Page Speed and SEO
What is Page Speed?
Page Speed is the amount of time that it takes for a webpage to load. A page’s loading speed is determined by several different factors, including a site’s server, page filesize, and image compression.
That said:
“Page Speed” isn’t as straightforward as it sounds.
That’s because there are lots of different ways of measuring page speed. Here are three of the most common:
Fully Loaded Page: This is how long it takes for 100% of the resources on a page to load. This is the most straightforward way to determine how fast a page loads.
Time to First Byte: This measures how long it takes for a page to start the loading process.
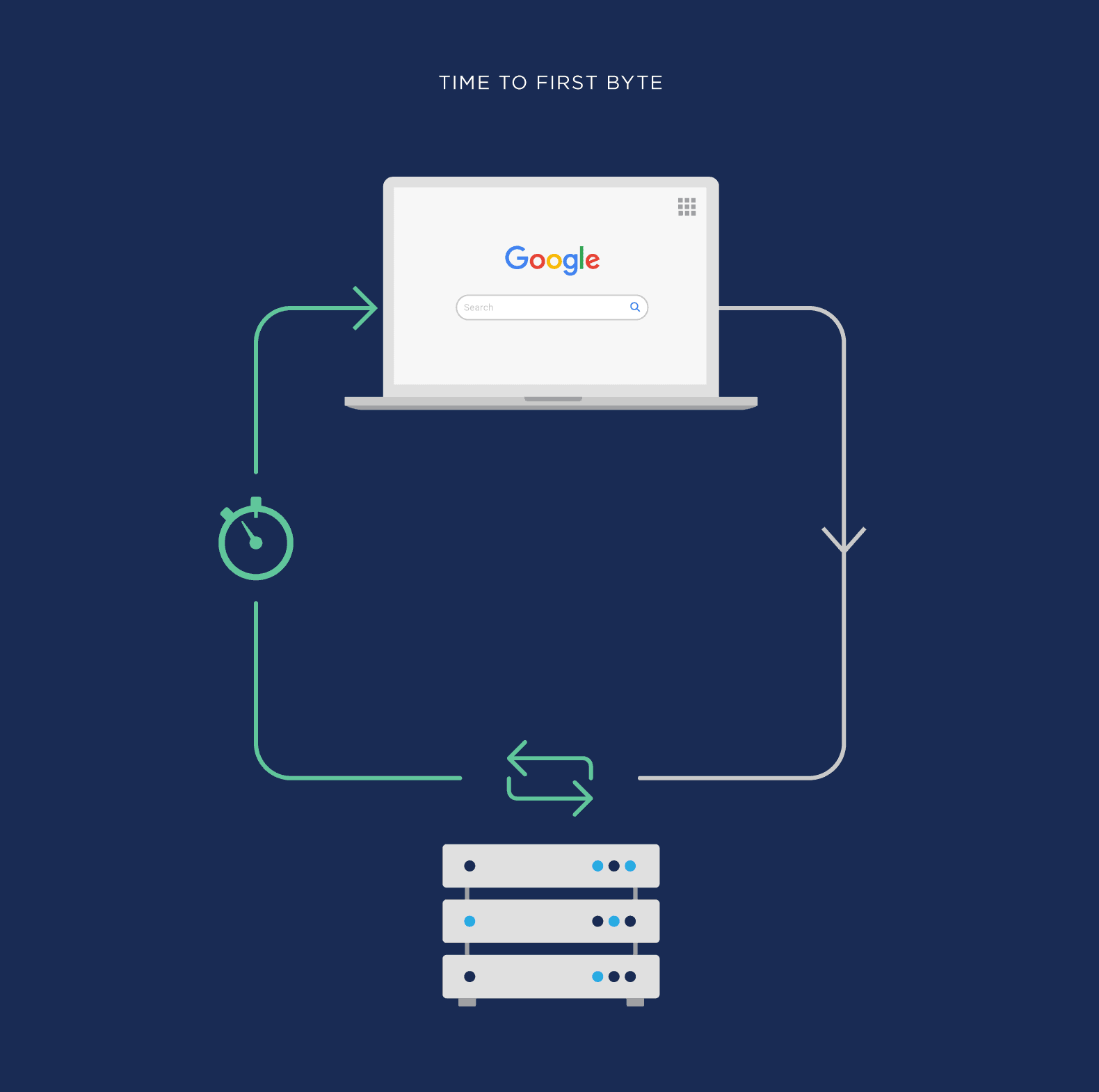
If you’ve ever landed on a page and stared at a white screen for a few seconds, that’s TTFB at work.
First Meaningful Paint/First Contextual Paint: Time it takes a page to load enough of its resources for a user to be able to read the content on that page.
For example, let’s say you have a blog post that takes 10 seconds to fully load.

That’s a long time… if you ONLY look at how long it takes for the entire page to load.
On the other hand, paying attention to First Meaningful Paint sometimes better represents how users actually interact with your page as it loads.
For example, let’s look again at the page that takes 10 seconds to load all of the page’s resources.
Even though it takes a while for the entire page to load, when a user first lands on the page, they get a “First Meaningful Paint” after 1.5 seconds.
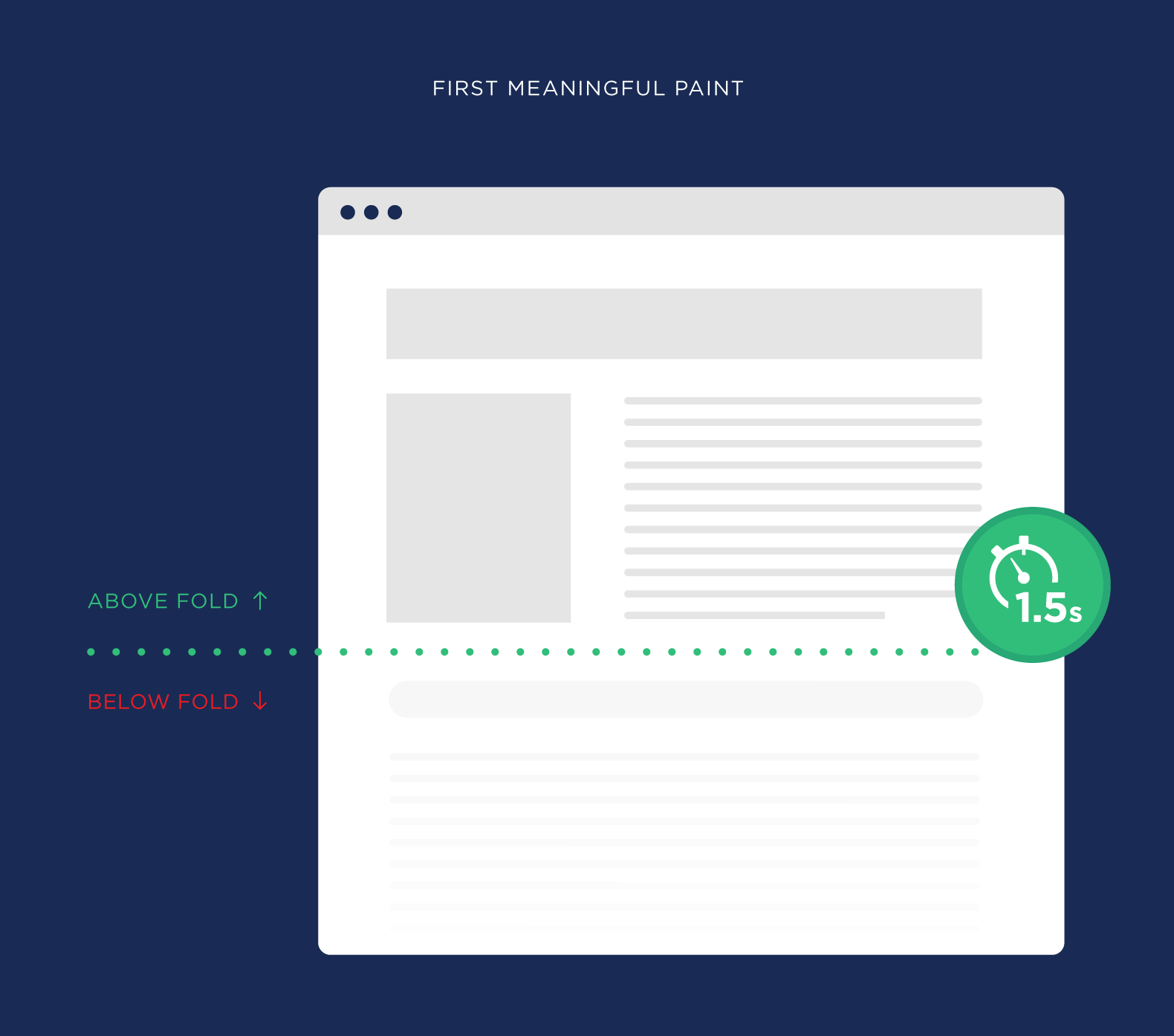
Which means they can start interacting with your page pretty much instantly. So to a user, your page is fast.
