19 NEW SEO Techniques
Written by Brian Dean
This is a list of updated SEO techniques.
These are the same strategies that I use to generate 438,950 organic visitors every month:
Let’s dive right in:
And here are the tactics you’ll learn about in this post.
- 1. Discover Untapped Keywords on Reddit
- 2. Optimize Your Site for Google RankBrain
- 3. Update, Upgrade and Republish Old Blog Posts
- 4. Write Compelling Title and Description Tags
- 5. Find Broken Link Building Opportunities on Wikipedia
- 6. Copy Your Competitors Best Keywords
- 7. Optimize Your Content to Maximize Social Shares
- 8. Link Out to Authority Sites
- 9. Send Authority to Underperforming Pages
- 10. Increase Email Outreach Response Rates
- 11. Write Long YouTube Descriptions
- 12. Optimize Content For Semantic SEO
- 13. Embed Long Tail Keywords In Title Tags
- 14. Use Wikipedia for Keyword and Topic Ideas
- 15. Find Link Building Opportunities From “Best of” Lists
- 16. Publish Content With At Least 1,447 Words
- 17. Remember the “First Link Priority Rule”
- 18. Create Your Own Keywords
- 19. Use Creative Seed Keywords
1. Discover Untapped Keywords on Reddit
Reddit is a keyword research goldmine.
(Especially when it comes to finding long tail keywords.)
Here’s exactly how to use Reddit for keyword research.
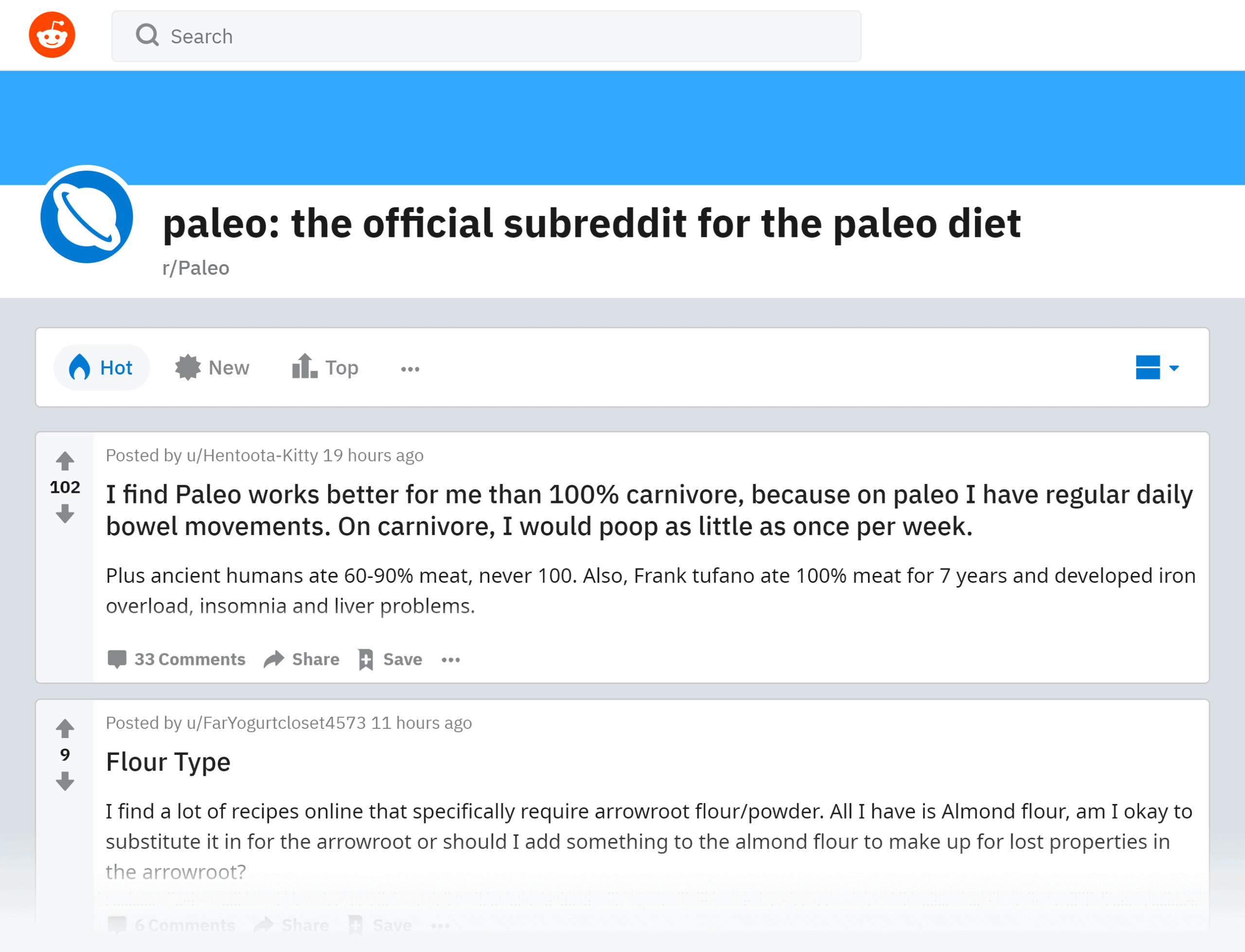
First, head over to Reddit. If you already know a subreddit where your target audience hangs out, head directly there.
For example, let’s say you wanted to write an article about The Paleo Diet. You want to go to the r/paleo subreddit.
If you’re not sure where your audience is on Reddit, no worries.
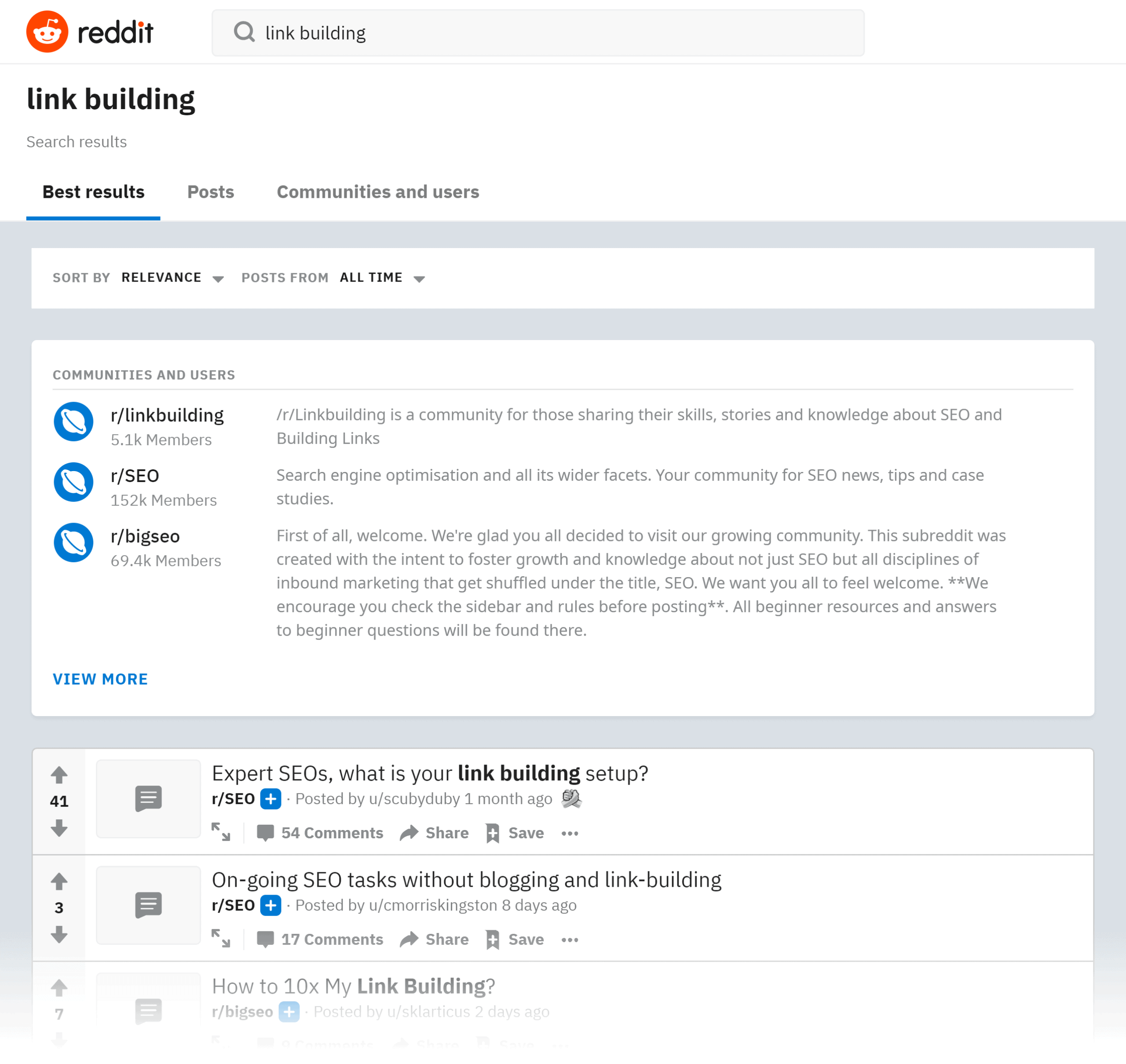
Just search for your topic…

…and see which threads and subreddits come up.
Finally, look for terms that appear again and again.
If people are talking about these topics on Reddit, chances are they’re searching for those same terms in Google.
For example, when I looked at threads on the topic of “link building”, I noticed terms like “content strategy” and “content strategies”.
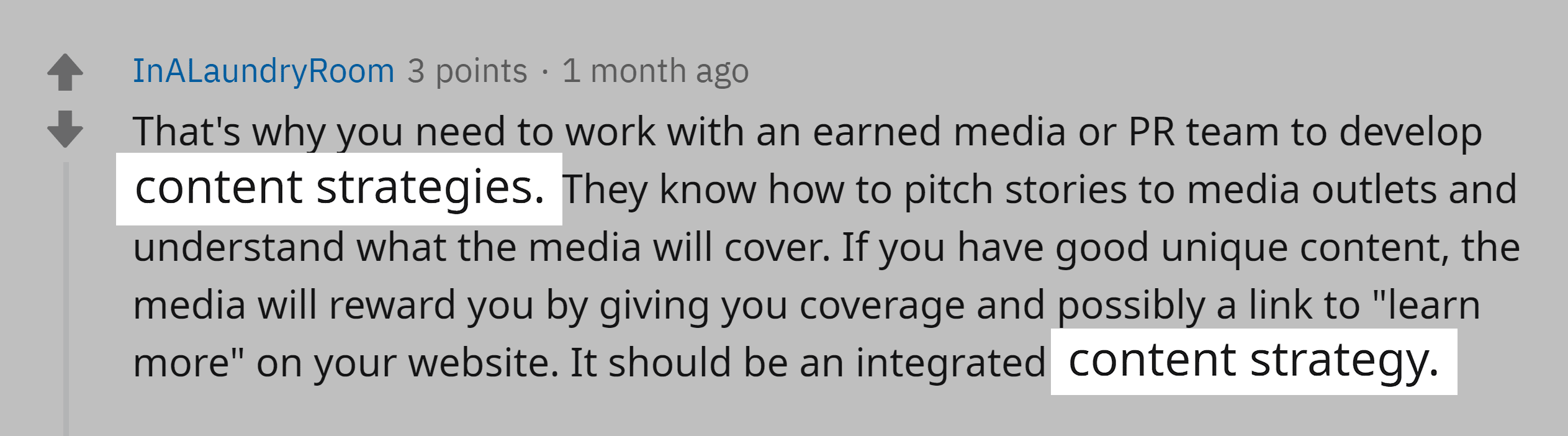
These are keywords that I would have never thought of on my own. Thanks Reddit!
2. Optimize Your Site for Google RankBrain
A while back, Google announced their RankBrain algorithm.
As it turns out, this update was a game-changer.
Why?
Google RankBrain is Google’s machine learning algorithm. This new ML algorithm allowed Google to accurately measure how users interact with the search results:
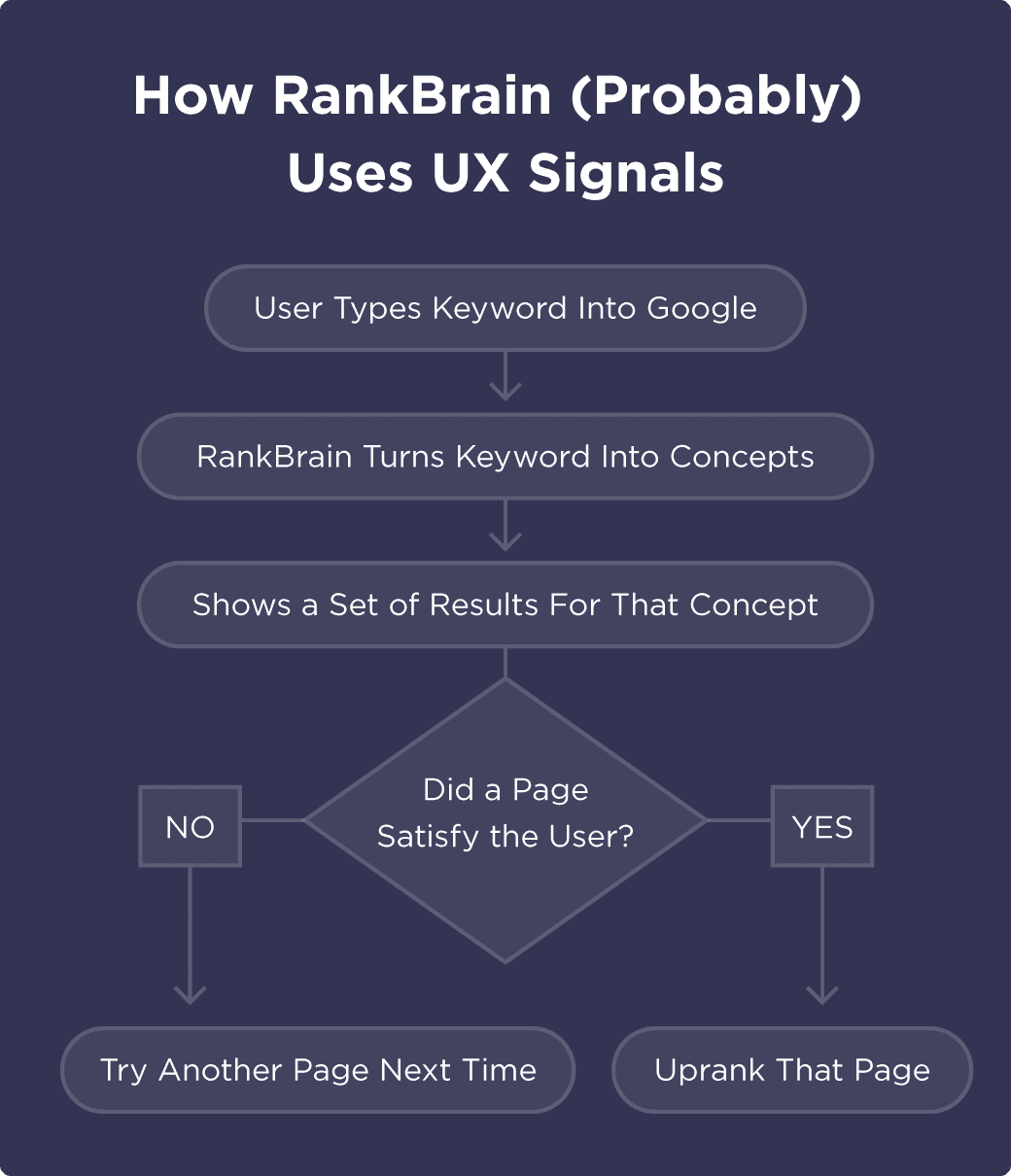
As you can see, the happier you make Google’s users, the higher you’ll rank.
