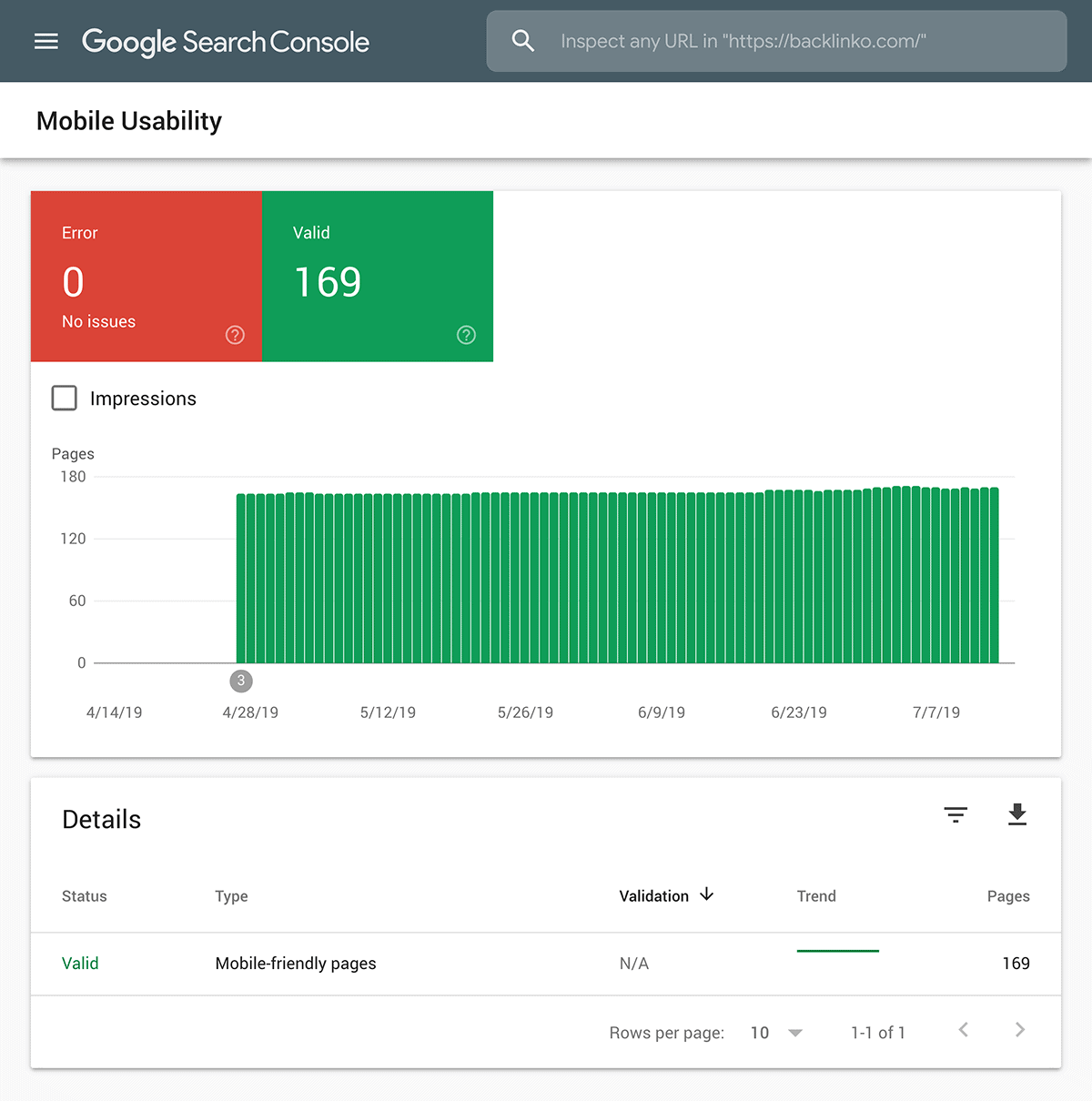
Considering that Google’s index is now mobile-first, you definitely want to make sure that your site is easy to use on mobile devices.
7. Optimize Images for SEO
Image SEO isn’t just for ranking in Google Images.
Google recently reported that properly-optimized images can help your pages rank higher in Google web search.

So if you use images on your page, you want to make sure they’re optimized for SEO.
Fortunately, this is REALLY easy. All you need to do is keep these two image SEO best practices in mind.