Bottom Line?
There are lots of different ways of measuring page speed. And there’s no “right” metric that beats all of the others. They all have pros and cons.
Instead, focus on improving your page loading speed for ALL of the metrics that you find.
Why Is Page Speed Important for SEO?
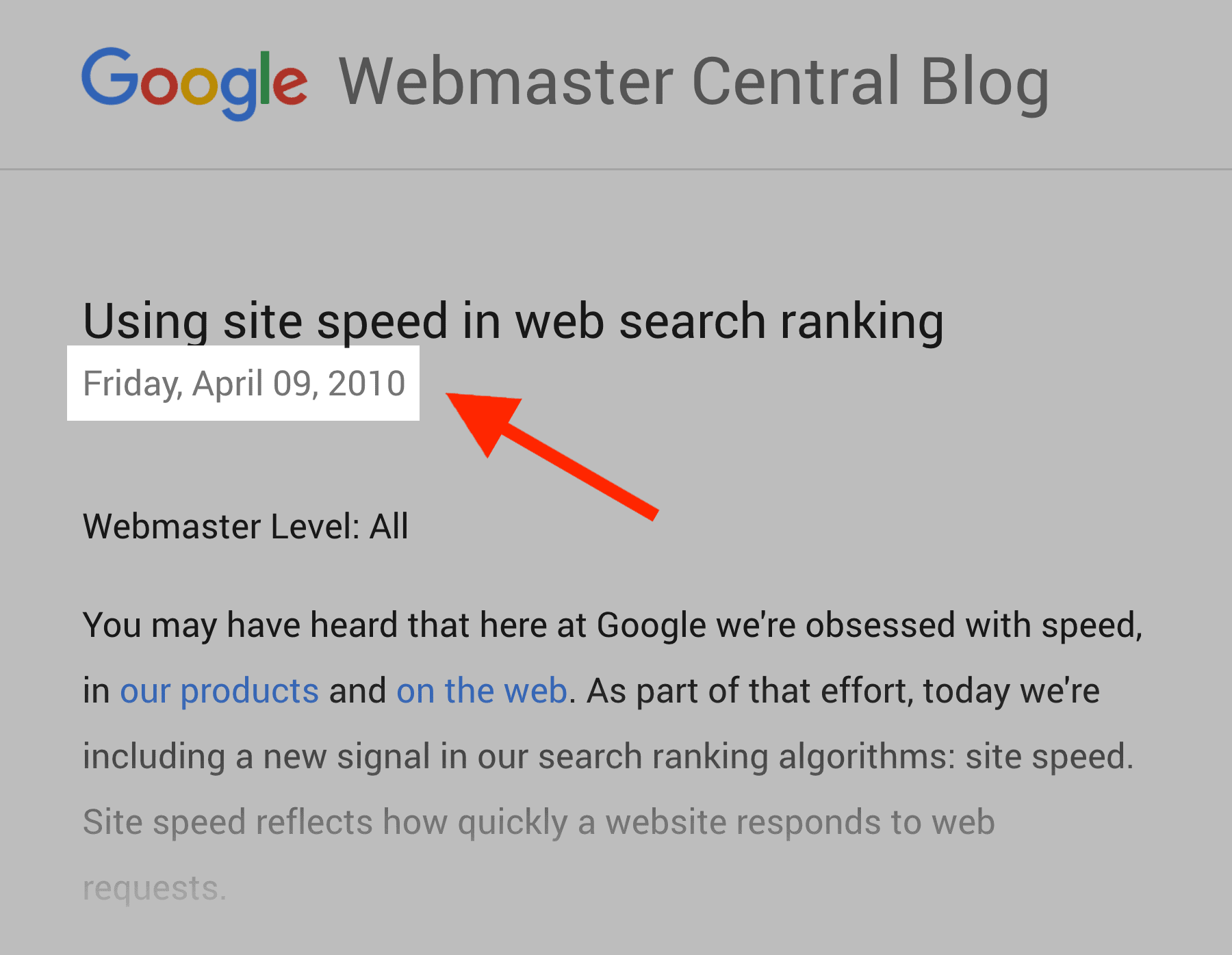
Google has used page speed as a ranking factor since 2010.
