What Is a URL Slug?
A URL slug is the part of a URL that identifies a specific page on a website.
It comes immediately after the slash following the domain name, and it helps both users and search engines understand what the page is about.
For example, in the URL:
https://backlinko.com/seo-competitor-analysis
The slug is:
seo-competitor-analysis
Well-crafted URL slugs play a significant role in SEO and user experience.
Why Your URL Slugs Matter
URL slugs are important for SEO because they directly communicate what the page is about to search engines and users.

In other words: a clear slug tells both search engines and users what to expect when they access that link.
Google’s John Mueller has confirmed that words in a URL are a ranking factor:
“We use the words in a URL as a very very lightweight factor…and if this is the absolute first time we see this URL… then we might use the words in the URL as something to help rank us better.”
However, this influence is lightweight compared to the quality of your content.
Consider these examples:
example.com/seo-tips
This one is clear and direct. You know what you’re going to learn about if you click on the link.
In contrast, this URL’s slug lacks context on what the page is about:
example.com/article123
The first is more likely to attract clicks and shares because it’s clear at a glance what the page is about. And search engines like Google will also gain some useful context about the page’s content.
Important: Don’t rush to change all your existing URL slugs if you haven’t optimized them yet. This can have negative effects on your SEO if you don’t take the right precautions, like setting up 301 redirects.
Best Practices for Creating Optimized URL Slugs
Follow these best practices to optimize your URL slugs:
1. Keep Them Short and Descriptive
Shorter slugs are better for both users and search engines because they’re easier to read and understand.
For example:
blog-seo-tips
Is more effective than:
how-to-improve-your-seo-blog-performance
Short slugs provide a clear and concise description of the page’s content.
However, there’s no magic length or formula for creating slugs that will improve your rankings. Just focus on making them user-friendly.
2. Use Keywords
Including primary keywords in your URL slug helps search engines and users understand the page’s topic. Which could have a small impact on how Google ranks your content for relevant search queries.
For example, the slug “seo-tips” might be optimized for the keyword “SEO tips.” This could have a small positive effect on your rankings, while staying readable and clear on what the page is about.
It can also improve your click-through rate. Because if users see that URL in search results for a relevant query, they may be more likely to click your article.

(But Google may not always show the slug in search results, like the Moz example above. And you often won’t see them in mobile results.)
While optimizing can help your SEO, avoid keyword stuffing or making the slug excessively long just to cram in keywords.
In other words, avoid slugs like:
example.com/what-is-seo-guide-to-seo-tips-for-seo
3. Avoid Special Characters and Capitalization
Special characters are symbols like &, %, and # that are not standard letters or numbers.
Including these characters in URL slugs can cause technical issues, such as browsers or crawlers not being able to process the URL.
Avoid using capitalized words too. This doesn’t just improve readability: it can also prevent broken links. Because URLs are often case-sensitive.
For example, a good URL slug is:
digital-marketing-tools
While a poor one is something like:
#5-Best-Digital-Marketing-Tools
Emojis fall under special characters, and you should avoid them too. While they might look interesting, they’re not user-friendly and can be difficult to type (or impossible, depending on the device).
4. Use Hyphens, Not Underscores
There is one special character you should use in URL slugs, and that’s the hyphen.
Google recommends using hyphens instead of underscores to separate words in your URL slugs.
So they should look like this:
yourdomain.com/digital-marketing-guide
Rather than:
yourdomain.com/digital_marketing_guide
5. Remove Stop Words
Stop words are common words like:
- The
- And
- Is
- A
- To
- By
- For
- In
They’re words we use every day in our speech. But you can remove them from URL slugs without sacrificing readability. In fact, you can even improve it.
For example, consider the following slug:
the-best-seo-strategies-for-your-website
By removing stop words, it becomes simply:
best-seo-strategies
This change not only shortens the slug but also improves clarity by focusing only on the essential words. It still tells Google and users what the page is about. But in fewer than half the words.
Bonus: Concise slugs are easier for users to read and remember, and therefore also easier to share.
6. Avoid Dates (and Sometimes Numbers)
Avoiding dates in your URL slugs helps future-proof your content and prevents unnecessary updates or redirects.
Given you likely need to update your content regularly to ensure accuracy and the best experience for your users, including dates can almost guarantee that you’ll need to change the URL slug in the future.