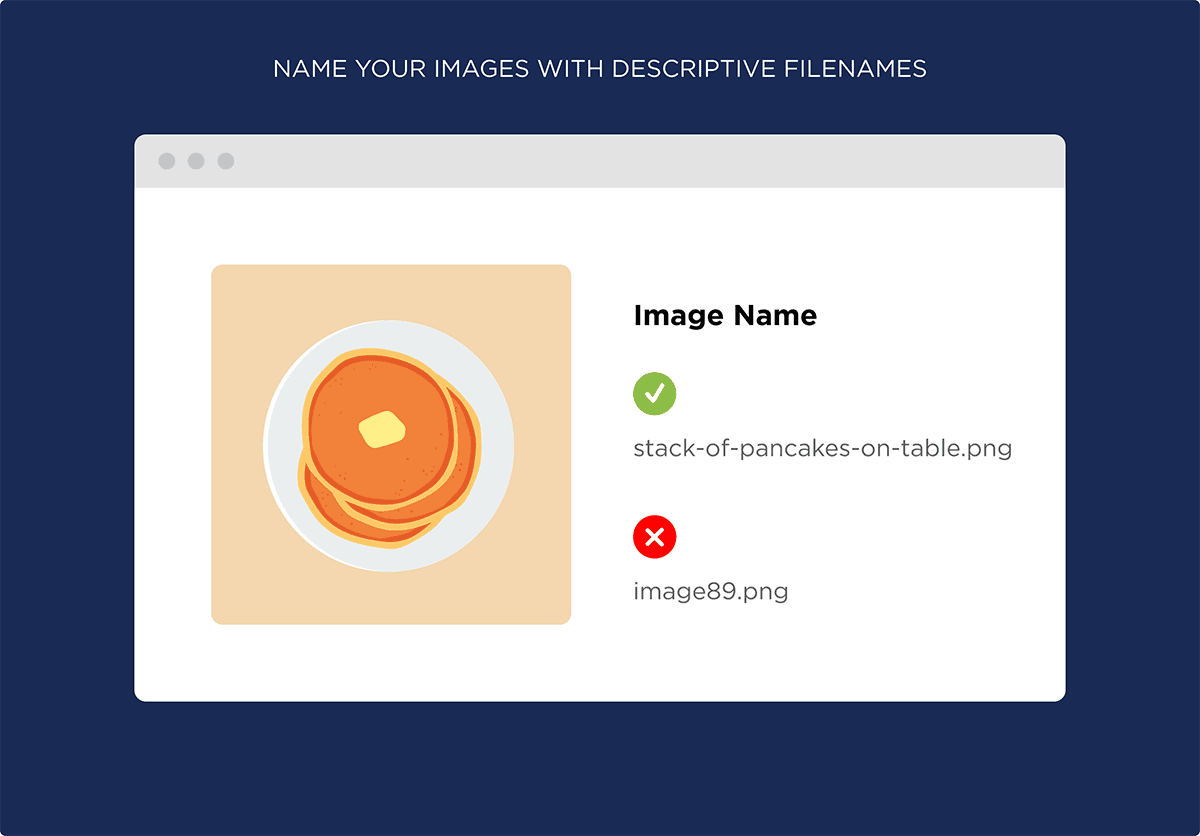
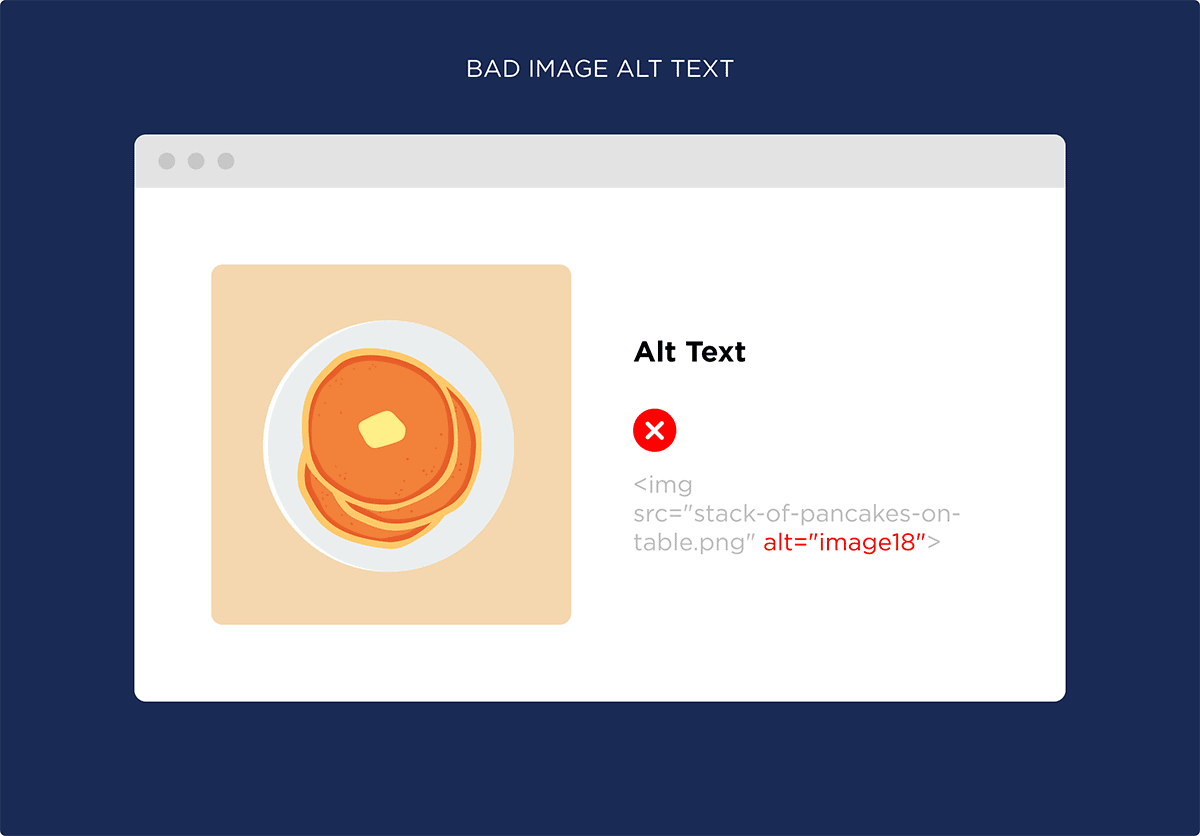
Name Your Images With Descriptive Filenames: Google can’t “see” images (yet). And your image’s filename is one thing that helps them understand the content in your image.
For example, let’s say you have an image of pancakes on your site.