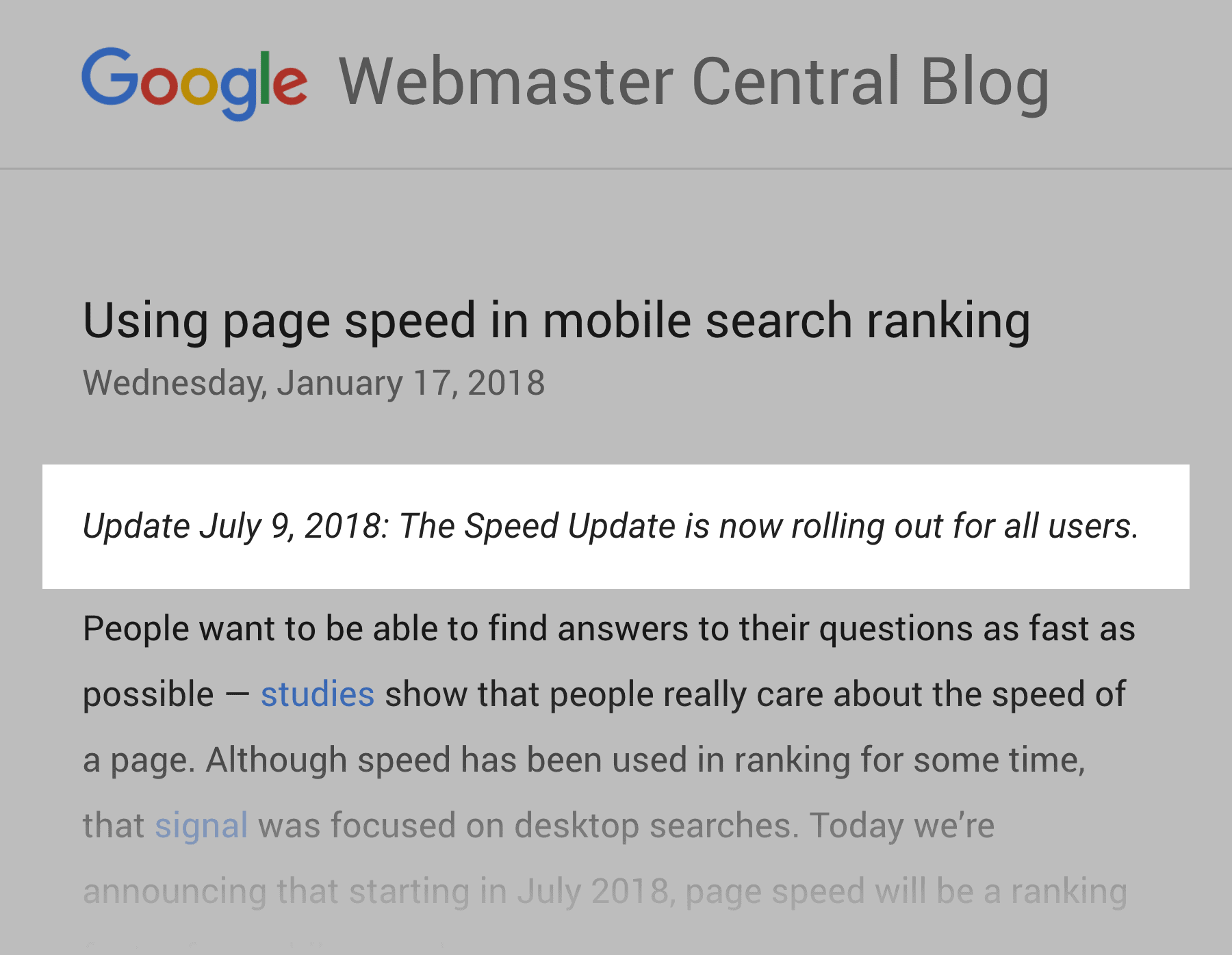
And in 2018 Google ramped up the importance of page speed with The “Speed” update.
In short:
A slow loading website can hurt your Google rankings.
The question is: how does Google determine your site’s loading speed? Do they look at how long it takes for 100% of the page to load? Or TTFB?
They haven’t made any official statements on it. But considering that they report on all of these metrics in their PageSpeed Insights tool tells me that they probably use a combination of different page speed measurements:
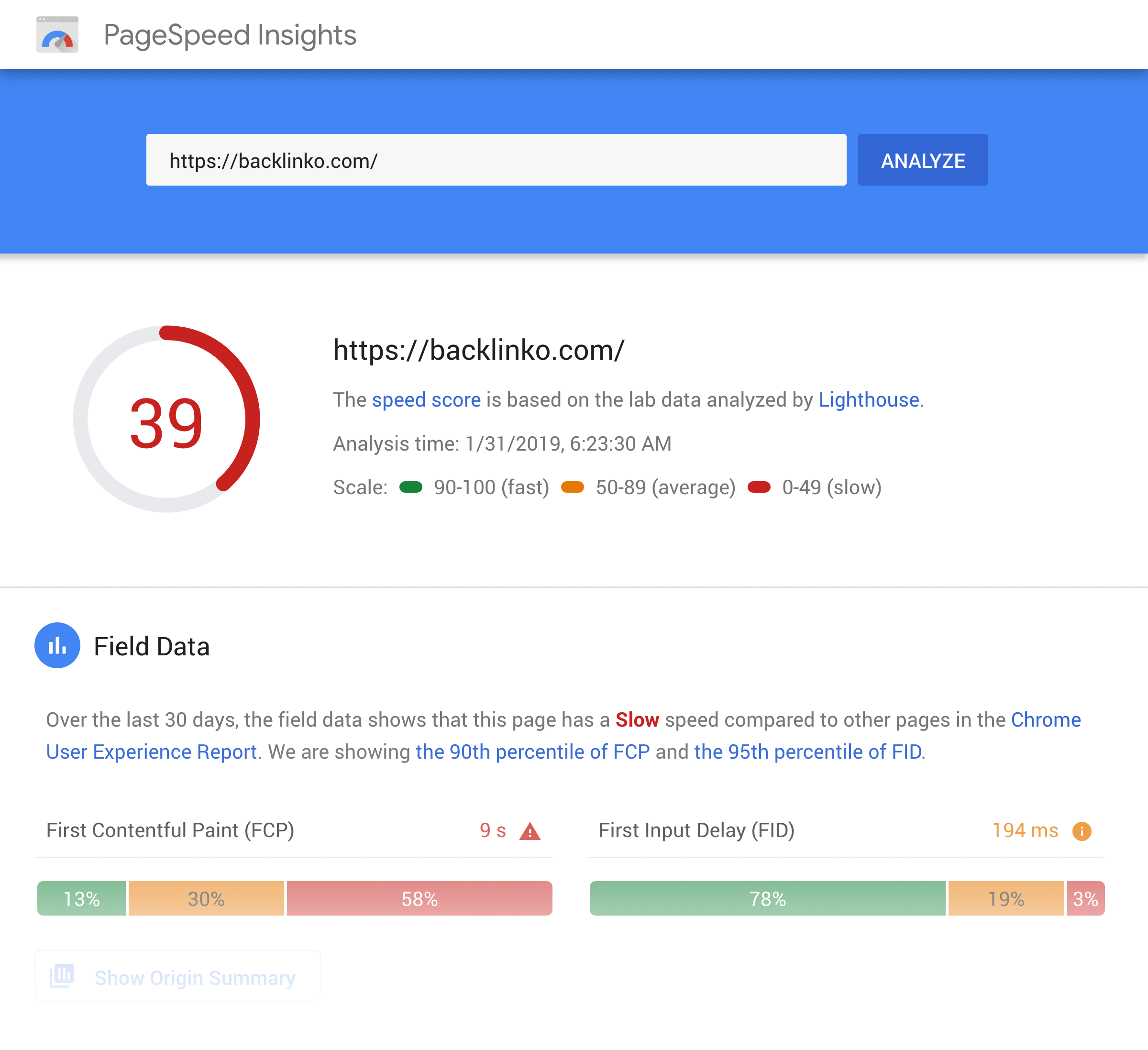
With that, here’s how to improve your site’s loading speed.
Best Practices
Compress Images
I put this first because it’s usually the biggest win.
After all, images usually take up 50-90% of a page’s size.