Sure, backlinks, keywords and other traditional signals are still important. But RankBrain is becoming more and more important.
In fact, Google went on to say that RankBrain was one of their “top 3” ranking signals:

So, how do you optimize your site for Google RankBrain?
Here are two simple, easy-to-implement tips that are working super well right now:
First, improve your organic click-through rate (CTR).
Google RankBrain wants to see that lots of people are clicking on your site in the search results.
That tells Google:
“People love this result. Let’s boost it to the top of the page so it’s easier to find”.
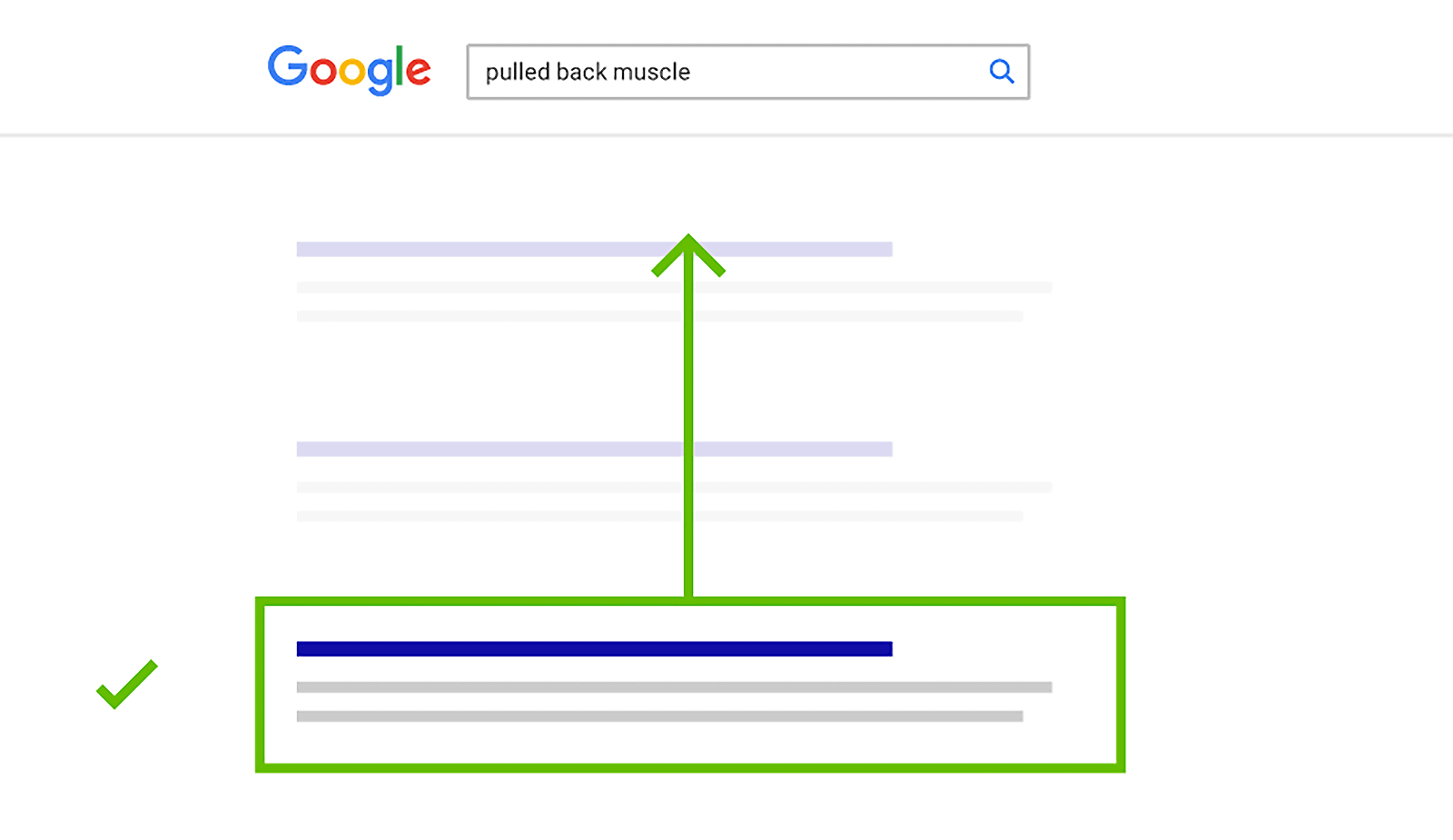
But if people don’t click on your result? Google will drop your site like a stone.
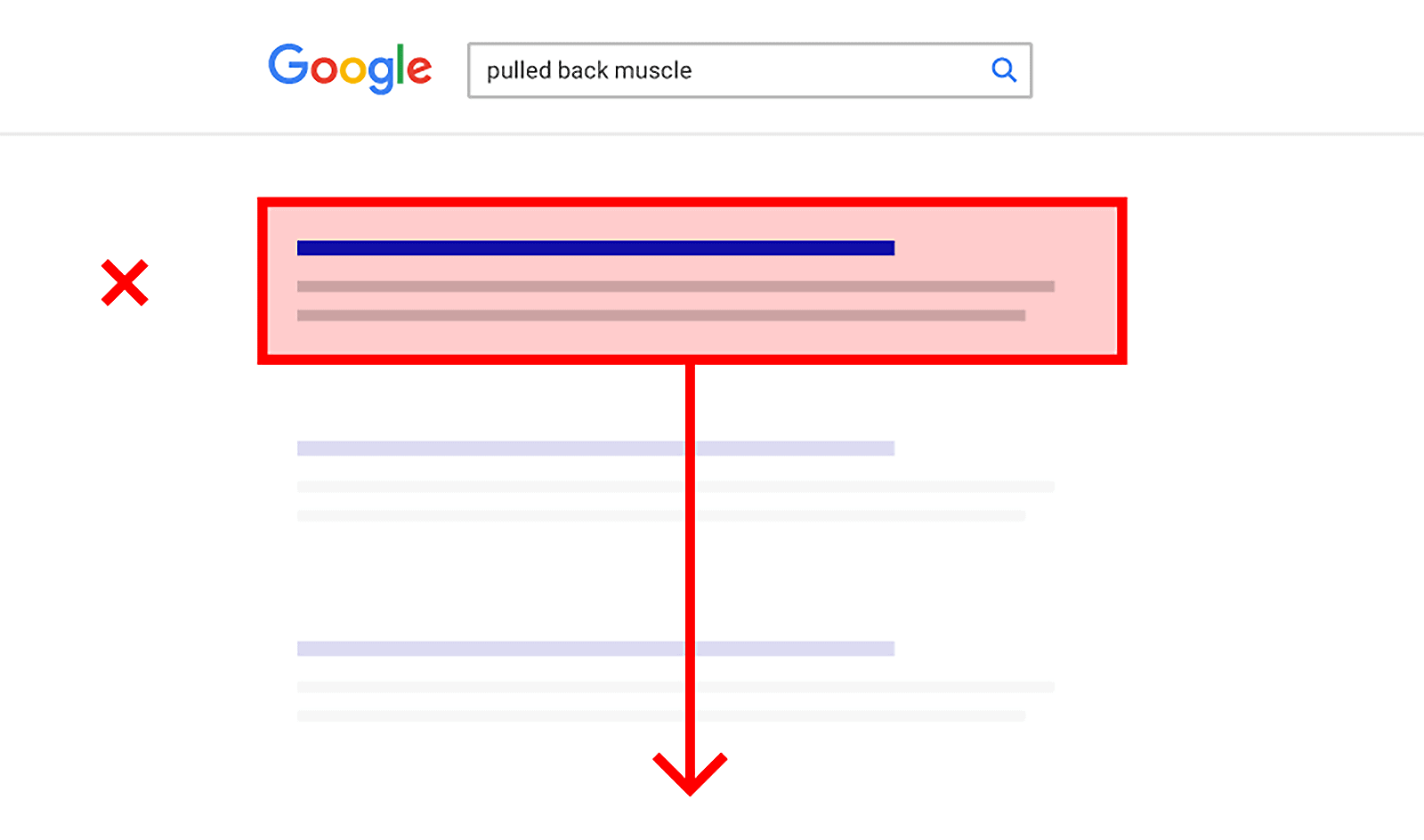
And that’s why optimizing your site for organic CTR is so important.
One of the easiest ways to get more clicks is to add numbers to your title and description tag.
Here’s a real-life example from one of my blog posts:

Research shows that people online are more likely to click on content that contains a number.
So when you include a number in your content’s title (and in your meta description), you can increase your CTR significantly.
Next, improve your bounce rate and “Dwell Time”.
Again, Google RankBrain wants you to publish content that makes its users happy.
And if users leave your site (also known as a “bounce“) after 3 seconds? That’s a user experience signal that tells Google that people don’t like your content.
In fact, my analysis of 11 million Google search results discovered that sites with a good dwell time ranked above sites with a poor dwell time:
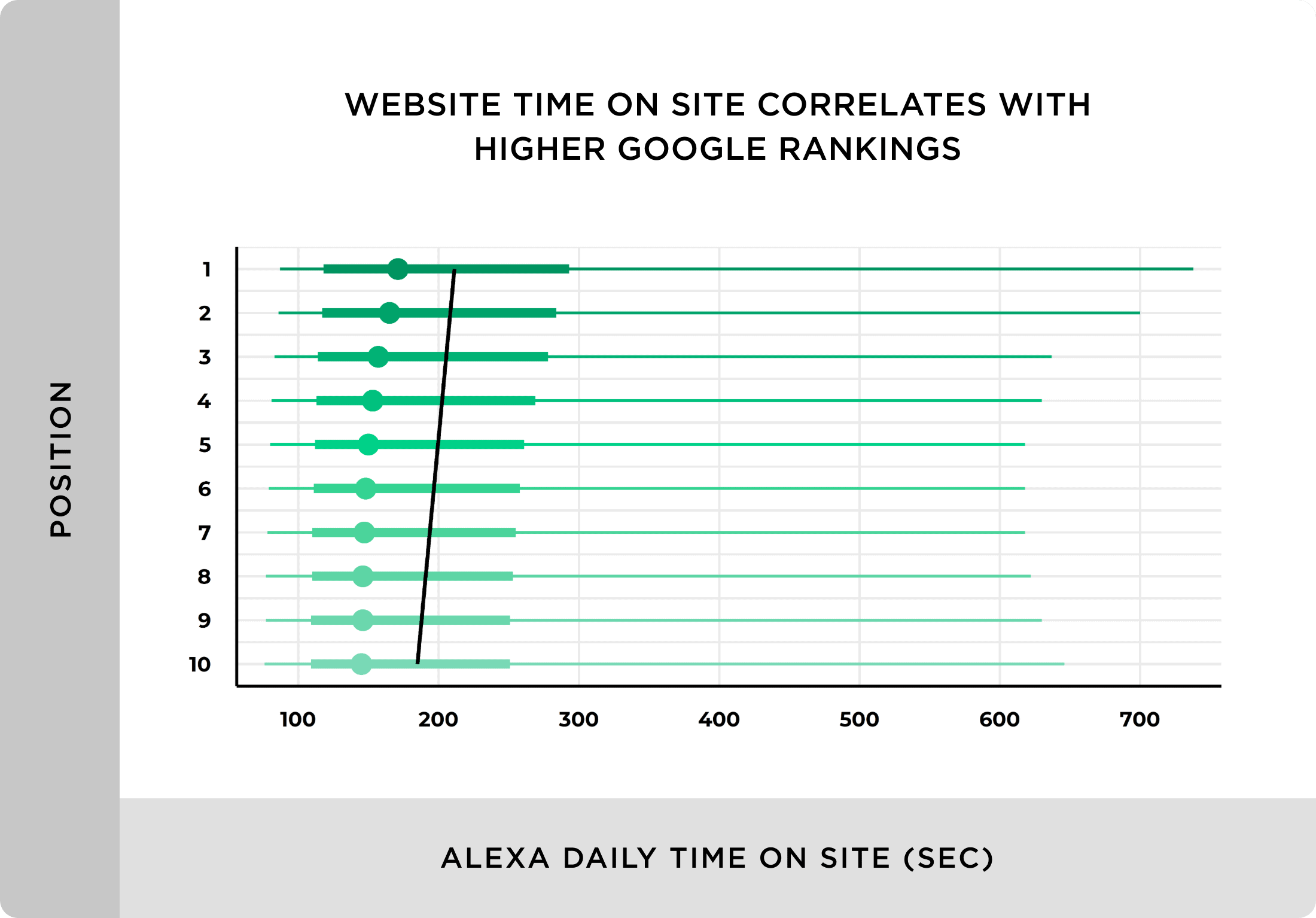
See how that works? The better your bounce rate, the better you rank.
And the longer searchers stay on your site (known as “Dwell Time“), in general, the higher you’ll rank.
How do you actually improve your Dwell Time and bounce rate?
Write compelling introductions that encourage people to take action.
In other words, avoid intros like this:
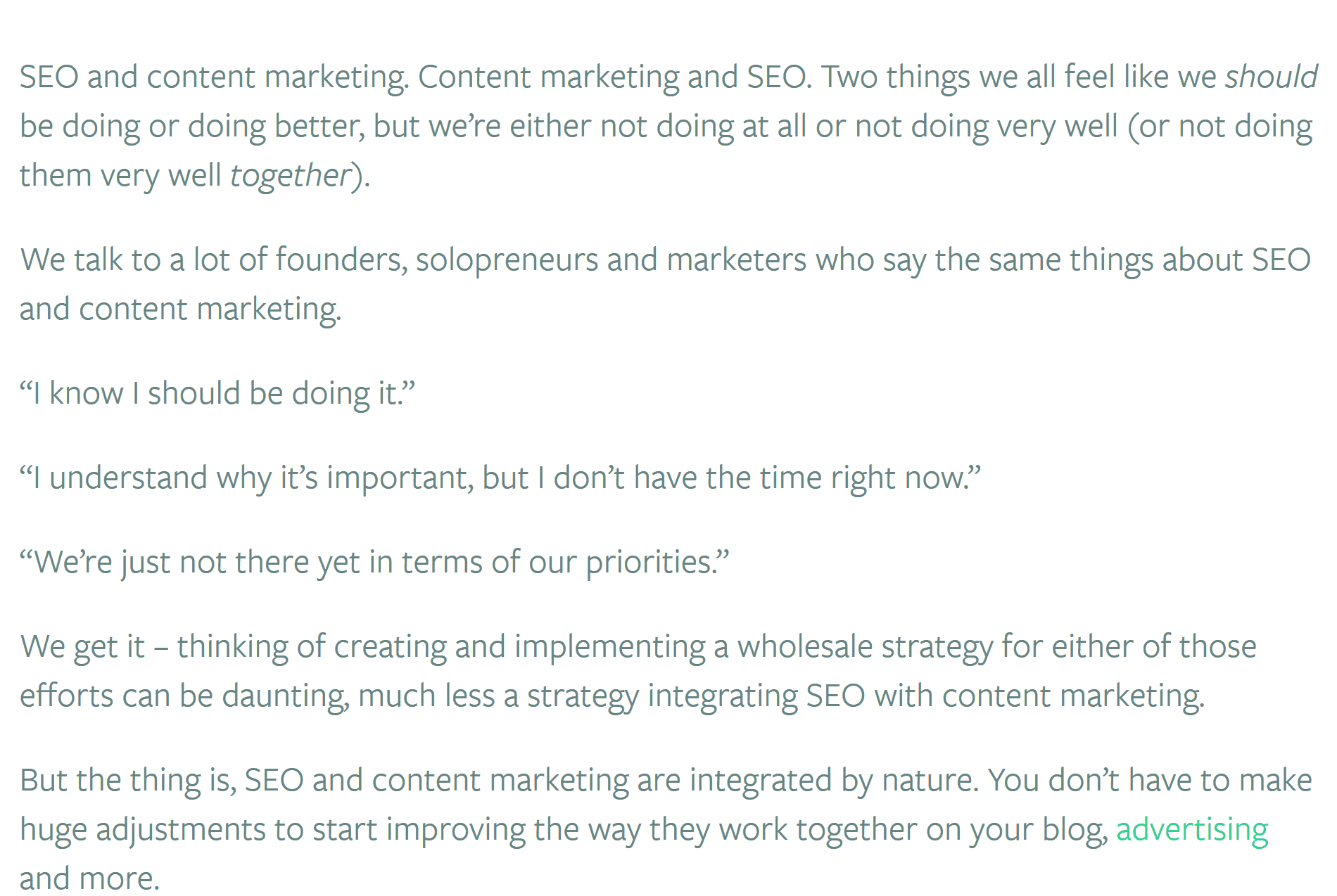
If someone lands on this intro, they’re going to bounce as fast as possible.