You wouldn’t want to name that image something like: image89.png.
Instead, use a filename that describes what’s in your image.
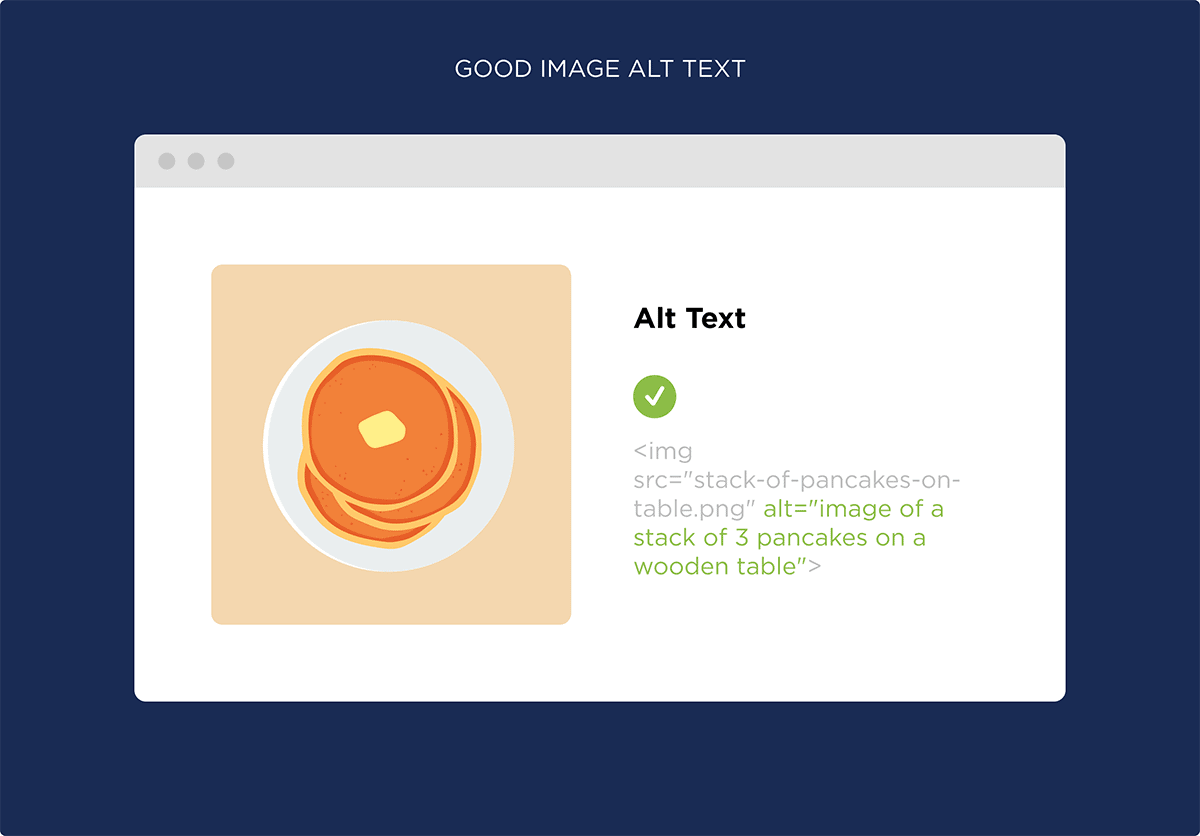
Use Image Alt Text: Google has said that they largely rely on alt text to understand images.