(And loading speed)
For example, look at this page speed report from a page on my site:
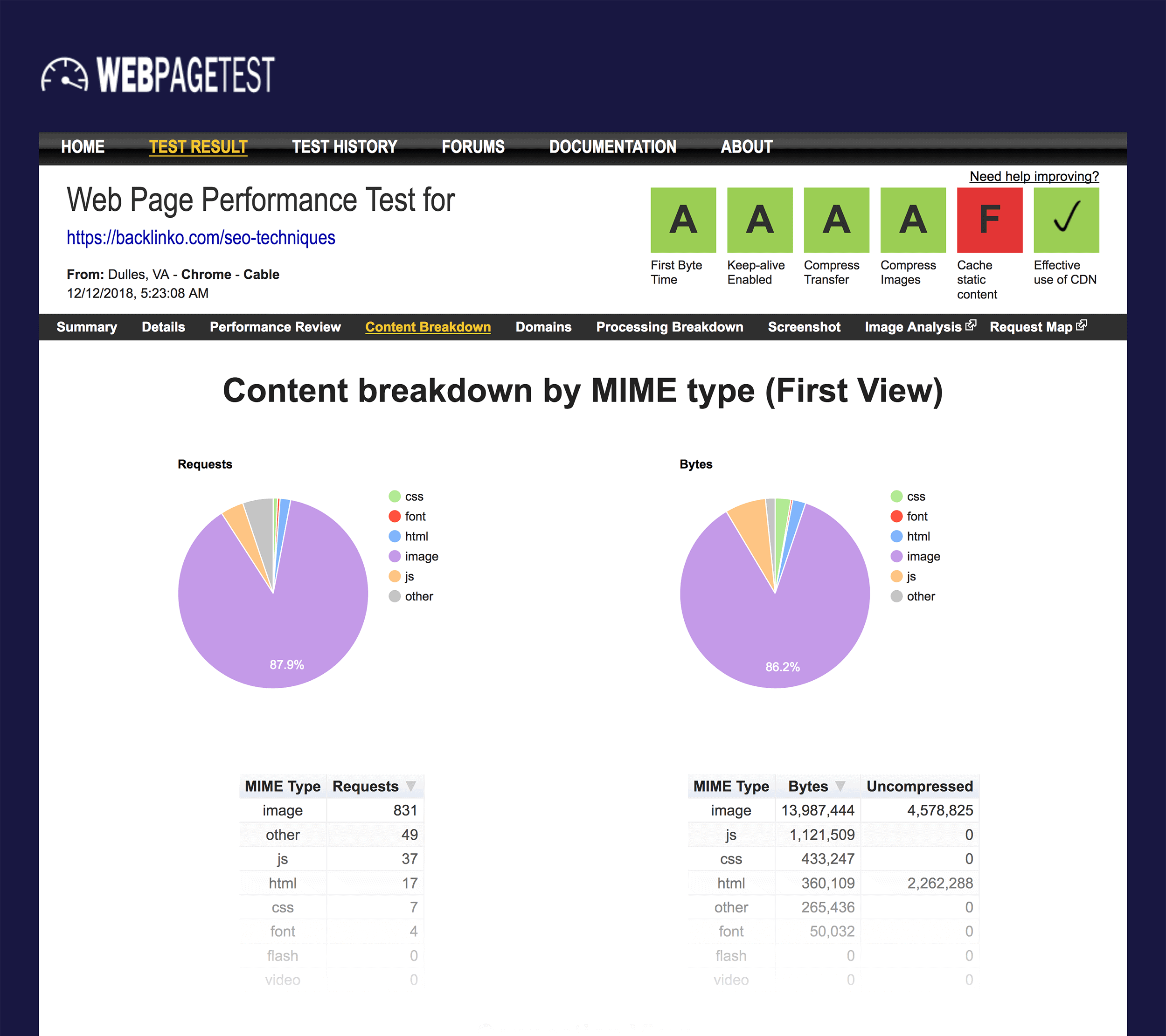
As you can see 86.2% of the page size is due to images:
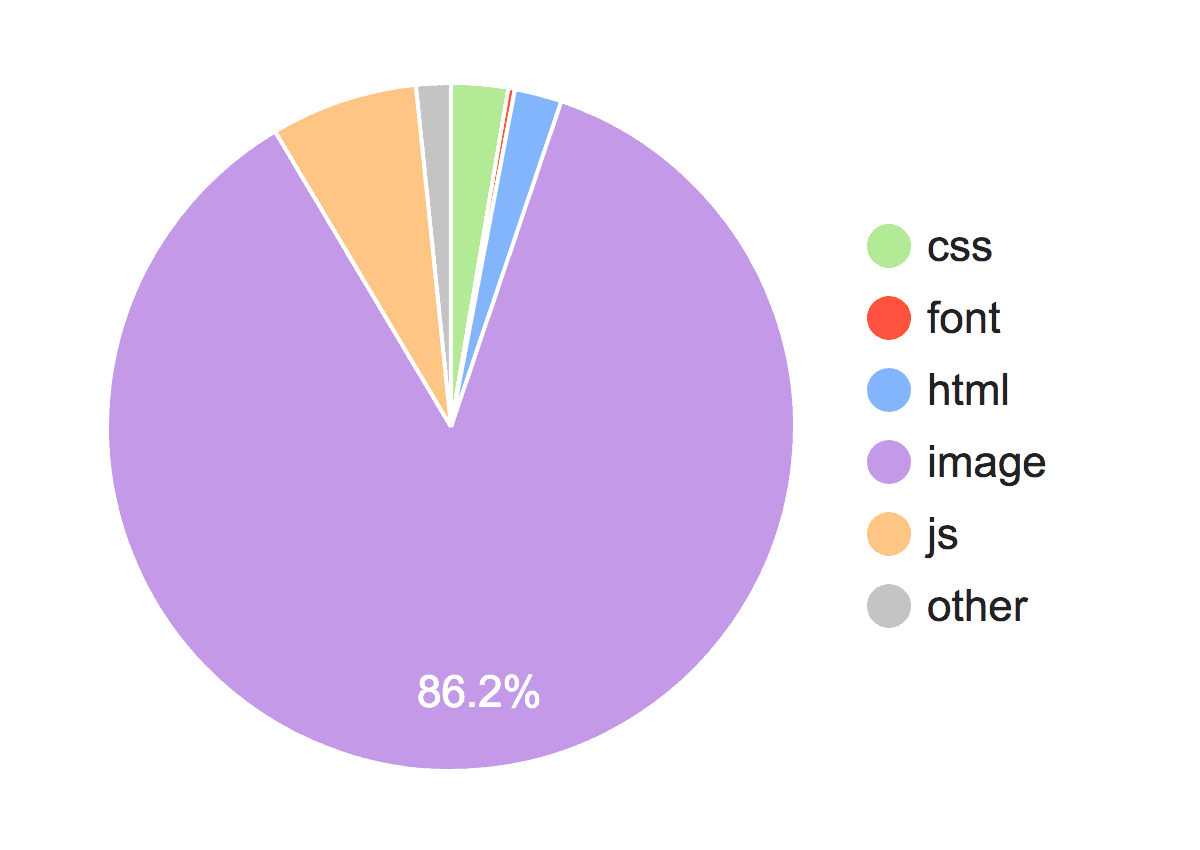
So the more that you can compress your images, the faster your page will load.
How?
If your site runs on WordPress, then I highly recommend a plugin called WP Smush:

It automatically compresses any image that you upload to the WordPress media library. And at least according to the creators of the plugin, this can reduce your image file size by 14.2%.
Not using WordPress? There are still plenty of image compression options out there, like Caesium and the Mass Image Compressor.
Unlike back in the day, most of the compression tools now either use lossless compression or only reduce image quality to a point that’s barely noticeable.
For example, we compress 100% of the images here at Backlinko. And they still look nice and sharp:

Clean and Compress Your Code
In other words: minify the resources found on your page.
This includes:
- HTML
- CSS
- JavaScript
- And any other code found on your page
Your first step should be to clean up any bloated code that you have on your page. This extra code could be from features that you don’t have on your site anymore. Or from shoddy developer work.