Instead, get STRAIGHT to the point, like this:
Boom. Anyone landing on that page knows exactly what my piece of content is about.
I also recommend breaking up your content into mini, bite-sized chunks.
In other words, you want your content to look like this:

As you can see, this copy is super easy to read.
And it’s especially easy to read on a phone or tablet. Considering that most Google searches are now done on mobile devices, readability is more important for SEO than ever before.
3. Update, Upgrade and Republish Old Blog Posts
A few years years ago I got an email out of the blue:
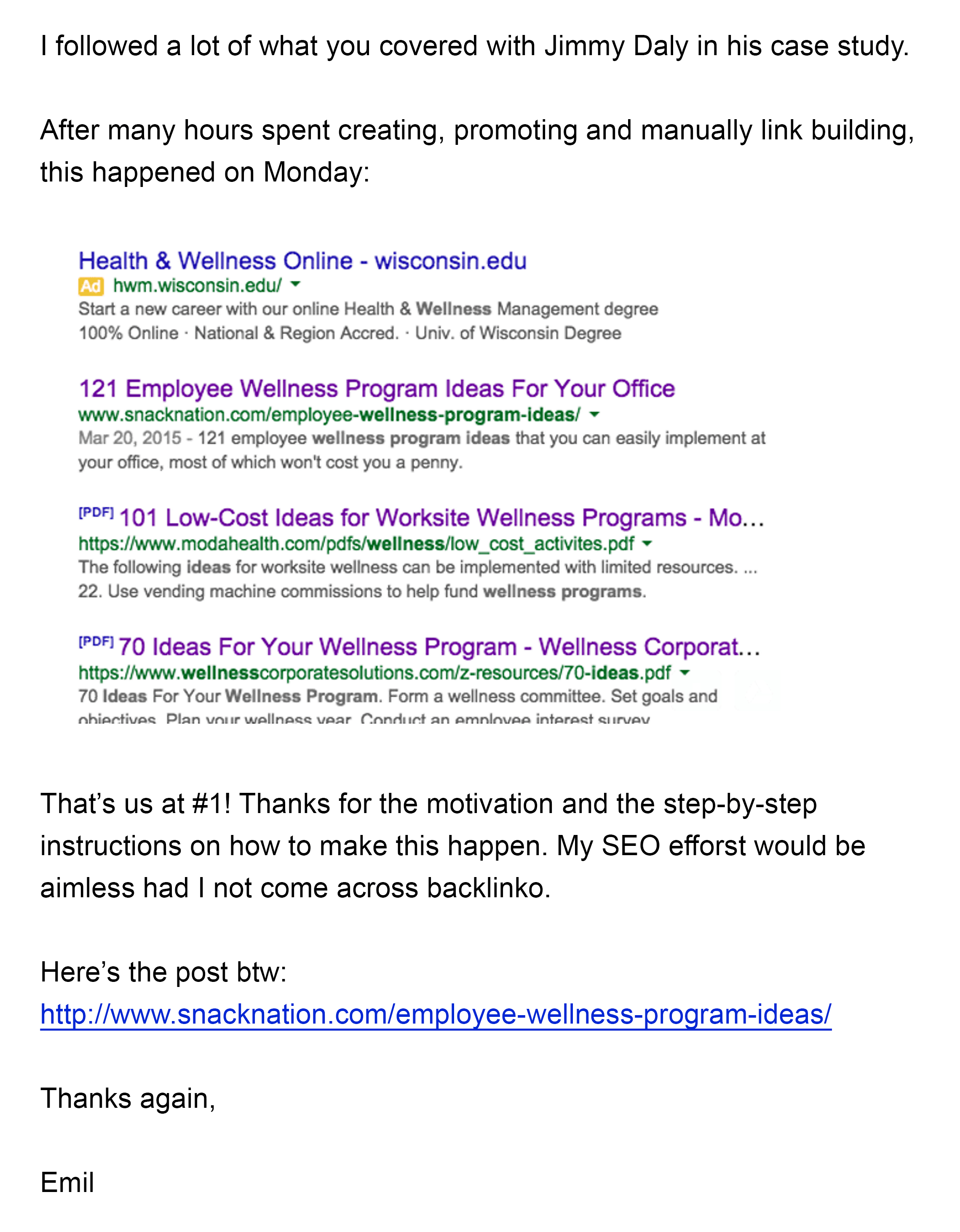
Turns out Emil used The Skyscraper Technique to achieve these impressive results.
Not only that, but Emil wanted to share his great content with the Backlinko community.
That’s when I had an idea:
Instead of writing a new post for Emil’s case study, why don’t I add it to an existing post?
So that’s what I did.
Specifically, I added Emil’s case study to this old post:
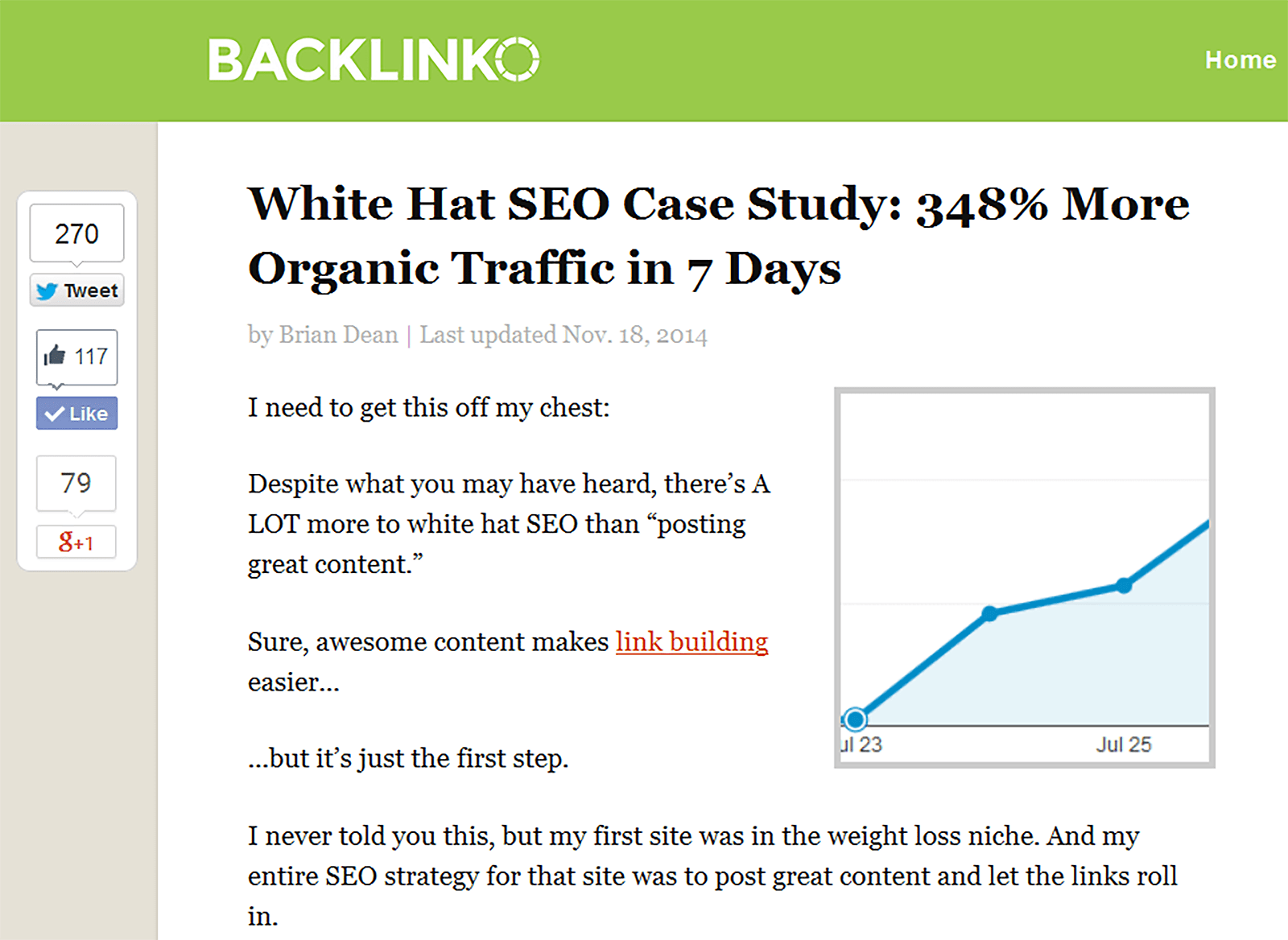
(I also updated the images and added some new tips.)
The final result?
A new and improved version of the post:

To make sure the new post got the attention it deserved, I re-promoted it by sending an email to my newsletter subscribers:
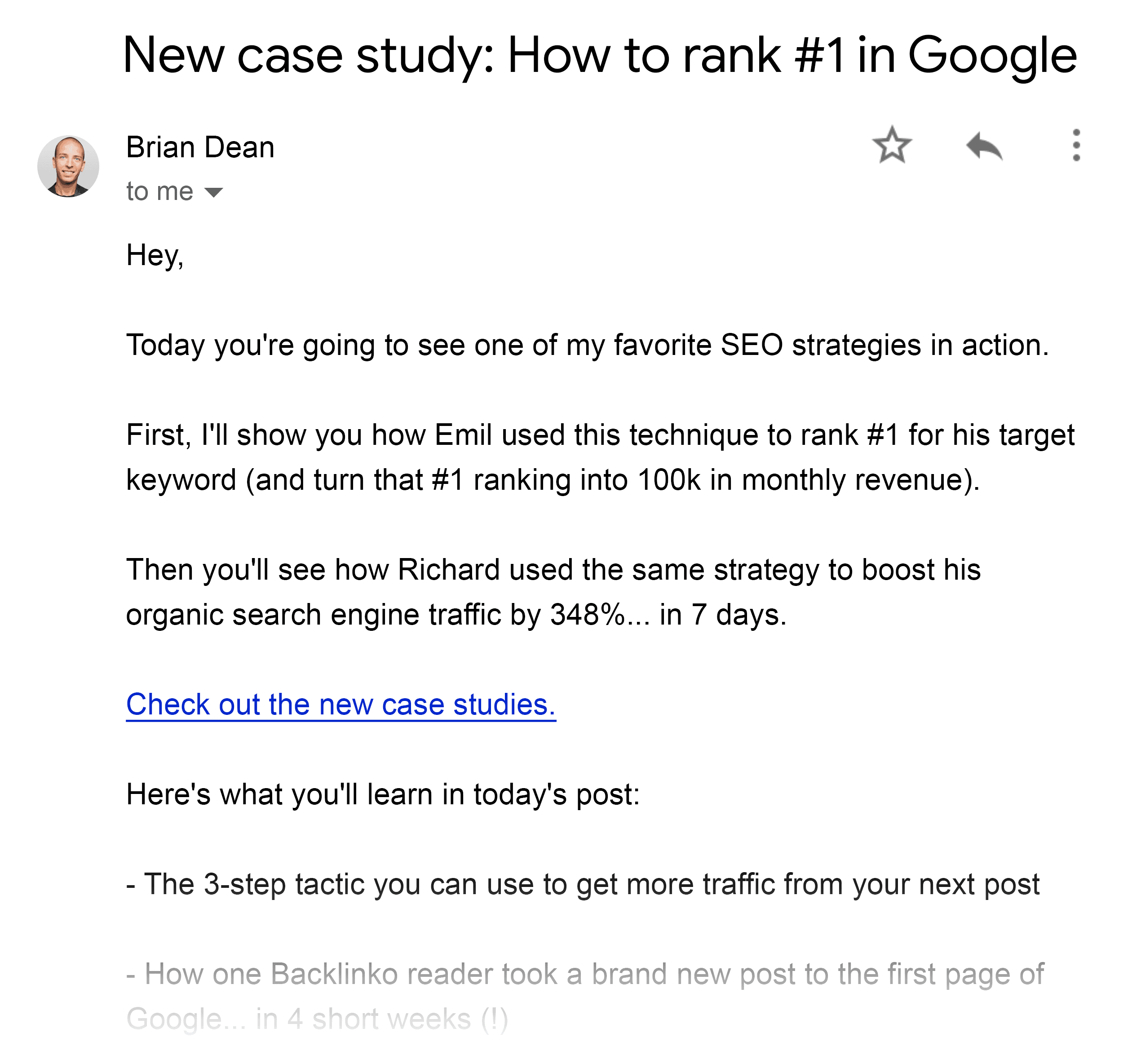
I also shared it on social media:

The result?
A 118.91% increase in organic traffic to that page.