It takes a few extra seconds to write alt text for each image. But in my experience, it’s worth it.
For example, you wouldn’t want your picture of pancakes to have alt text like this.
Just like with your filename, you want to write descriptive alt text that lets search engines know what your image is all about.
8. Use Internal Linking
Internal linking is one of the easiest SEO best practices to use.
All you need to do is add a link from one page on your site to another page on your site.
That said, you don’t just want to add a bunch of random internal links. Yes, random internal linking is probably better than no internal linking at all.
But if you want to get the most out of internal links, I recommend implementing these tips.
Use Keyword-Rich Anchor Text: Google uses your anchor text as a clue to what a page is all about.
For example, the anchor text in these links helps Google understand what each page is about.

Needless to say, you want to use anchor text that includes your main keyword.
For example, this internal link is linking to my page about “on-page SEO”.

And, as you can see, my internal link’s anchor text has that exact term in it.
Send Authority to Pages That Need It: In general, you want to internally link to pages that don’t have much (if any) link authority.
When you do, you’ll send much-needed authority to that low-authority page… which can boost its Google rankings.
With all that said:
I wouldn’t overthink this step. In fact, I just tend to link from OLD pages to NEW pages.
Old pages tend to have more authority than new pages.
And this little shortcut helps me use internal links without having to analyze every page on my site.
9. Publish Amazing Content
If you’ve tried to learn SEO before, you’ve probably heard about the importance of “high-quality content”.
And it’s true: publishing original, helpful content can help you rank higher in Google.
The thing is, what most people consider “high-quality content” has changed over the last few years.
I’ll explain:
Back in the day, you could publish a 1,000-word blog post and blow people away.
Today? A 1000-word blog post is nothing special.
In fact, a blogging survey by Orbit Media found that the average blogger now spends over 3 hours on a single post.
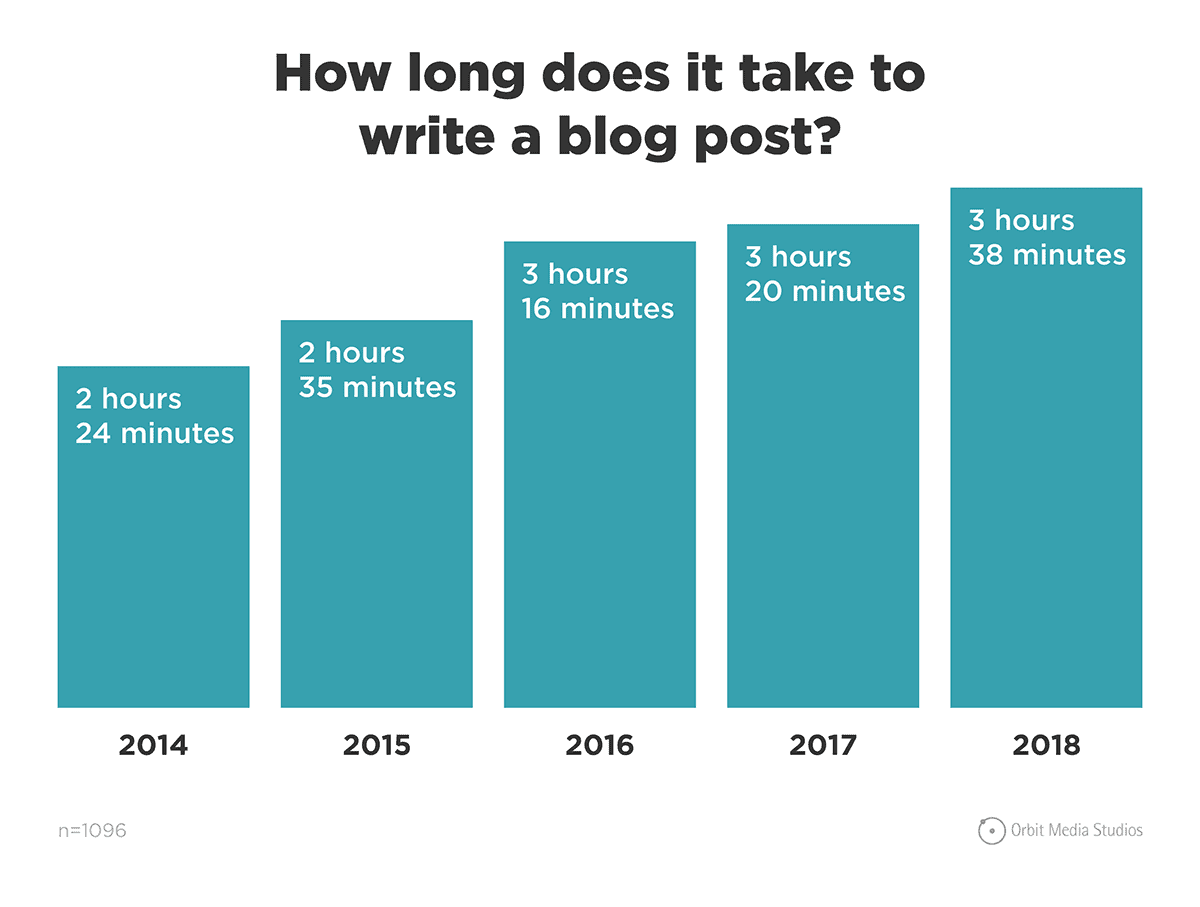
(That’s 44% more time than in 2014.)
The bottom line?
If you want to rank your content today, your content marketing game needs to be on point.
Which usually means an investment of time, money, and staff… or all 3.
For example, we published an industry study on email outreach.

To publish this one post, we had to:
- Find a data partner.
- Collect and analyze the data.
- Write up the report.
- Edit the report.
- Create a PDF of the study methods.
- Design charts and graphs.
- Promote the post on social media and via email.
- Reply to comments.
In total, this single post took 20+ hours to complete.
Overall, the effort was worth it. It brought in a ton of traffic the week we published the post.
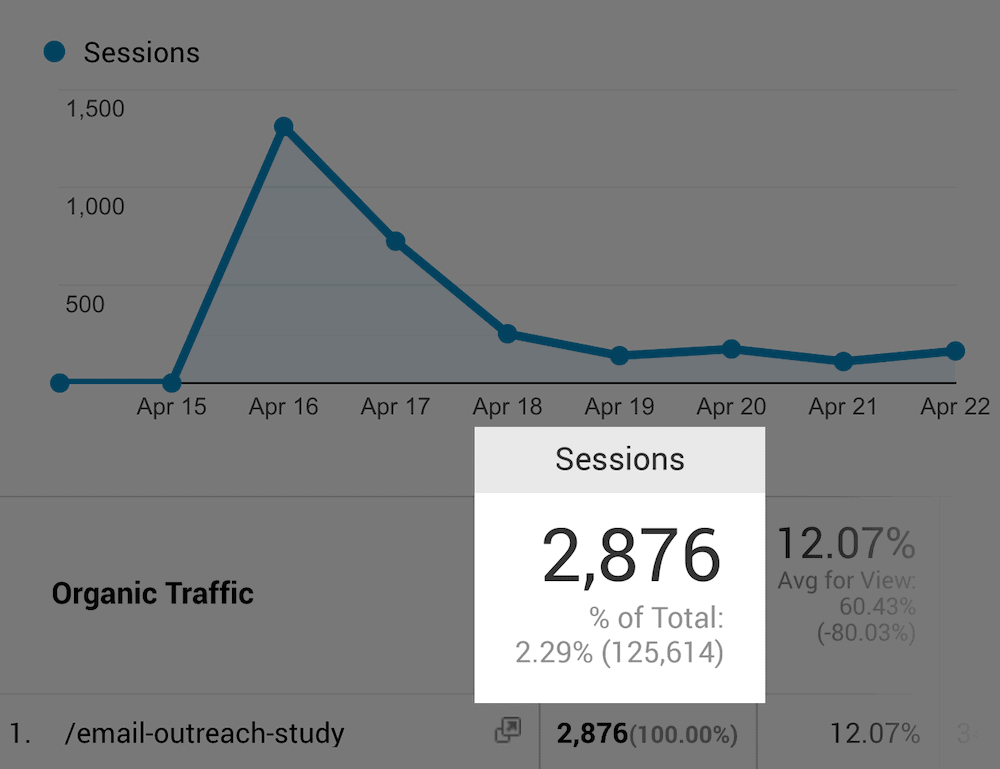
And people still share the post on social media and link to it from their blogs.