For example, an article with the slug “best-cell-phones-2024” will seem outdated in 2025. Even if you update the rest of the content.
You’d need to update the slug and set up redirects, which isn’t ideal, and it’s pretty easy to get wrong.
Instead, just use “best-cell-phones” to ensure it stays relevant—no matter what year it is.
The same applies to numbers in lists:

For example, if you use “5-best-email-marketing-tools” you’ll need to update it if you alter the list to add more SEO tools or remove some in the future.
Instead, use “best-email-marketing-tools” to keep the slug evergreen.
However, some websites use dates to organize archives. This can be a useful structure, and is typically unlikely to cause any major problems.

But in general, keeping slugs free of dates and unnecessary numbers is a good practice to keep them relevant in the long run.
Examples of Good and Bad URL Slugs
Here are two examples of good and bad URLs, with context to explain why they do (or don’t) follow the best practices above:
Good URL Slug Example
An example of a good, well-optimized URL slug for an article on starting a blog is:
example.com/blogging-guide
This slug is effective because:
- It’s short, descriptive, and includes a relevant keywords (blogging)
- It tells both users and search engines exactly what the page covers
- It uses lowercase letters and hyphens to separate words
Bad URL Slug Example
A bad, poorly optimized URL slug example for a post on starting a blog would be:
example.com/123abc%blog-post
This slug isn’t great because:
- It contains irrelevant characters
- It doesn’t tell you anything about the post’s content
- Special characters like % can cause technical issues
Tools for Optimizing Your URL Slugs
Here are three tools that can help you optimize your URL slugs and spot issues with them:
1. Yoast SEO
Yoast SEO is a popular WordPress plugin that helps you optimize your website for search engines.
It provides tools for editing and optimizing URL slugs directly within the post editor. So you don’t need to do any coding.

If your website runs on WordPress, this is a super easy way to ensure your URL slugs are optimized from the moment you hit publish.
But you can also use the tool for your Shopify website:

2. Semrush
Semrush’s Site Audit tool analyzes your website’s health and performance. And as part of its audit, it checks the optimization of your URL slugs.
Semrush scans your site for issues like overly long URLs:

Incorrect URL slug formats:
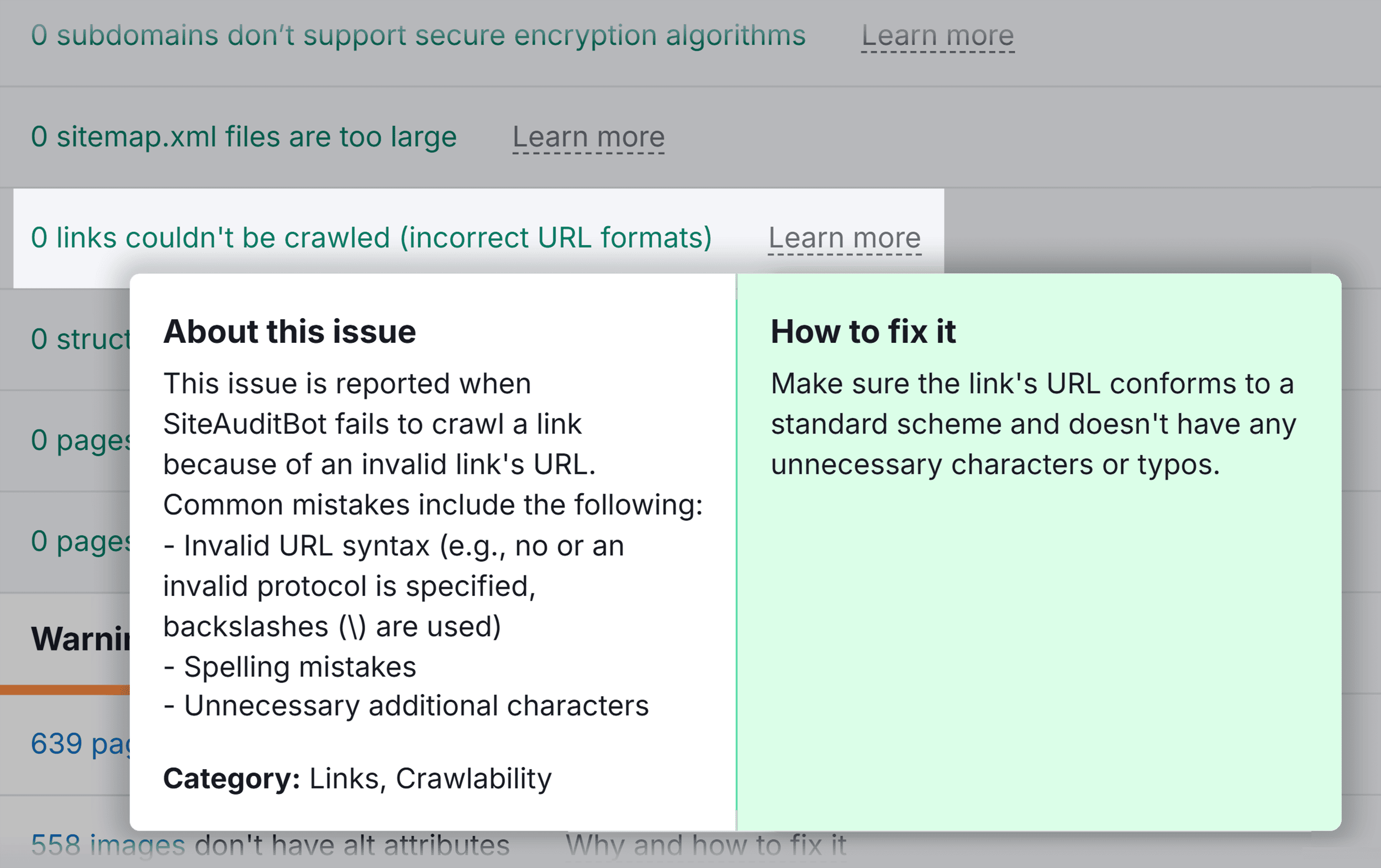
And URLs with underscores in them:

This makes spotting issues with your URLs at scale a breeze.
Note: A free Semrush account lets you audit up to 100 URLs at a time. Or you can use this link to access a 14-day trial on a Semrush Pro subscription.
3. Google Search Console
Google Search Console is a free tool provided by Google to monitor your website’s presence in search results. You can also use it to troubleshoot issues with your URL slugs.
You can do this using the “Performance” report.
This report shows data on impressions, clicks, and average position for your URLs.
You want to look for pages that have lots of impressions but few clicks.
These discrepancies may indicate problems with your URL slugs.

Click any of the URLs with lots of impressions but few clicks to compare the search queries driving those impressions.
If there’s a mismatch between the queries and the URL slug, it might suggest that the slug isn’t aligned with user intent. In other words: what the user wants to get from a given search query.
For example, a page on the best ground coffee with the slug “best-coffee” might have high impressions for queries like:
- Best coffee shops near me
- Best organic coffee
- Best instant coffee
- Best coffee machines
But each of these queries has a very different search intent. So even if your page ranks for a query like “best coffee shops near me,” users are unlikely to click it if they don’t see that your URL slug matches their query.
Adjusting the slug to better match the query could improve click-through rates. In this example, you might change it to “best-ground-coffee” instead.
Optimize Your URL Slugs as Part of Your SEO Strategy
Your website’s rankings depend on many different factors, including content quality, backlinks, and overall site performance.
So while it’s important to optimize your slugs, remember that they are just one aspect of a successful SEO strategy.
To learn more about the fundamentals of search engine optimization, check out our guide to SEO best practices.