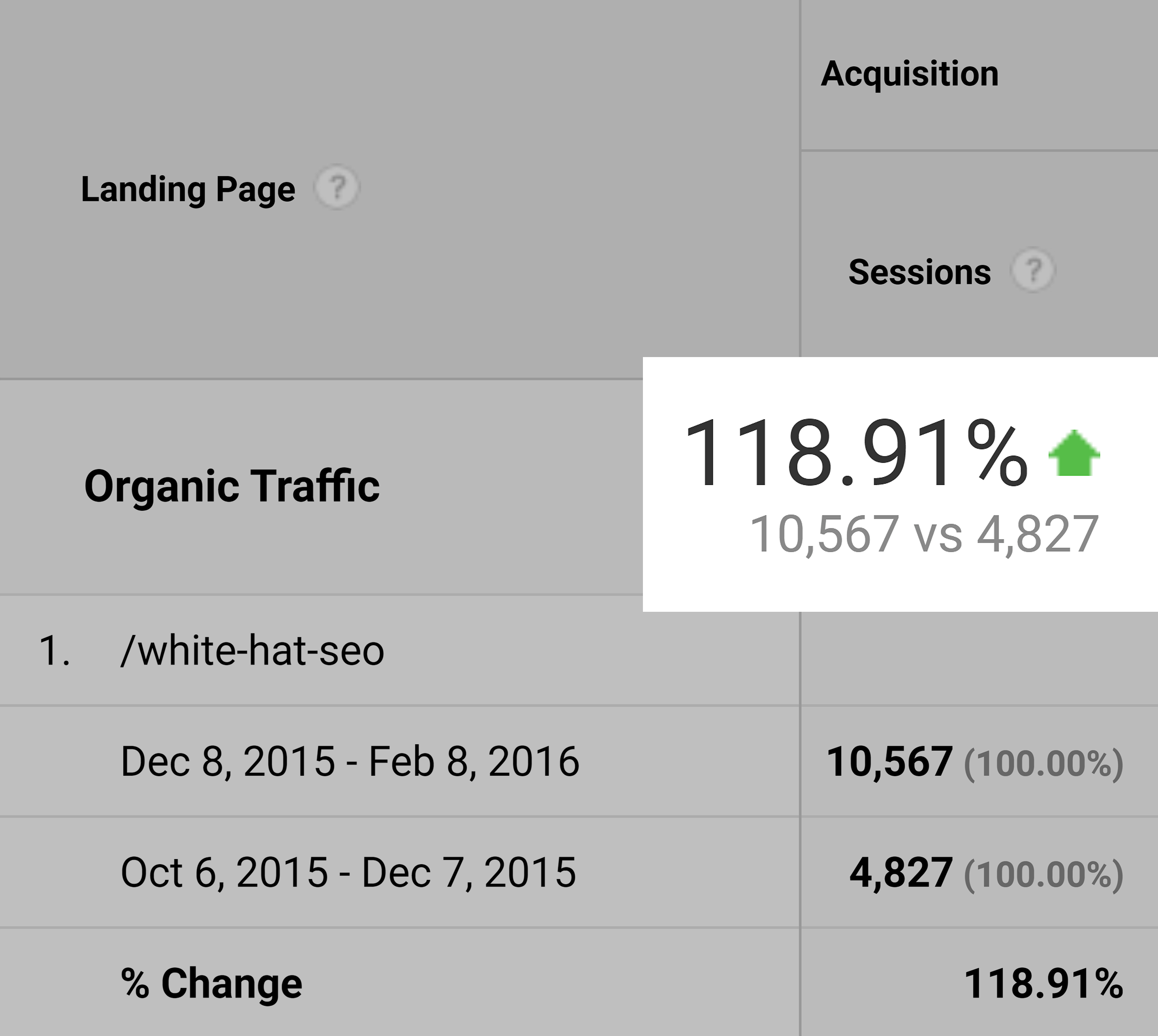
(In case you’re wondering, no, this wasn’t a fluke. I’ve used “The Content Relaunch” several times since then, and it’s worked great each time.)
4. Write Compelling Title and Description Tags
It’s no secret that compelling title and description tags get more clicks in the SERPS.
(And like I mentioned earlier, more organic clicks=higher Google rankings.)
The question is: How do you know what people want to click on?
Look at that keyword’s Google Adwords ads.
You see, ads that you see for competitive keywords are the result of hundreds (if not thousands) of split tests.
Split tests designed to maximize clicks.
And you can use copy from these ads to make your title and description tags more compelling.
For example, let’s say you were going to publish a blog post optimized around the keyword “best mattress”.
First, take a look at the ads for that keyword:
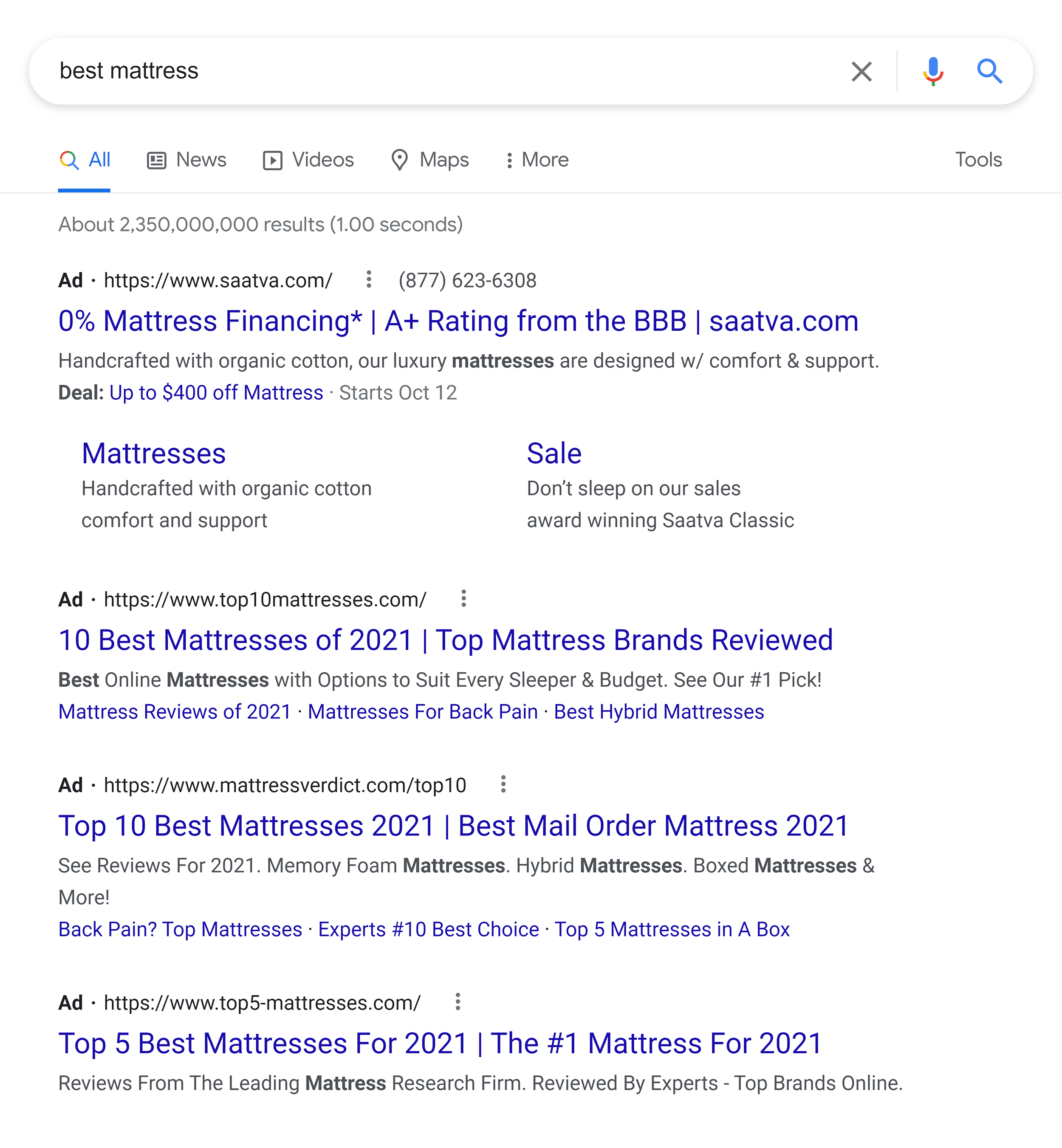
Keep an eye out for interesting copy from the ads that you can work into your title and description:
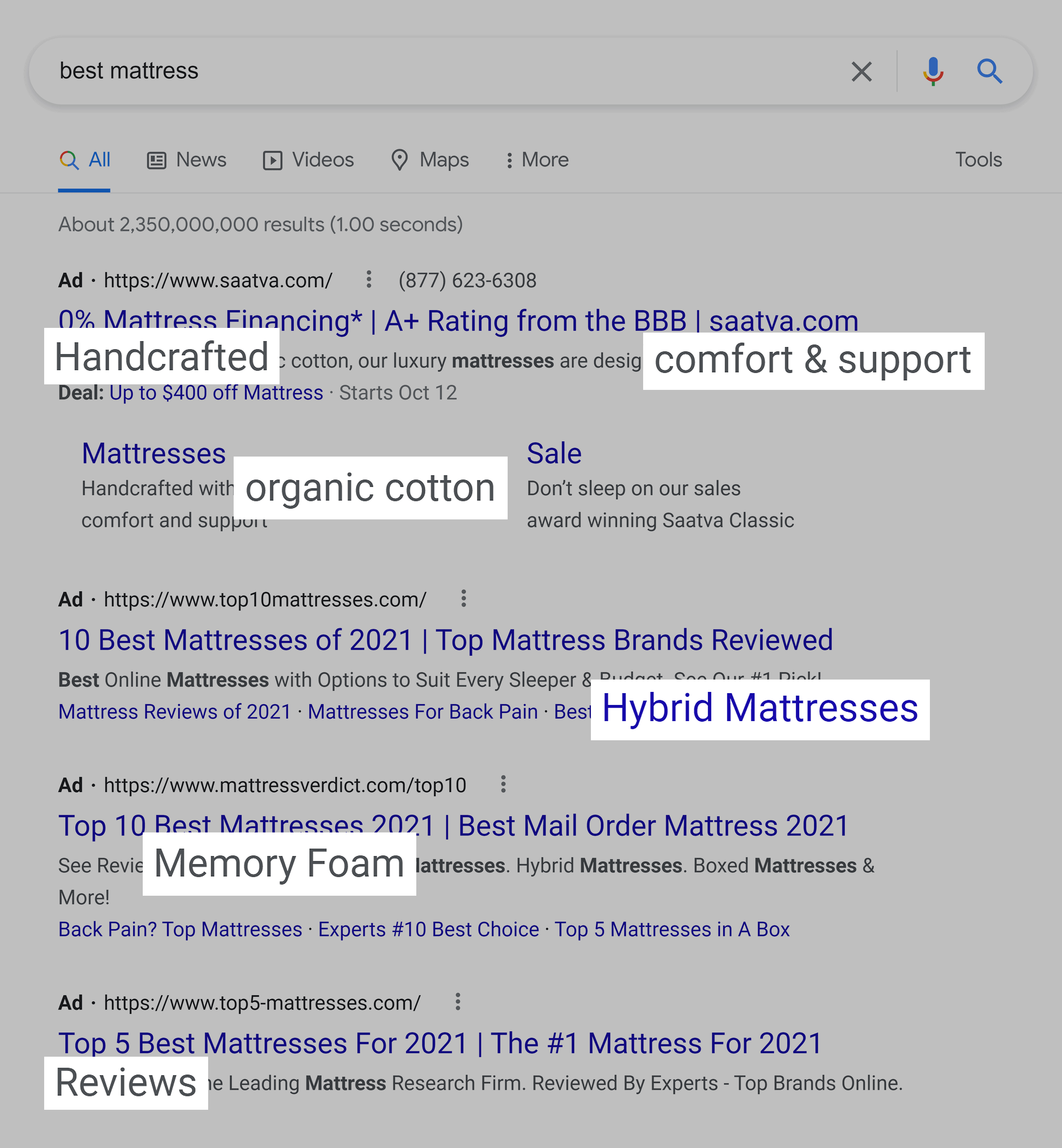
As you can see, these tags include words that are proven to generate clicks. So when you include these terms in your page’s title and description, you’ll likely get more clicks:
5. Find Broken Link Building Opportunities on Wikipedia
[Note: This is an advanced SEO strategy. So if you’re new to search engine optimization, feel free to skip this tip.]
Broken link building is one of my favorite link building strategies.
There’s only one problem: finding broken links is super time-consuming.
That is unless you know about a little-known wrinkle in Wikipedia’s editing system.
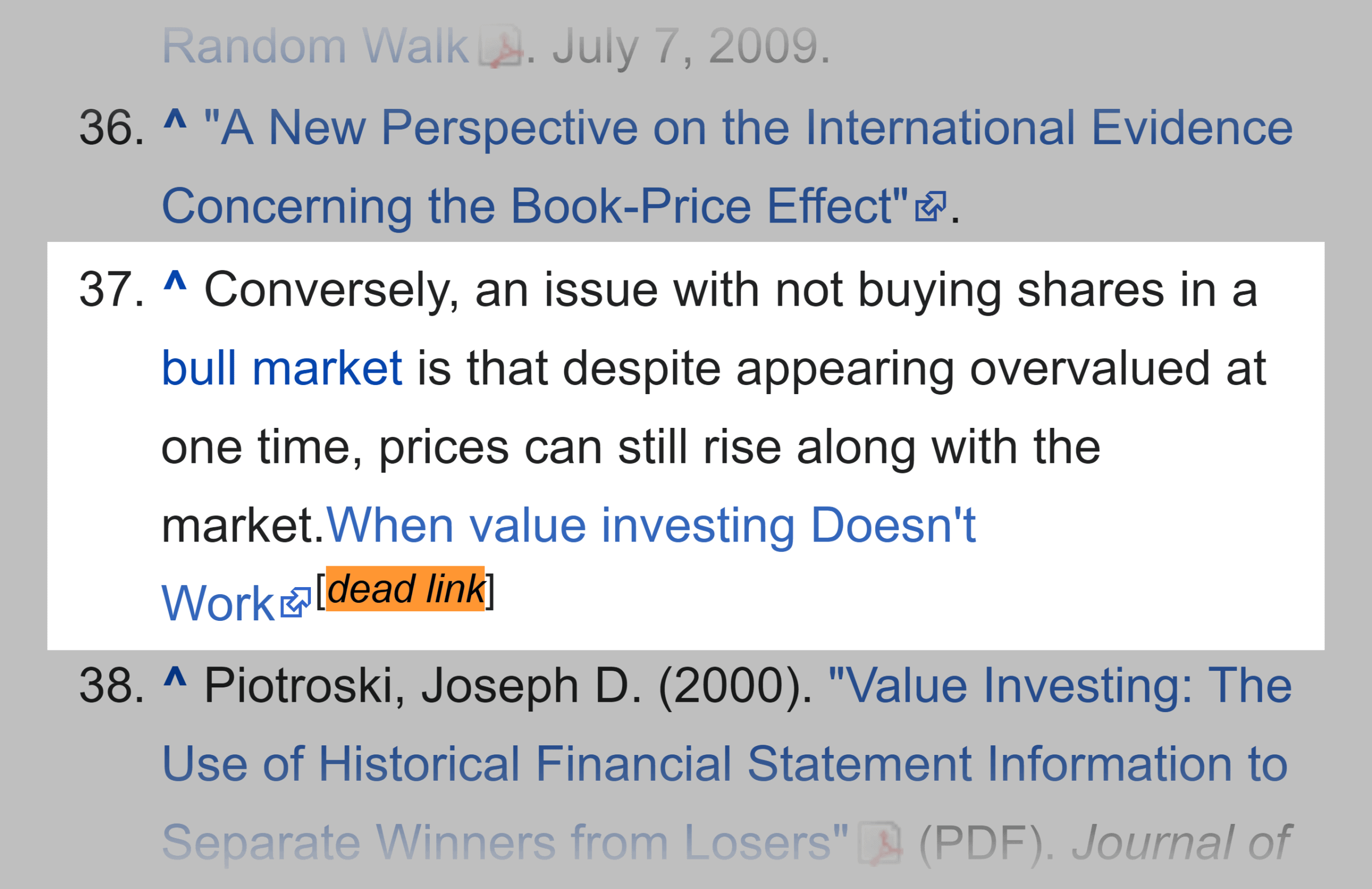
You see, when a Wikipedia editor stumbles on a dead link, they don’t delete the link right away.