Either way: the cleaner your code, the faster things will load.
(Yes, that rhymes 🙂 )
Then, compress your code using a program like GZip.
Upgrade Hosting
This is one tip that I don’t see enough people talking about.
You can clean up your code and compress image all day long. But if you spend $4.99/month on hosting, your site isn’t going to load quickly.
That’s because you’re sharing a server with a million other websites.
There are a million web hosts out there. So I can’t recommend one in particular.
But I can say that as a general rule: when it comes to hosting, you get what you pay for.
So if you’re serious about improving your site’s loading speed, it might be time to upgrade to a premium host or to a dedicated server.
Activate Browser Caching
This allows users to store parts of your page in their browser cache.
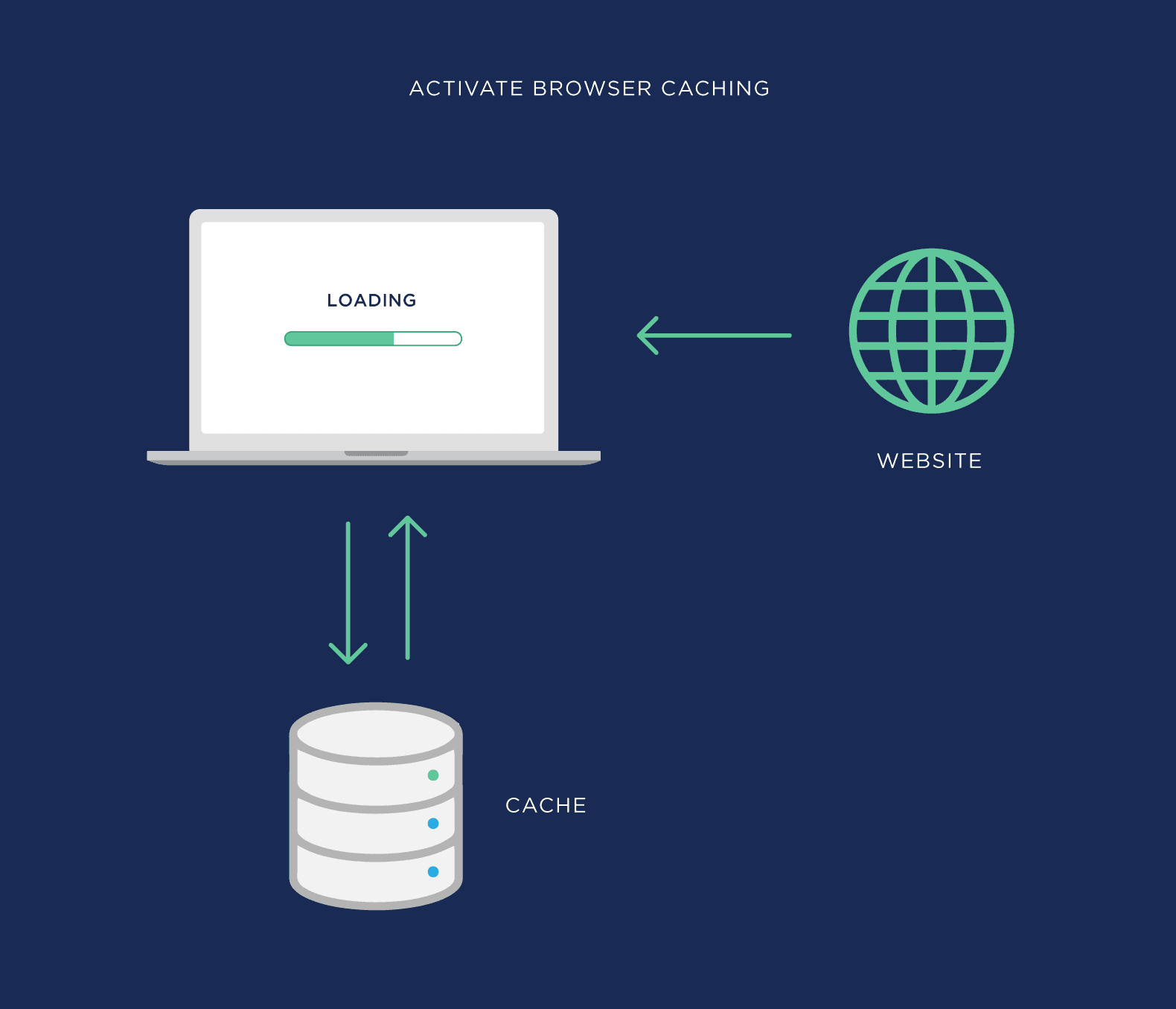
So the next time they visit your site, it loads MUCH faster.

Unfortunately, this won’t help your page load any faster for first-time visitors. But it’s great for improving your loading speed for people that have visited your site before.
You can set up browser caching in your .htaccess file. Or with a WordPress plugin.
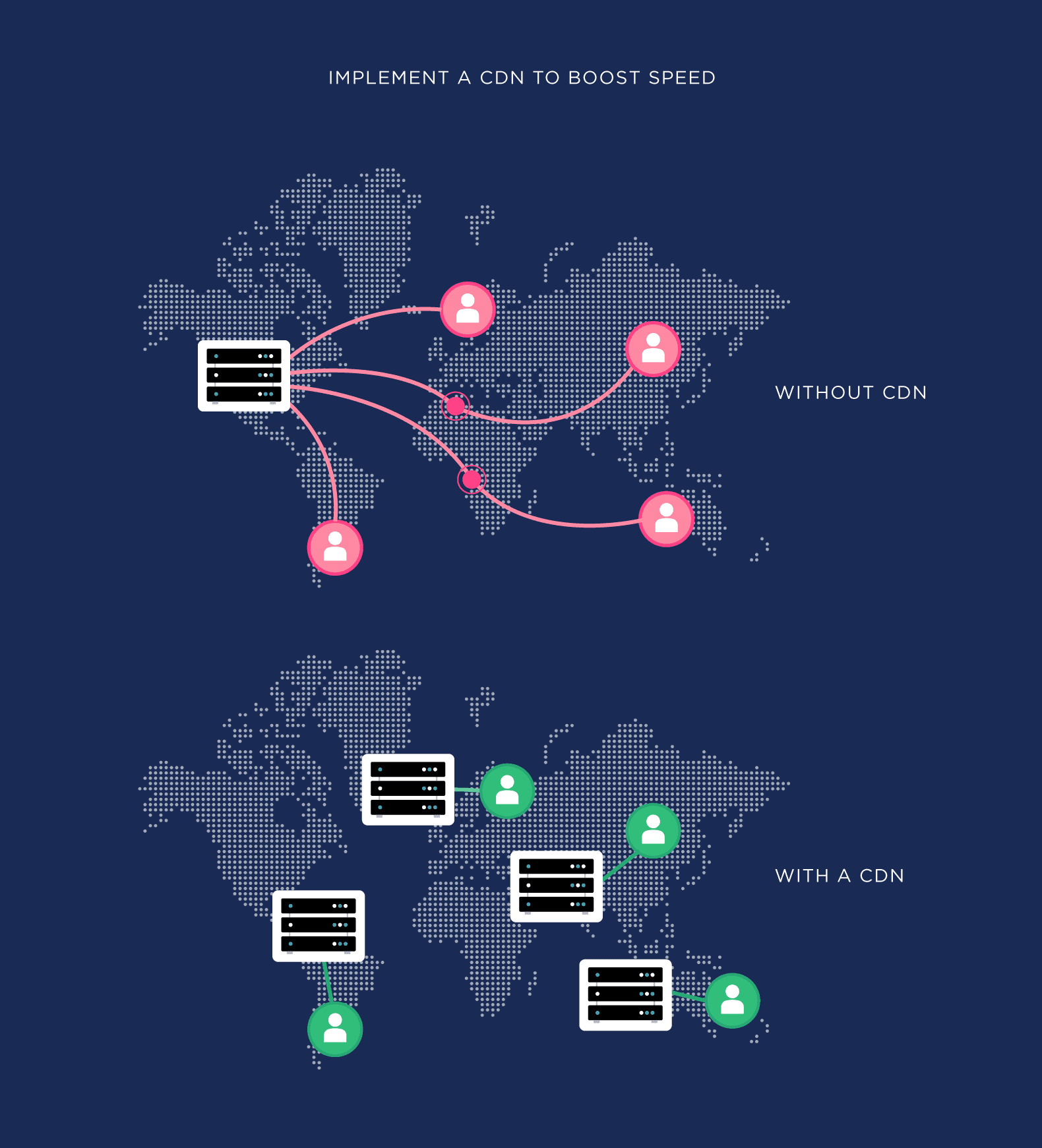
Implement a CDN
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) is one of the easiest ways to boost your site’s loading speed.