There’s no getting around the fact that creating content that stands out in 2021 takes a ton of work.
(More work than publishing a bunch of “high-quality content”.)
But if you’re willing to publish amazing stuff, you have a good shot of ranking in Google for your target keywords.
10. Build Backlinks To Your Website
It’s 2024. Are backlinks still an important Google ranking signal?
Yup!
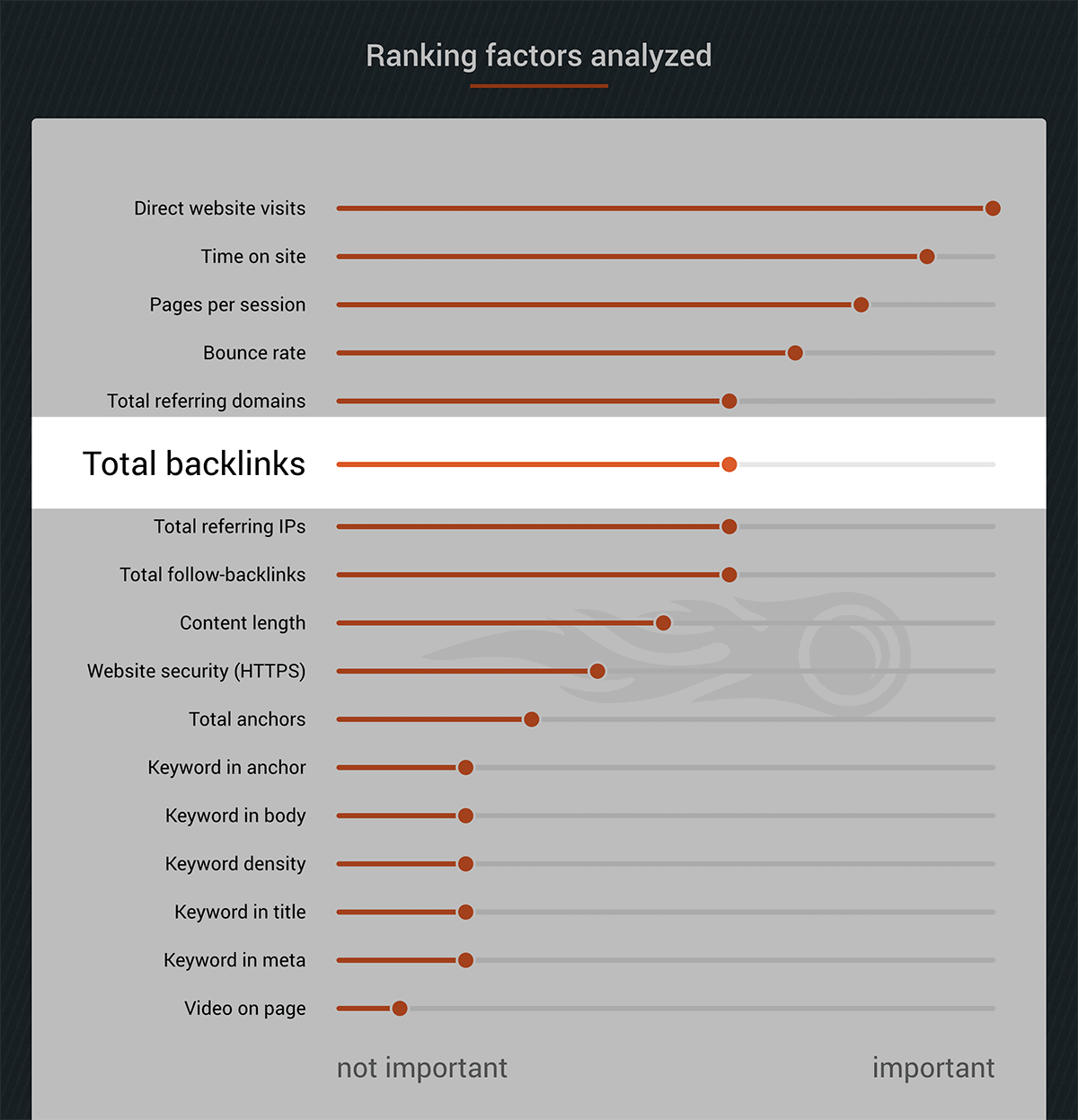
A recent study by SEMrush found that backlinks were strongly correlated with higher Google rankings.