Instead, they add a footnote next to the link that says “dead link”:
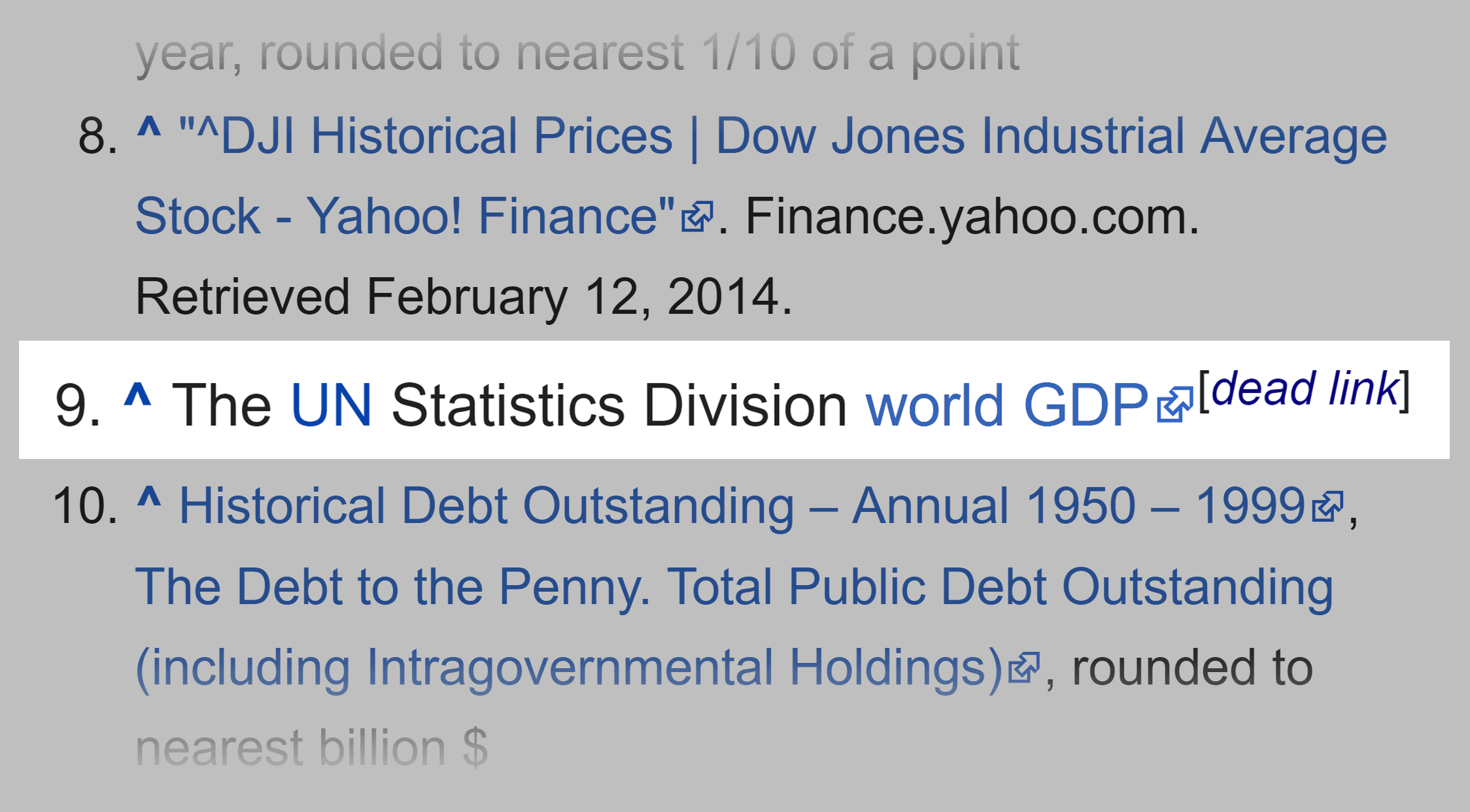
This footnote gives other editors a chance to confirm that the link is actually dead before removing it.
And that simple footnote makes finding broken links pretty simple.
Here’s how:
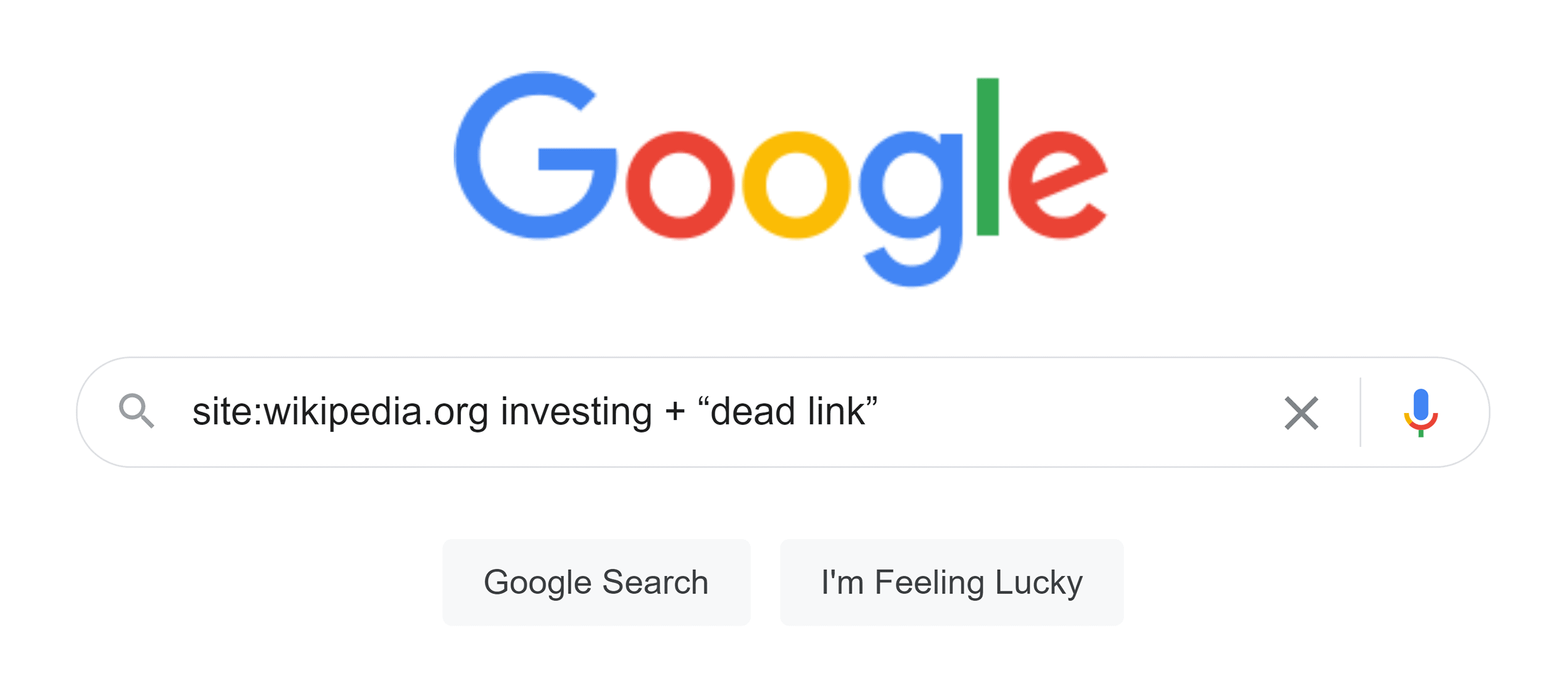
First, use this simple search string:
site:wikipedia.org [keyword] + “dead link”
For example, if you were in the investing space you’d search for something like this:
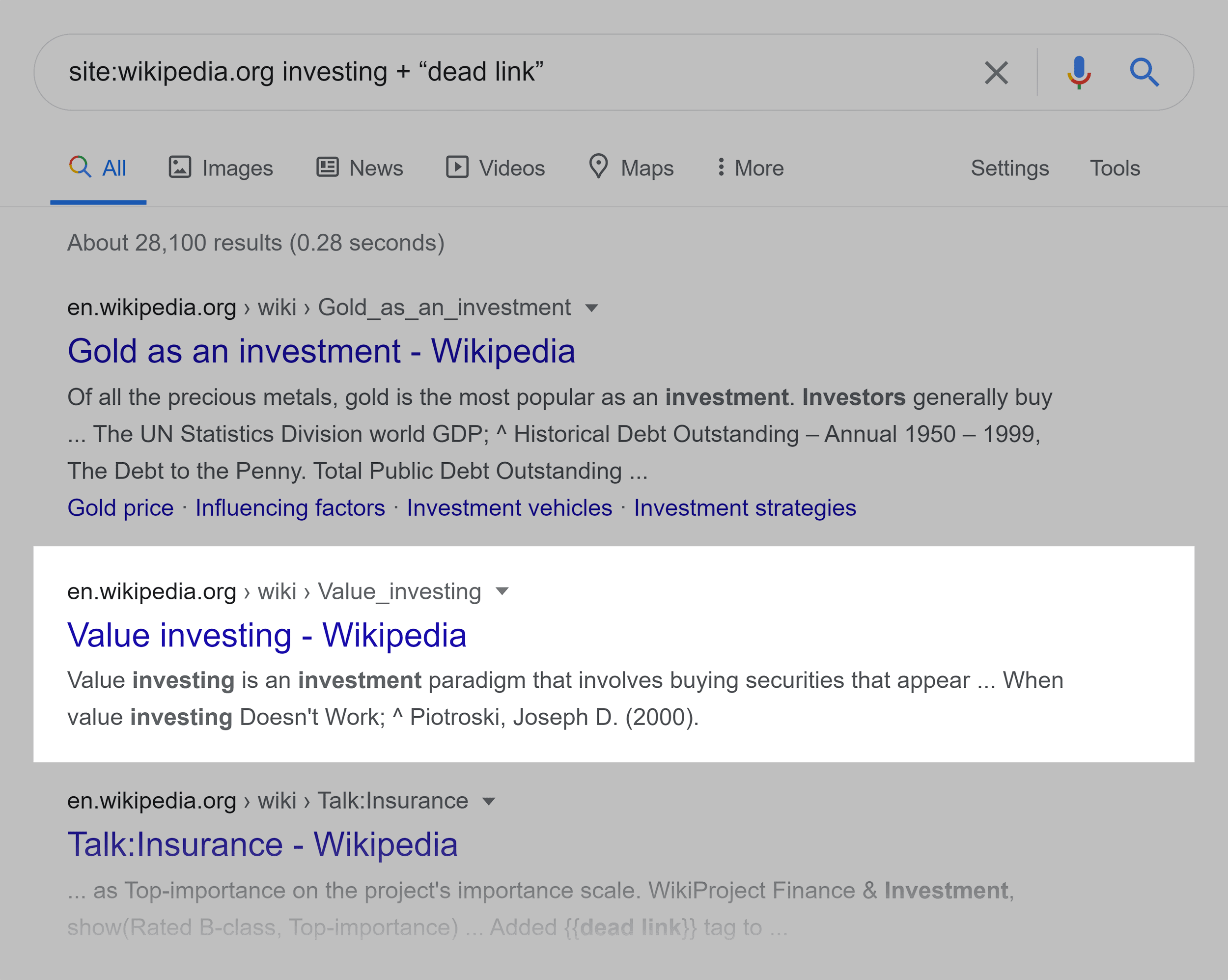
Next, visit a page in the search results that’s relevant to your site:
Hit ctrl + f and search for “dead link”.
Your browser will jump to any dead links in the references section:
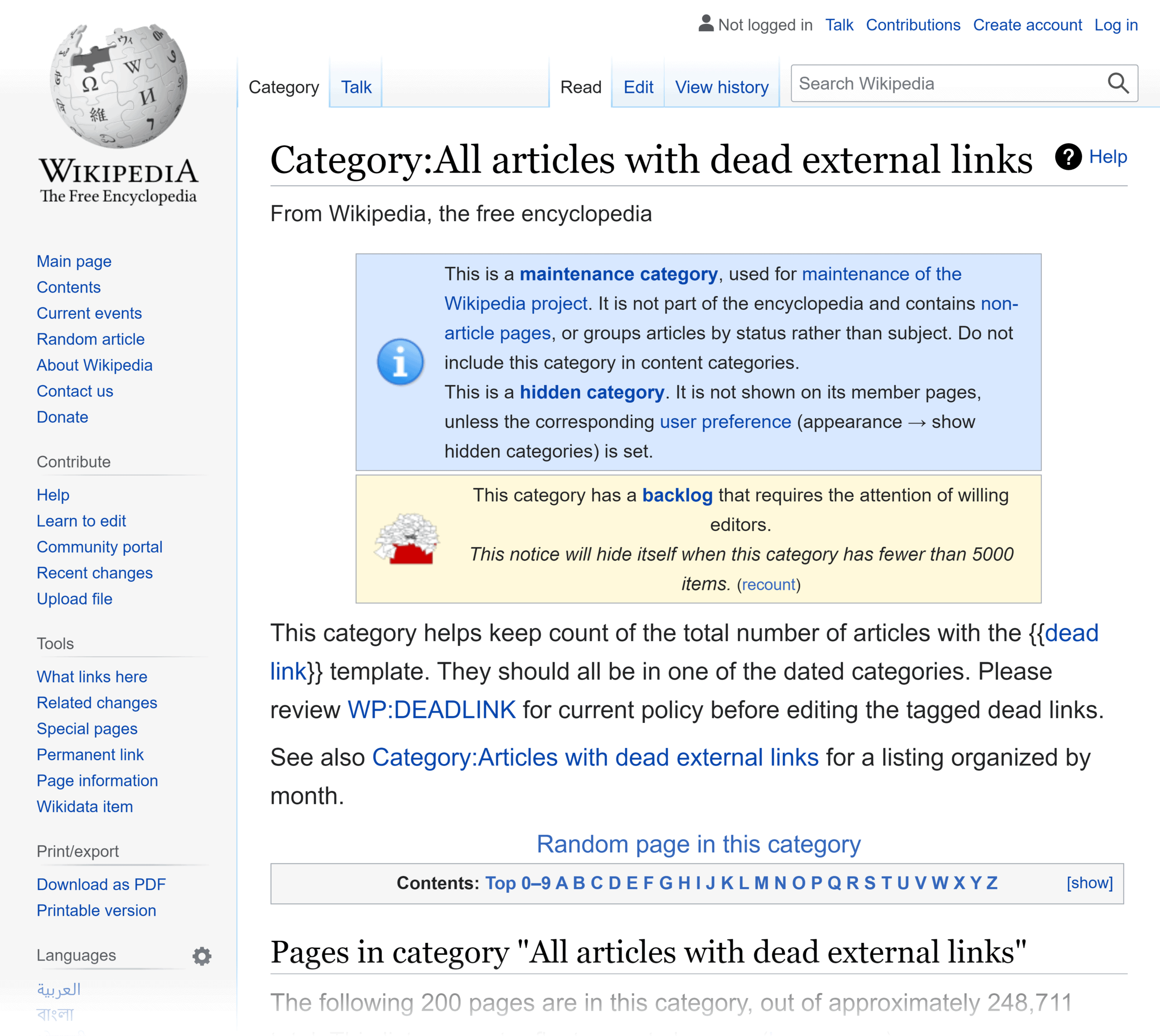
Pro Tip: Wikipedia actually has a list of articles with dead links. This makes finding dead links in Wikipedia even easier.
So once you’ve found a dead link, what’s next?
Well, you could re-create that dead resource on your site and replace the dead link in Wikipedia with a link to your site.
But that would only land you a single link (and a nofollow link at that).