CDNs work by figuring out where your visitor is physically located… and then serving up your site’s resources from a server close to them.
Test With Multiple Page Speed Testing Tools
Now that you’ve implemented these steps, it’s time to see how you’re doing.
And I recommend testing your page speed using two different tools.
The first is Google PageSpeed Insights.
Google’s tool scans your page’s code for problems…
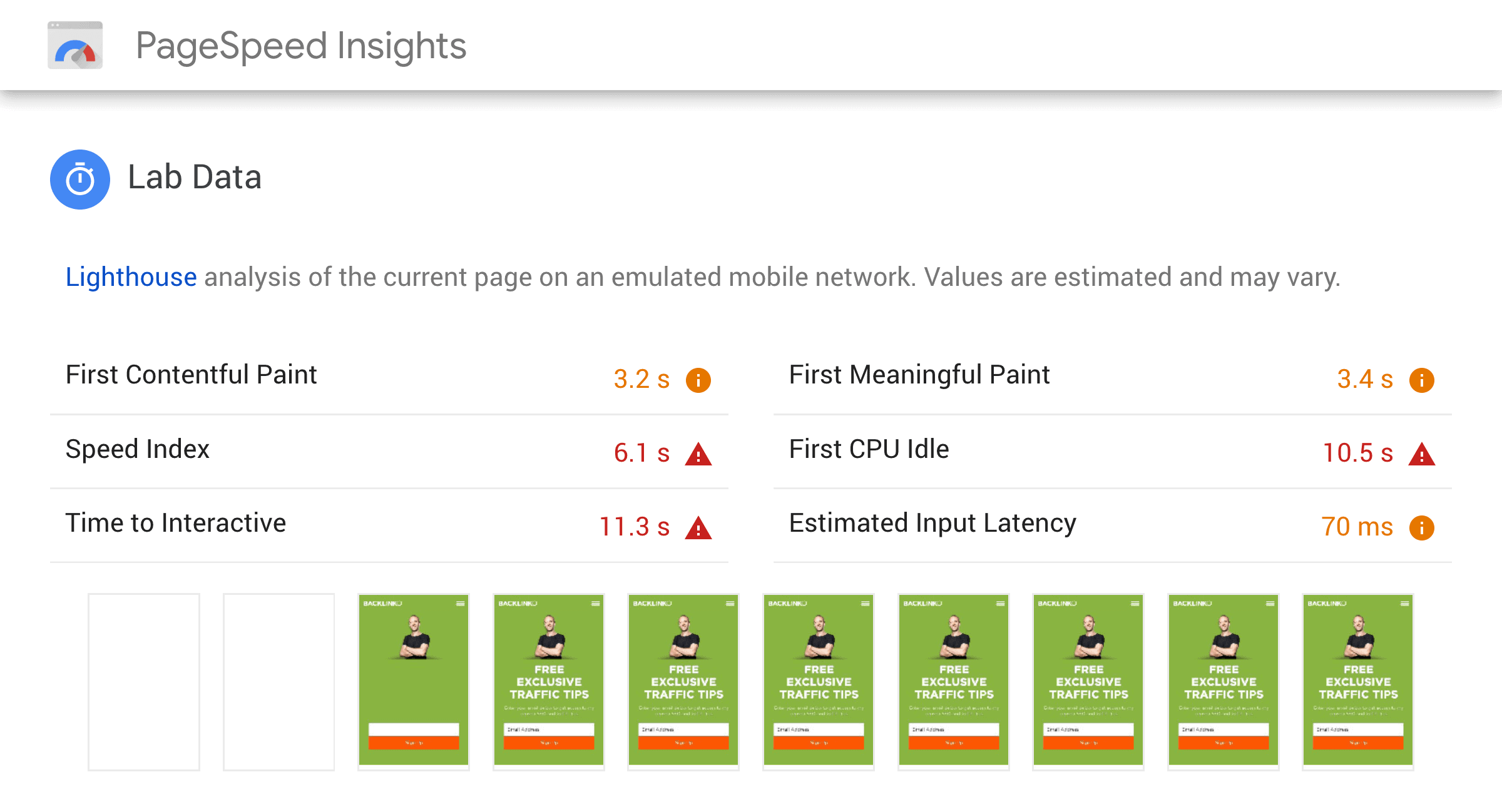
… and opportunities.