Here are a few ways you can build links to your site.
First, focus on content formats that tend to do best in terms of backlinks.
Our analysis of 900+ million blog posts found that what and why posts (along with infographics) got more links than other types of content (like video).
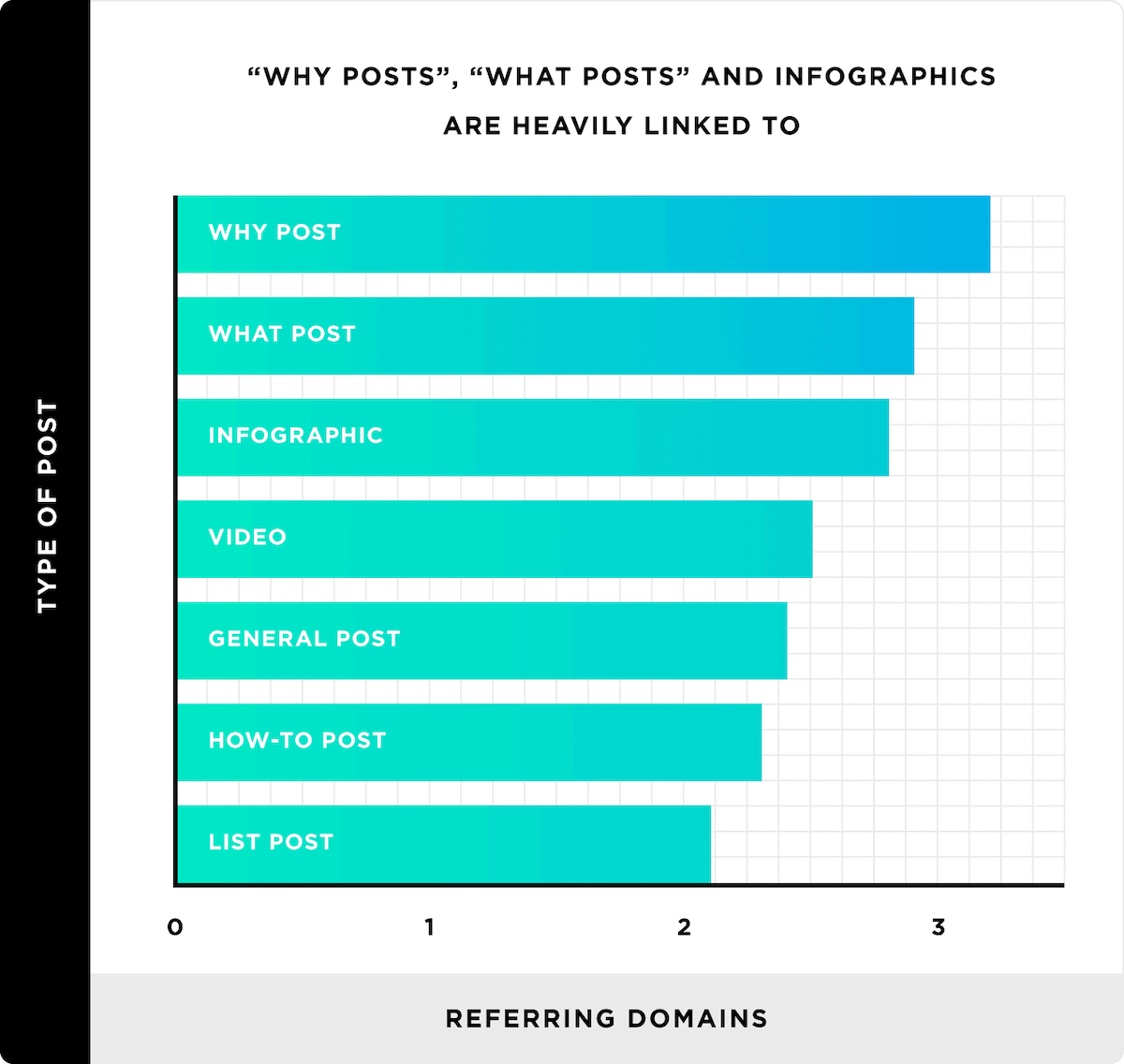
That’s not to say that publishing this type of content will automatically result in links. But, at least according to this study, it can increase the odds that other people will link to you.