Instead, I recommend reaching out to people that link to the dead resource. And let them know about your replacement content.
6. Copy Your Competitors Best Keywords
There are two ways to find keywords to optimize your content around:
Enter seed keywords into a tool.
OR
Find keywords that your competitors already rank for.
Both approaches can work. That said, I tend to have more luck simply looking at keywords that my competitors already rank for.
Here’s how:
First, find a competing site that’s already ranking well in Google. That way, you’re reverse engineering sites that already know what they’re doing.
For example, here’s a site that writes about the same topics that I do and b) is doing really well in terms of SEO.

Next, pop the site’s homepage into a keyword research tool like Semrush.

And you’ll get a list of keywords that the site ranks for:
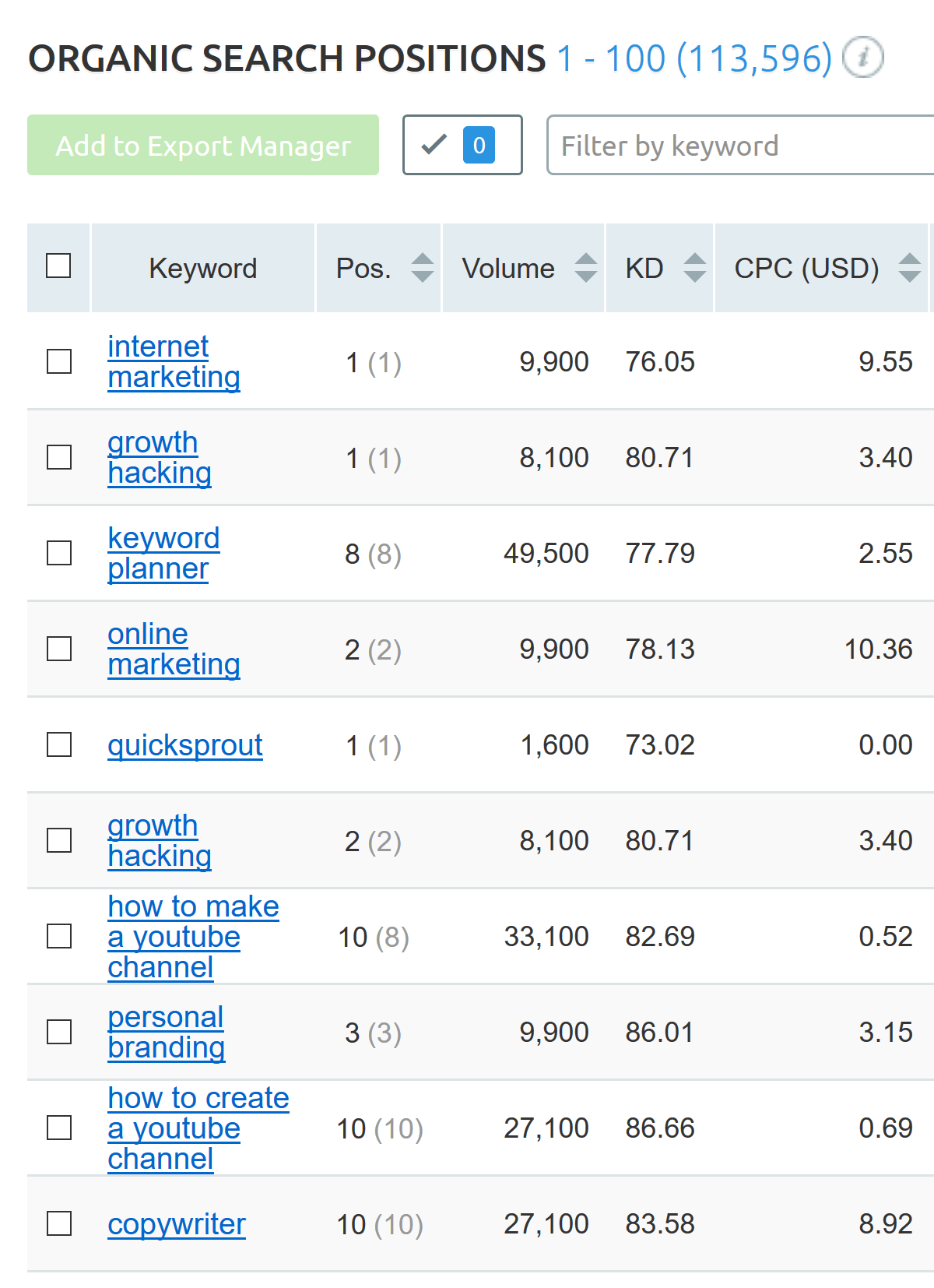
Of course, some of these keywords won’t make sense for your business. For example, they may target keywords that your customers don’t search for. Or maybe they’re ranking for ultra-competitive keywords that you won’t be able to rank for.
Either way, you should come away with a set of keywords that make sense for your business.
7. Optimize Your Content to Maximize Social Shares
Let’s face it: most content isn’t worth sharing.
And without shares (especially in the form of backlinks), you’re not going to rank in Google.
Fortunately, creating share-worthy content to enhance your off-page SEO strategy isn’t that hard.
For example, this post of mine about link building has done really well.
How well? It generated over 900,000 visits from social media, forums, blogs and search engines:

(I should point out that the guide’s design and promotion contributed to its success. But it all started with how the content itself was organized.)
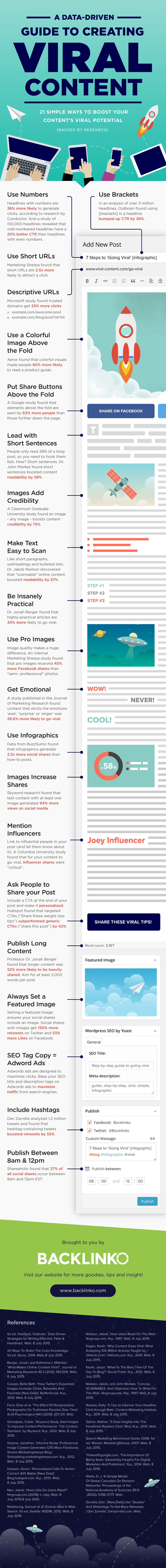
Specifically, my post follows the actionable tips from this infographic:
Now:
There’s a lot of material in this infographic. So let me highlight two SEO techniques from that infographic that are working best for me right now.
First, I use short URLs in almost every blog post.
For example, the URL for this post you’re reading is simply: backlinko.com/seo-techniques.
Why?
Short URLs tend to get more clicks.
Next, I put social share buttons prominently on the page.
You’ve probably noticed that little floating sidebar on the left-hand side of this page.

From lots of testing, I’ve found that these icons increase the amount of Facebook likes and Tweets that my posts receive.
Now, to be clear: Google probably doesn’t use social signals as a ranking factor.
(At least not directly.)
That said, social shares can bring you more traffic. And some of those people might link to you, which can help your rankings.
And now that your content is optimized for shares, you want to make sure your page’s on-page SEO is good to go.
8. Link Out to Authority Sites
Google evaluates your page partly on the quality and relevancy of that page’s outbound links.
This makes total sense if you think about it…
The pages you link out to tend to reflect the topic of your web page.
And pages that link to helpful resources also tend to be higher-quality than pages that only link to their own stuff.
In other words, pages that link out to awesome resources establish themselves as hubs of helpful content in the eyes of Big G.
In fact, this industry study found a correlation between outbound links and Google rankings.
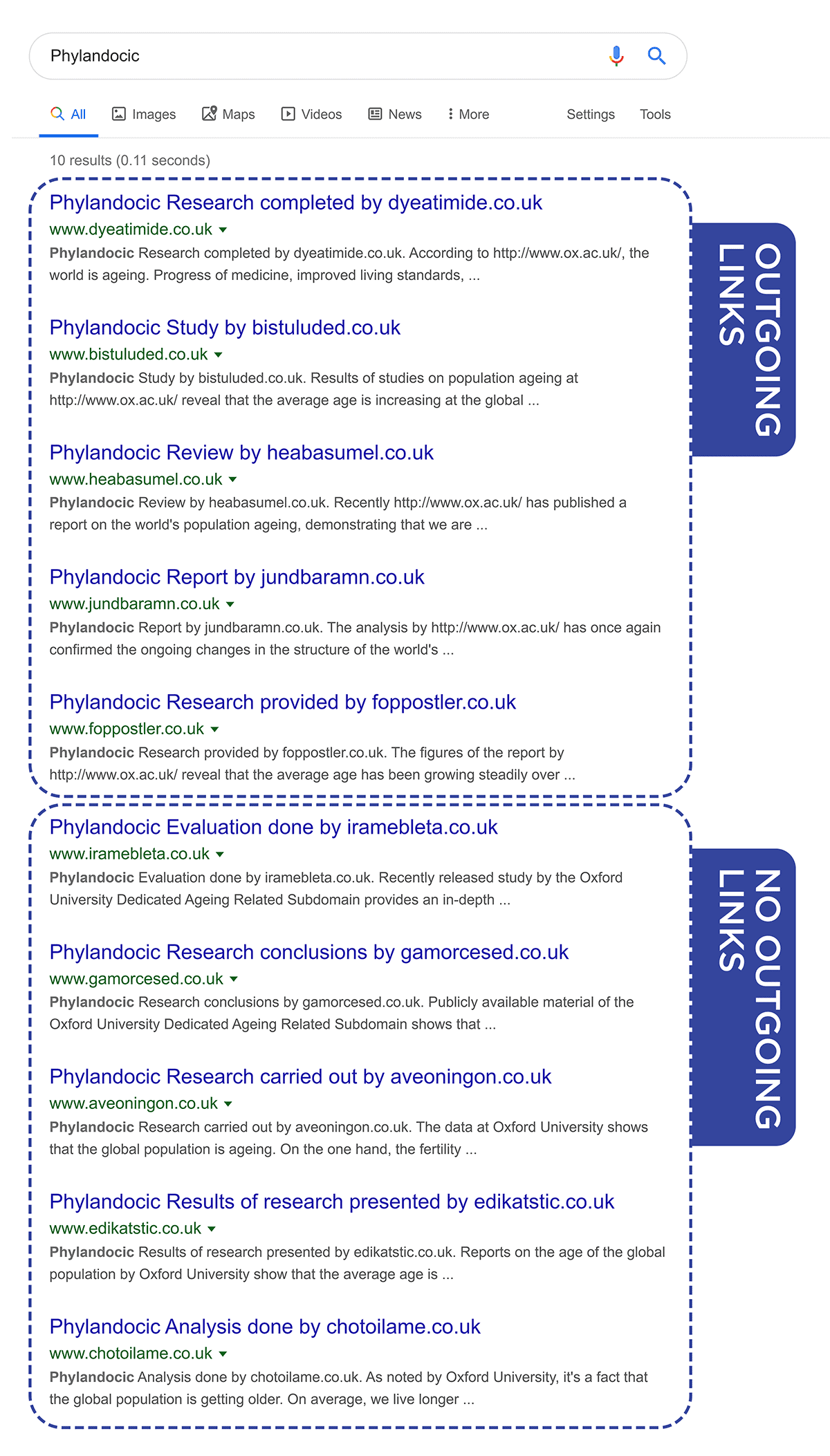
(As a bonus, outbound links are better for user experience too. After all, helpful external links help users find content that can help them learn more about the topics you discuss in your article.)
Bottom line:
Link to at least 3 quality, relevant resources in every piece of content that you publish.
This will show Google that your page is a hub of helpful info.
That said, external links are just ONE of many on-page SEO signals that Google looks at. For a comprehensive list, I recommend watching this video:
9. Send Authority to Underperforming Pages
Our recent Google CTR study found that less than 1% of Google searchers end up on the 2nd page.
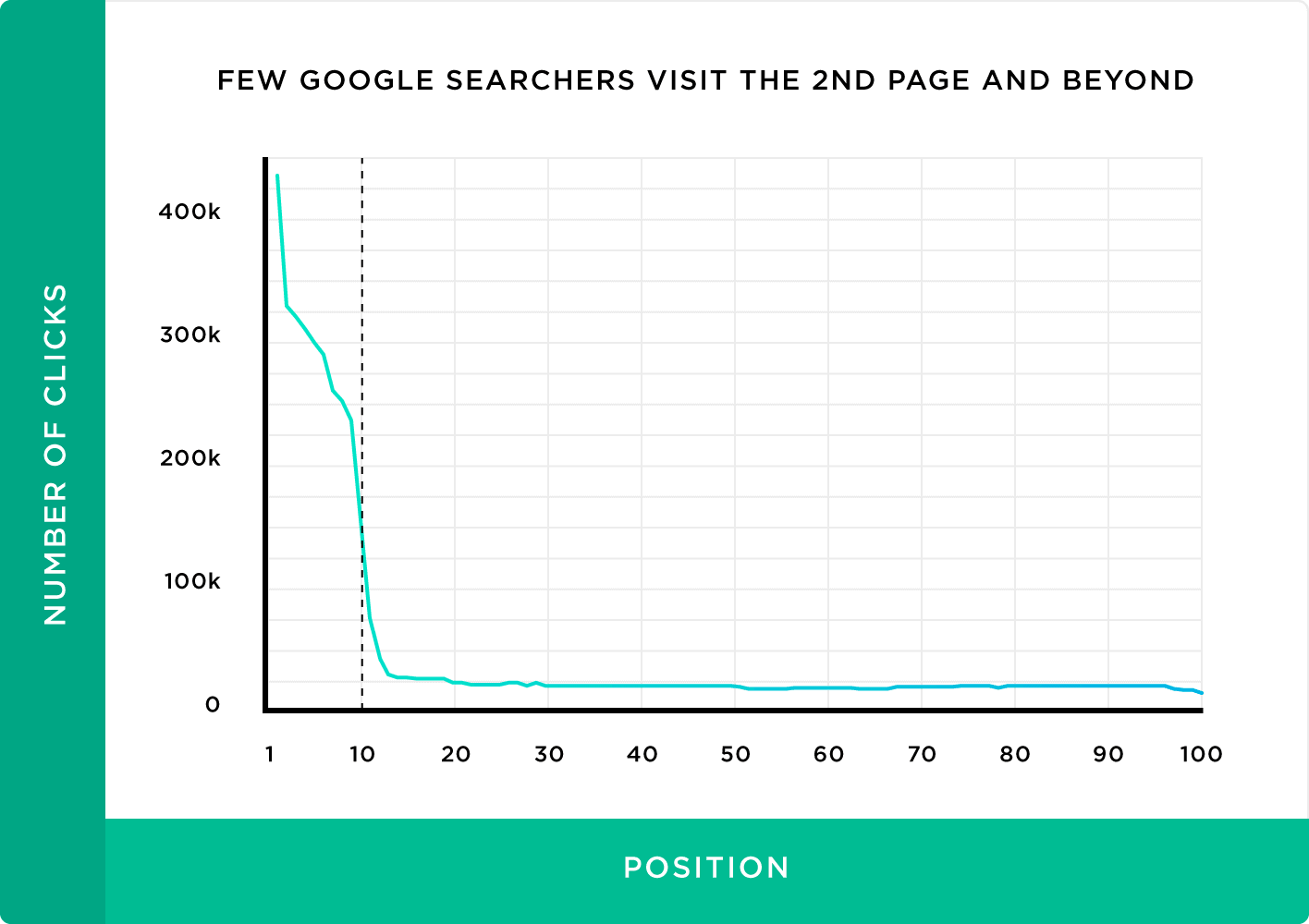
So how can you give those pages a boost so they hit the first page?