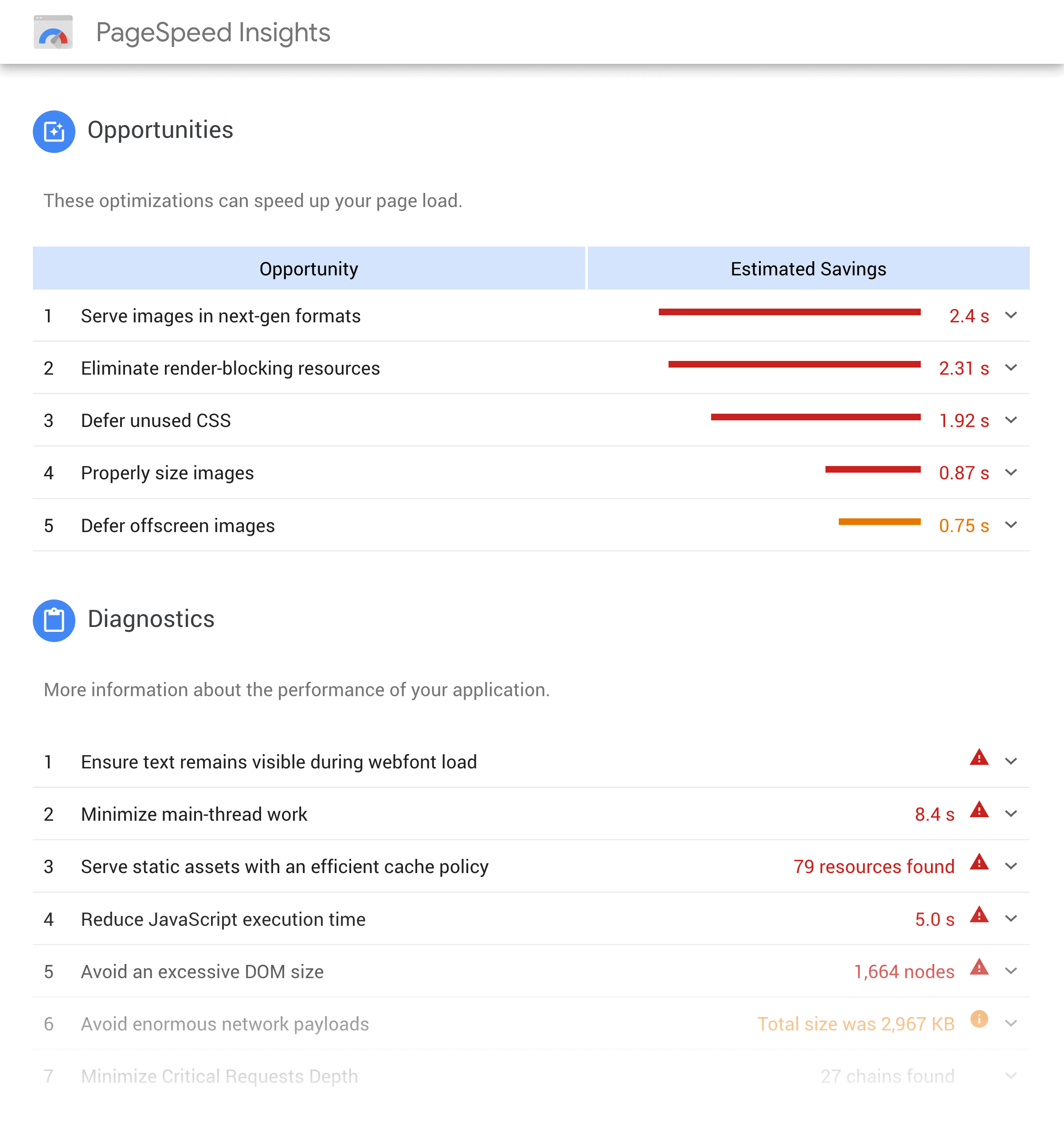
And they recently added a feature that reports on how long it takes for your site to load to actual human users (using Google Chrome Browser data).
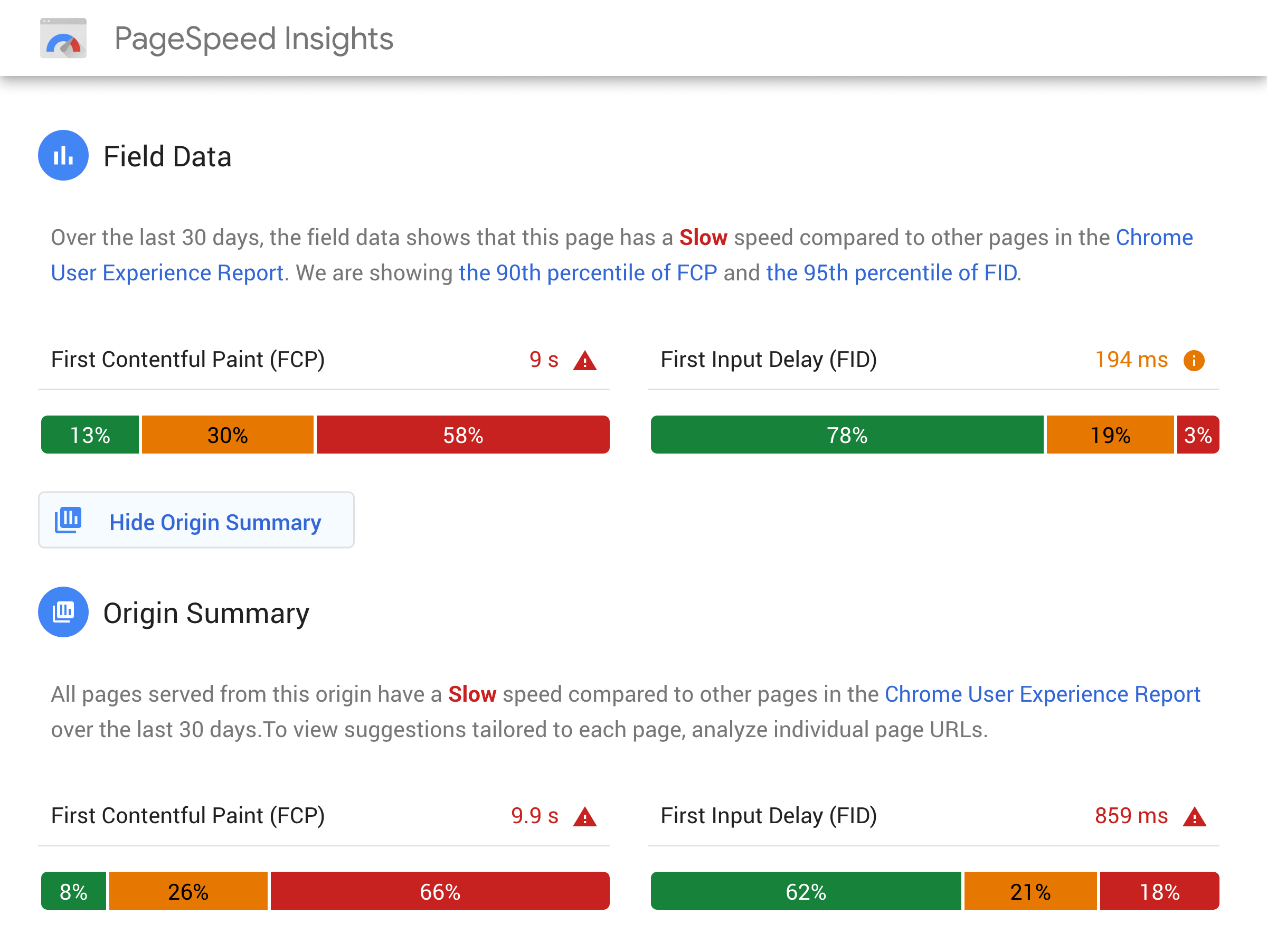
Which is SUPER useful.
One word of warning: you’ll sometimes find that the tool’s recommendations don’t make sense for your site.
For example, Google’s tool recommended that I “Serve images in next-gen formats”.