Second, create content with a “hook”.
A hook is an angle, a data point, or something controversial that will encourage people to naturally link to you.
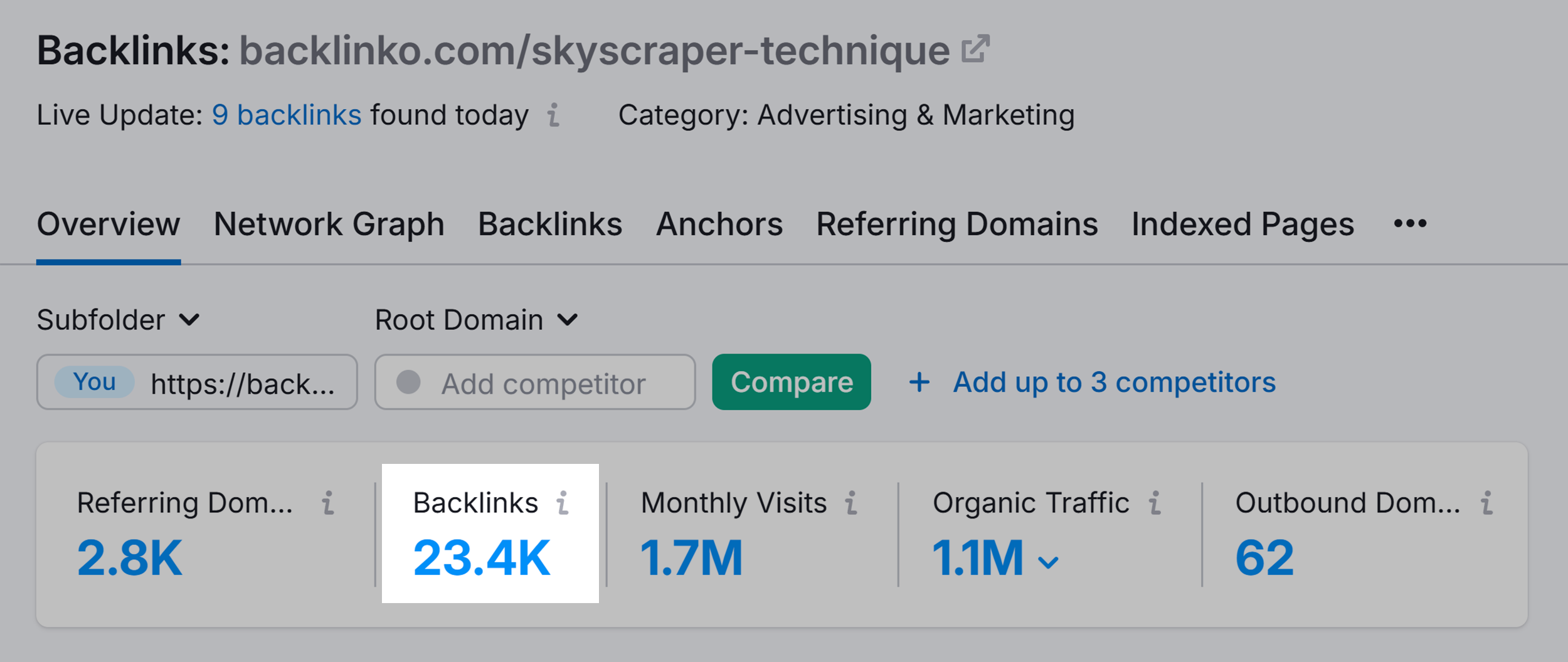
For example, a few years back I published a post about a strategy called “The Skyscraper Technique”.
Unlike most SEO case studies, this post contained a detailed, step-by-step process.

I also made sure to give the strategy a name to make it easy to remember.

And because my content contained multiple hooks, that page has 23.4k backlinks.
Learn More
Advanced Keyword Research Tutorial (5-Step Blueprint): A deep-dive into finding keywords for content, landing pages and more.
Link Building for SEO: The Definitive Guide: More tips and strategies for building backlinks to your website.
21 Actionable SEO Techniques That Work Great: A list of advanced SEO strategies that I recommend checking out after you’ve implemented the SEO best practices here.
25 Amazing Free SEO Tools: A hand-curated list of tools that can help you implement a lot of the strategies in this guide.