Throw some internal links their way.
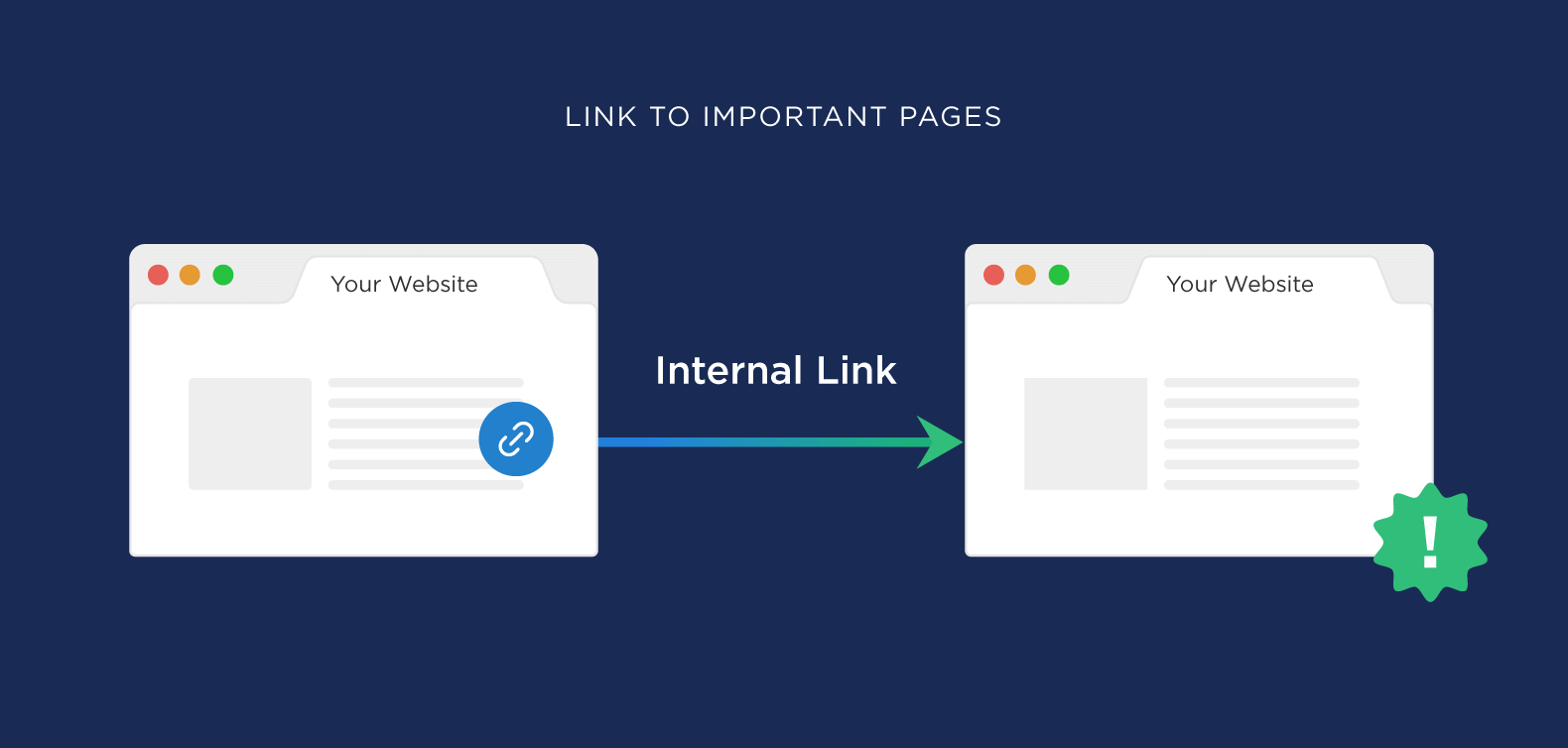
Here’s the 3-step process:
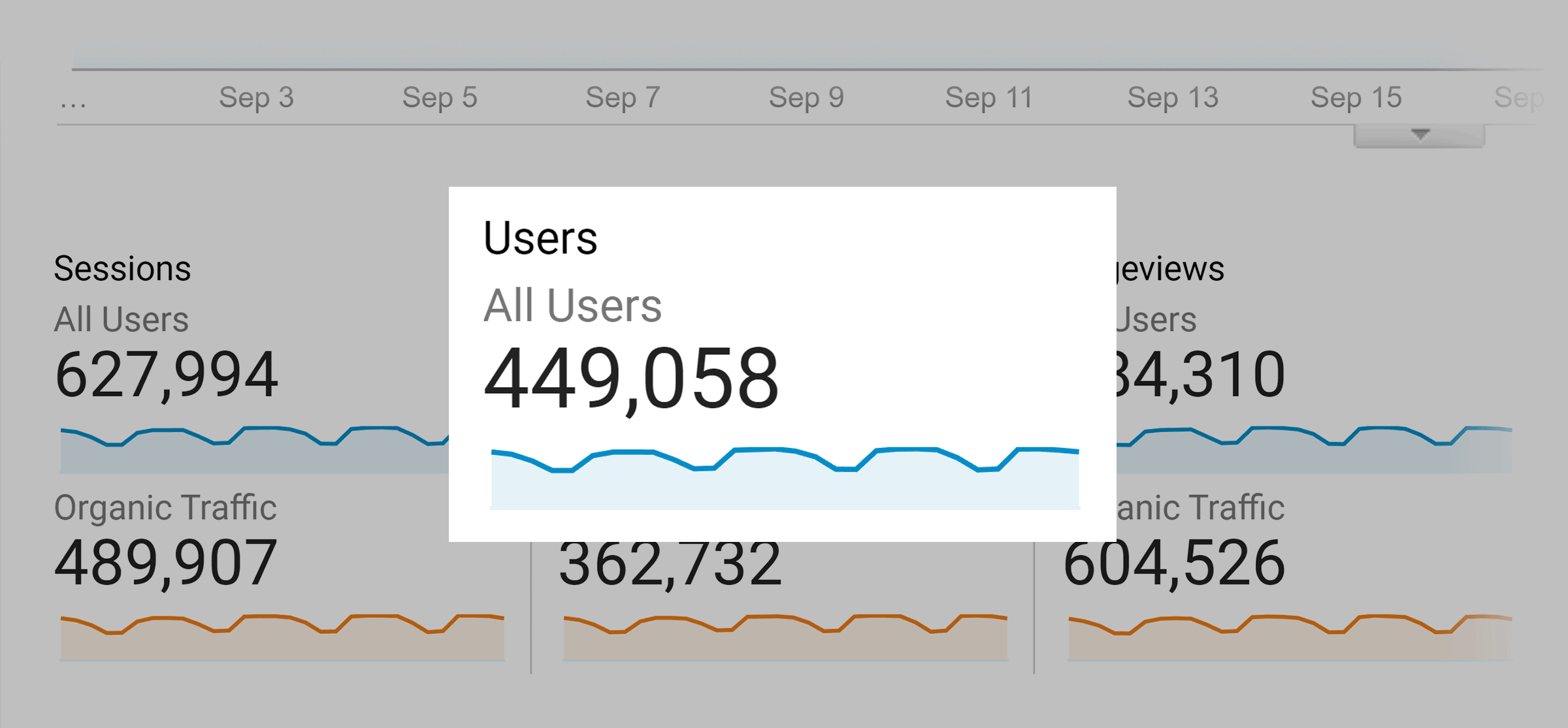
Step #1: Use Google Search Console to find keywords where you rank on the 2nd or 3rd page.
To find them, login to the Google Search Console and head over to the “Search results” report:
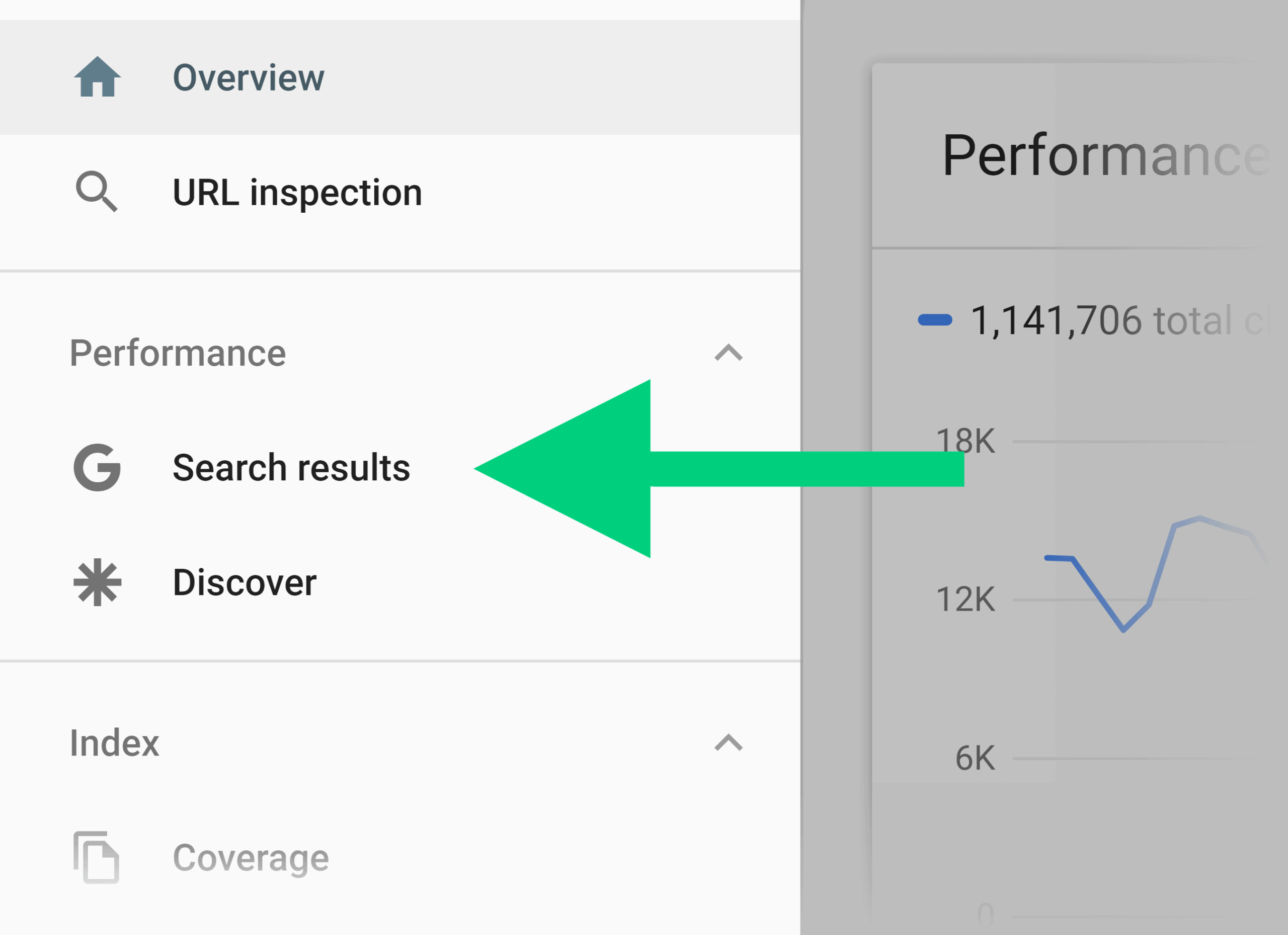
Make sure to hit “Average position”. That way you’ll see the average ranking for each keyword.
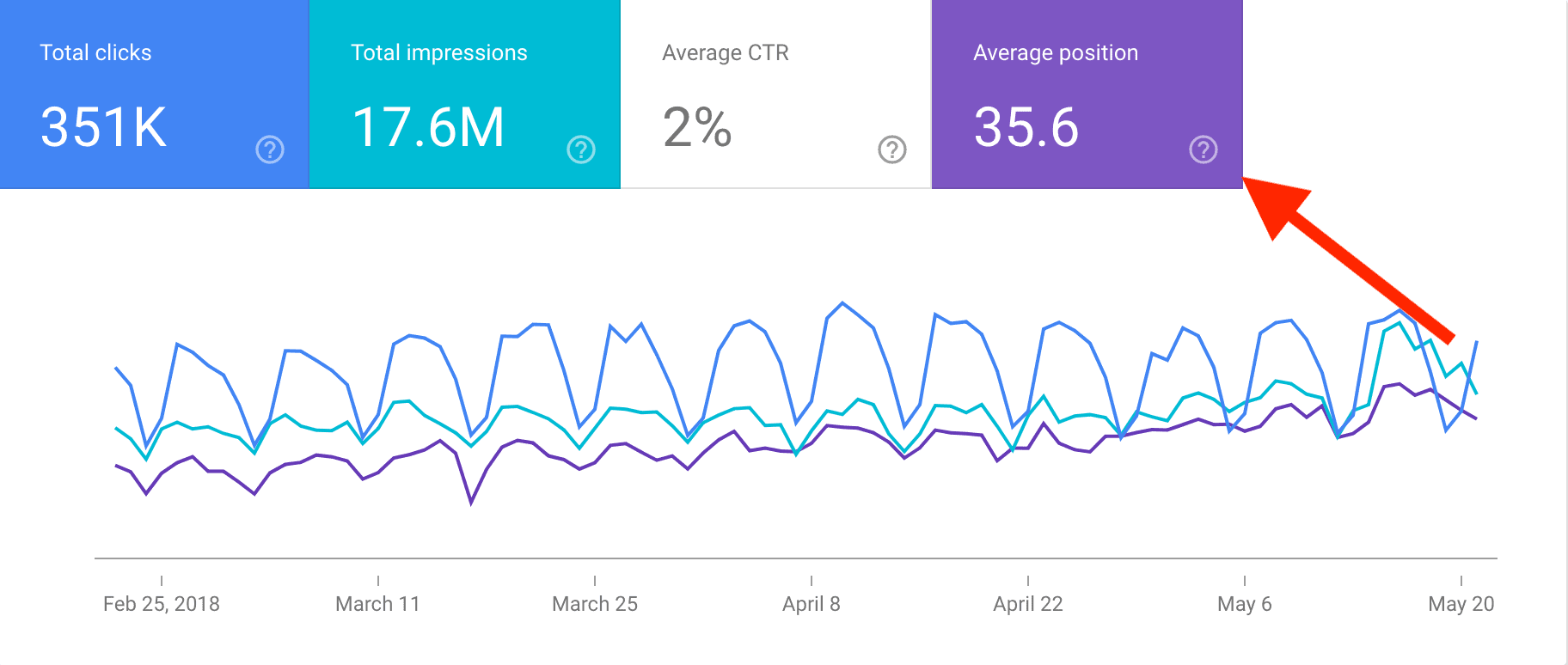
Then, sort the results by “Position”:
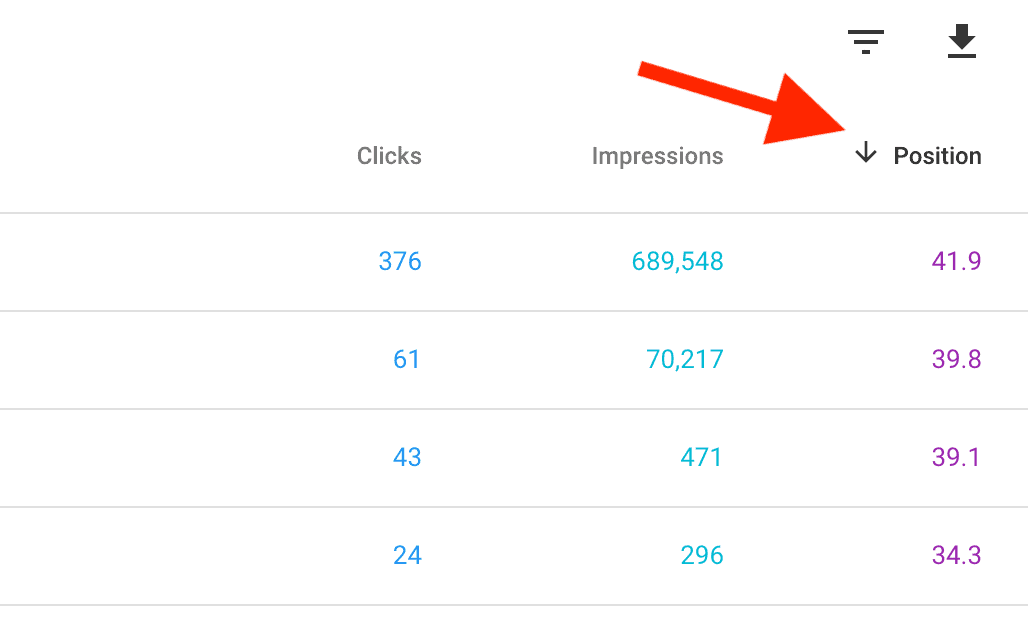
Next, look for keywords with an average position of 11-30.