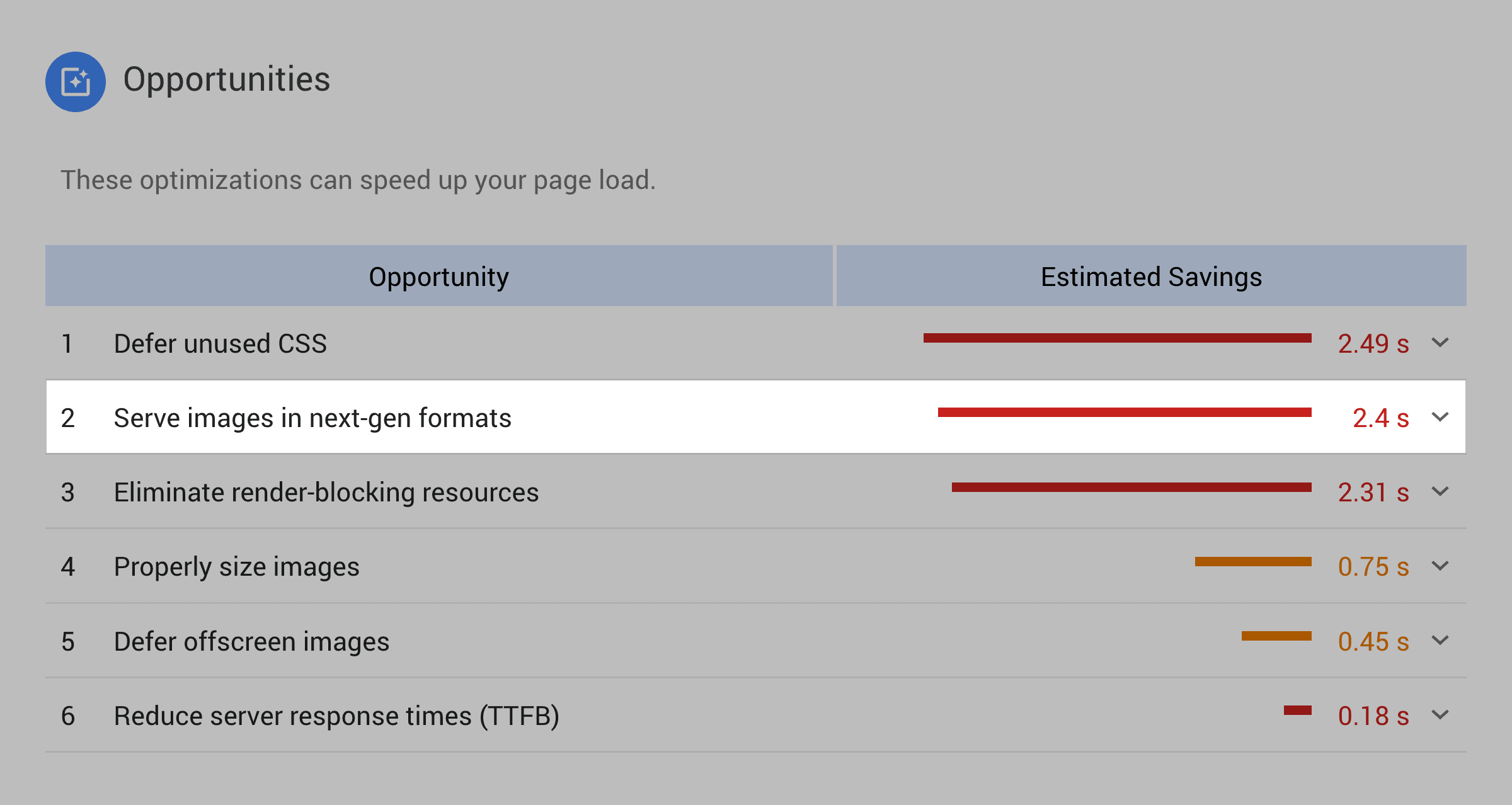
However, these “next-gen” formats aren’t supported by most browsers (including Safari and Firefox). So if you switch over to these next-gen formats, your site’s user experience is going to go down the drain.
That said: there are a ton of helpful insights in this tool. And I recommend implementing as many as you can.
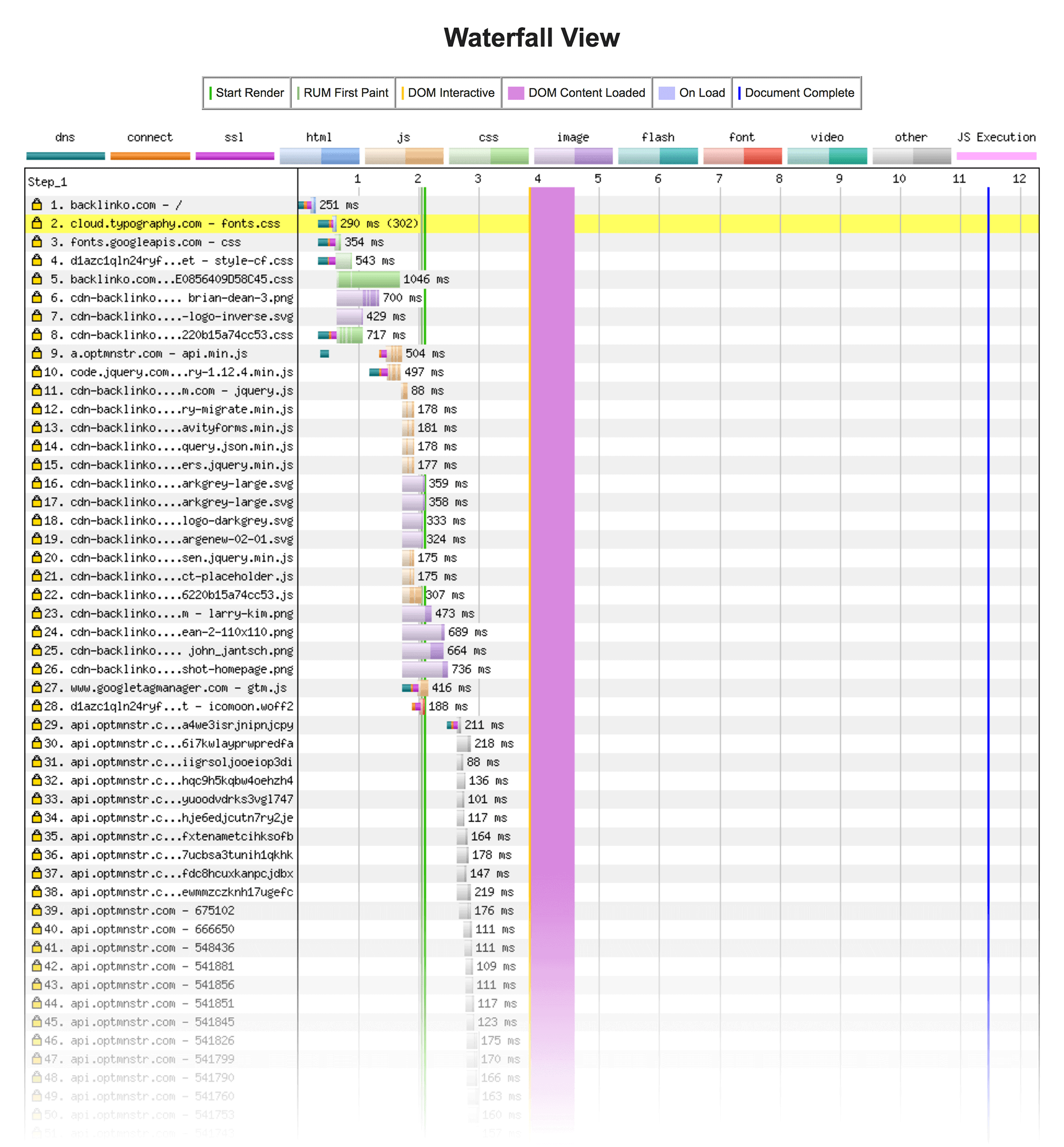
Next up, we have WebPageTest.org.
What’s cool about WebPageTest is that it loads your page in an actual browser. And it lets you know about specific parts of your page that take a long time to load.
Learn More
Mobile speed case studies – Push for faster page loads: 3 in-depth case studies that show how improving speed can translate into higher rankings and more organic traffic.