If you’re getting clicks from a keyword on page 2 or 3, you can be pretty sure that keyword has some decent search volume.
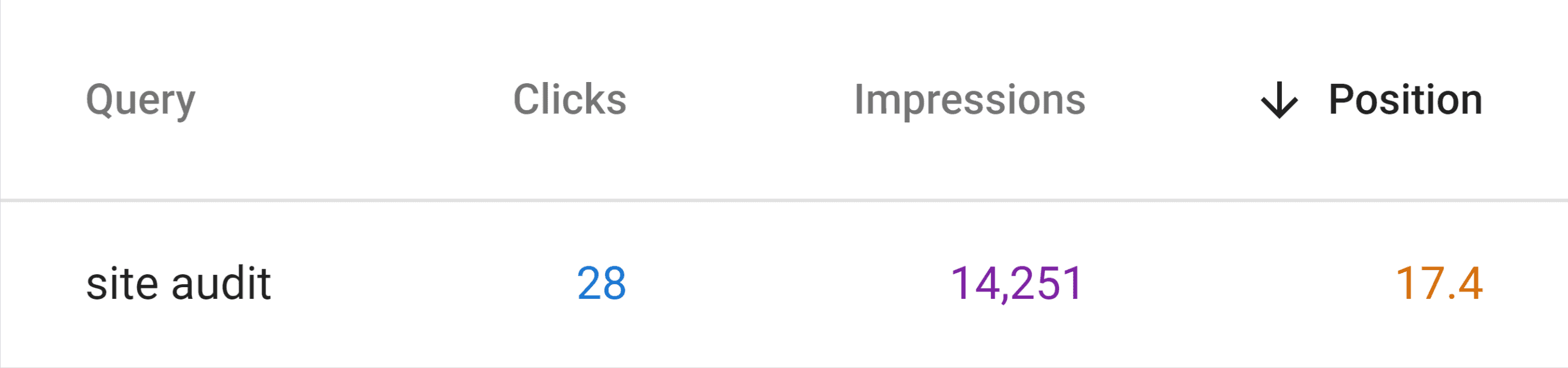
For example, this page from Backlinko is ranking #17 for the keyword “site audit”.
Even though I’m on the second page, I still get 28 clicks and 14,251 impressions per month for that keyword:
Sure enough, according to Semrush, that keyword gets 4.4k monthly searches with a suggested bid of $6.13.
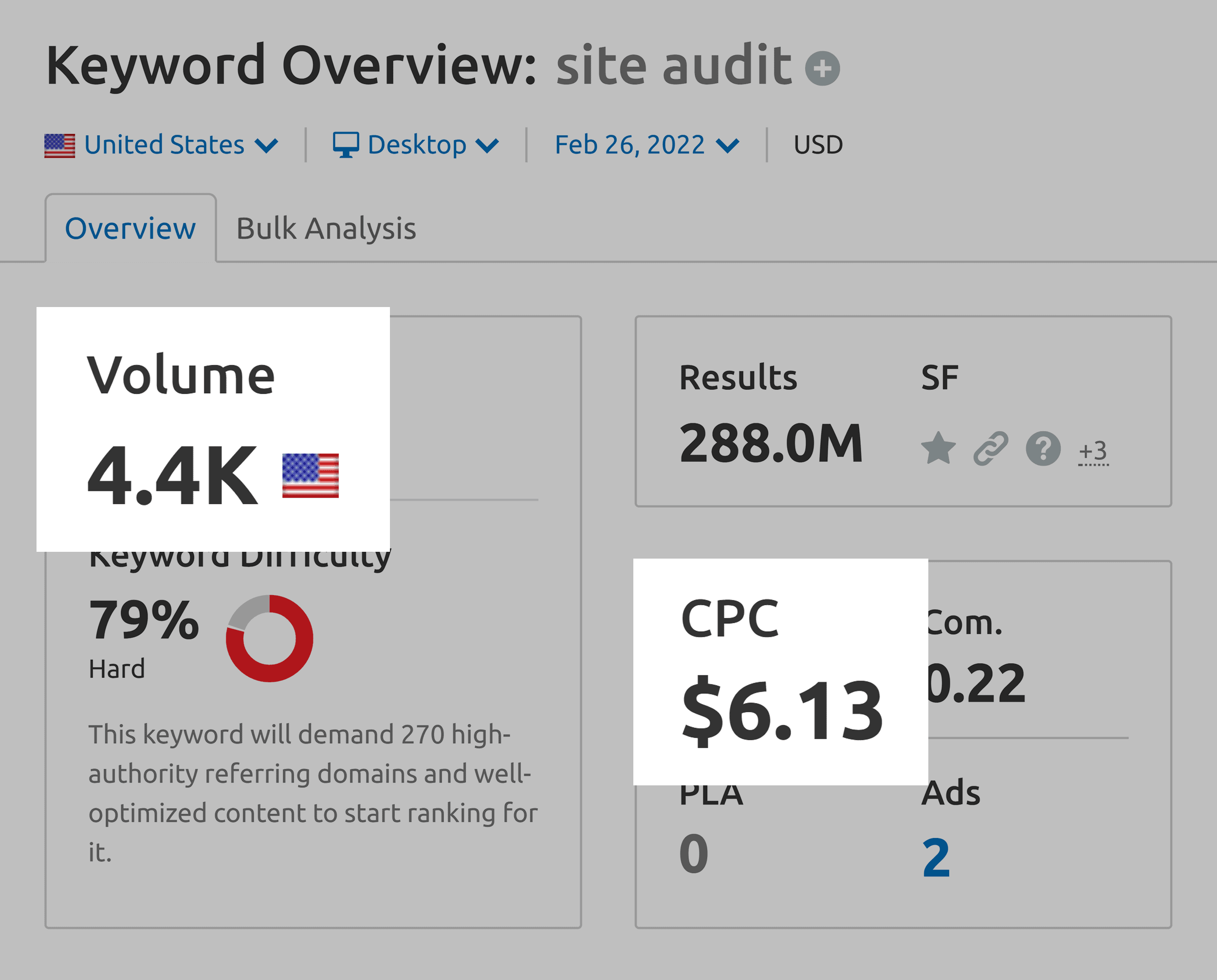
That means that it’s worth my time to get this post to Google’s first page.
Step #2: Identify authoritative pages on your site.
You can easily find the pages on your site with the most juice to pass around using Semrush.
Just enter your homepage URL into the tool and click “Search”:
Then click on “Backlink Analytics” in the left-hand sidebar and then on “Indexed Pages”.
That will show you the most authoritative pages on your site:
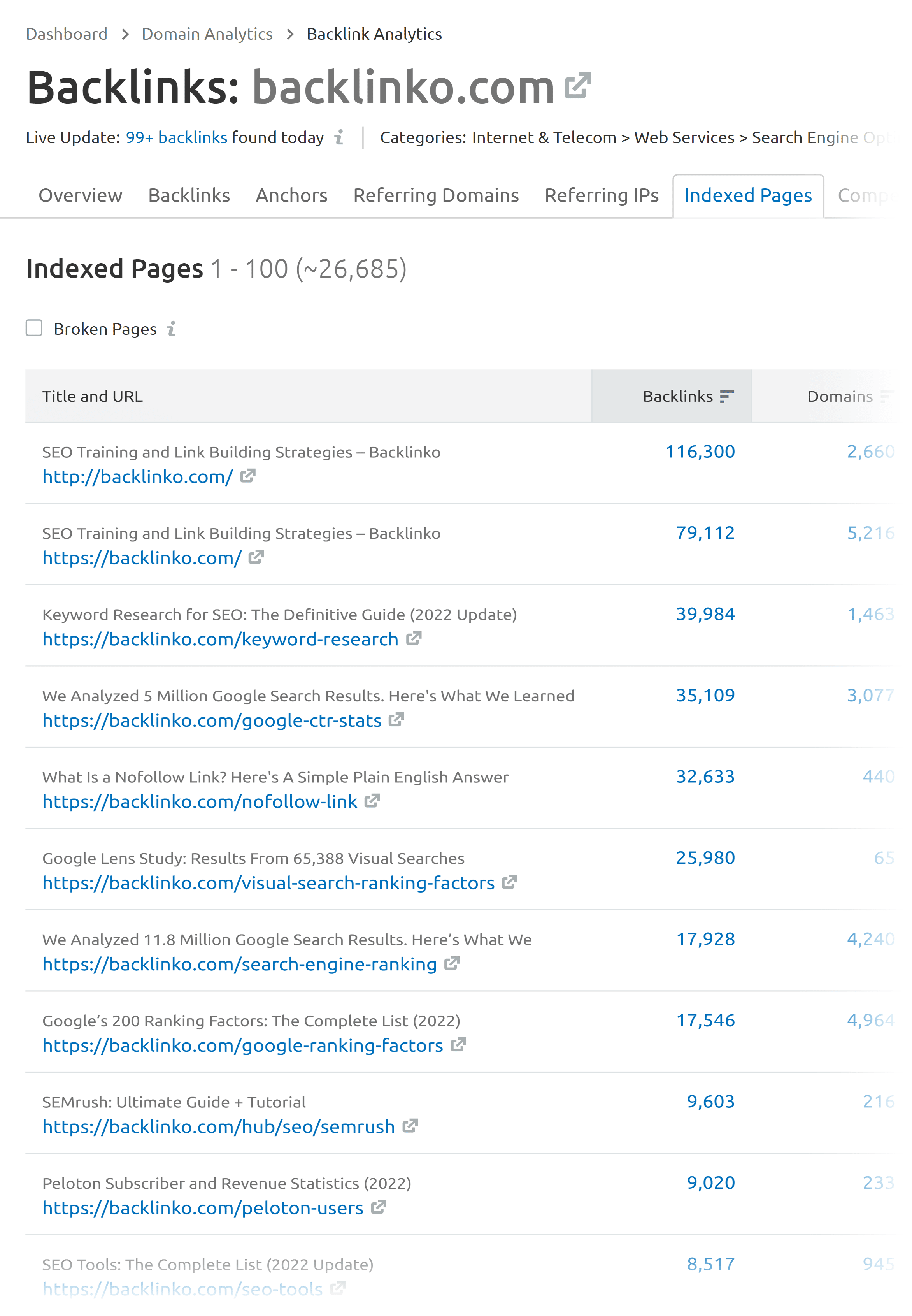
Step #3: Go to those landing pages and add internal links.
Finally, add internal links from those authoritative pages to the landing page that needs a boost.

10. Increase Email Outreach Response Rates
When someone sees an email from a random person in their inbox, two questions enter their mind:
“Who is this person?” and “What do they want?”
The faster you answer these questions in your outreach emails, the better your response rate will be.
But how can you do that?
Use the word “because” early in your email.
Research by Dr. Ellen Langer of Harvard University tested whether people waiting in line to use a copy machine would let a stranger cut in front of them.

When the stranger asked: “Can I use the copy machine before you?”, only 61% of people said “yes”.
But when the stranger asked: “Can I use the copy machine before you because I’m in a rush?”, 89% said yes.
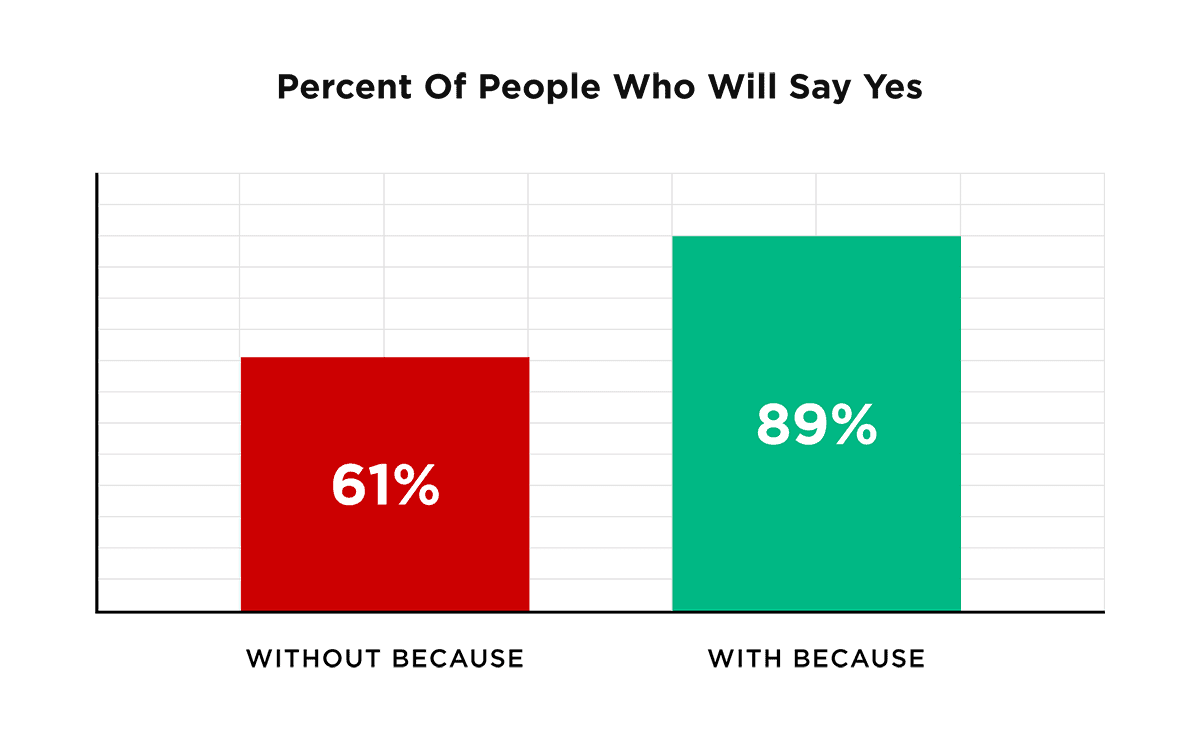
(That’s a 45% increase.)
It turns out that the word “because” makes your request seem more legitimate.
In the world of outreach, legit messages get better responses.
Here’s an example blogger outreach pitch that leverages the word “because” early on:
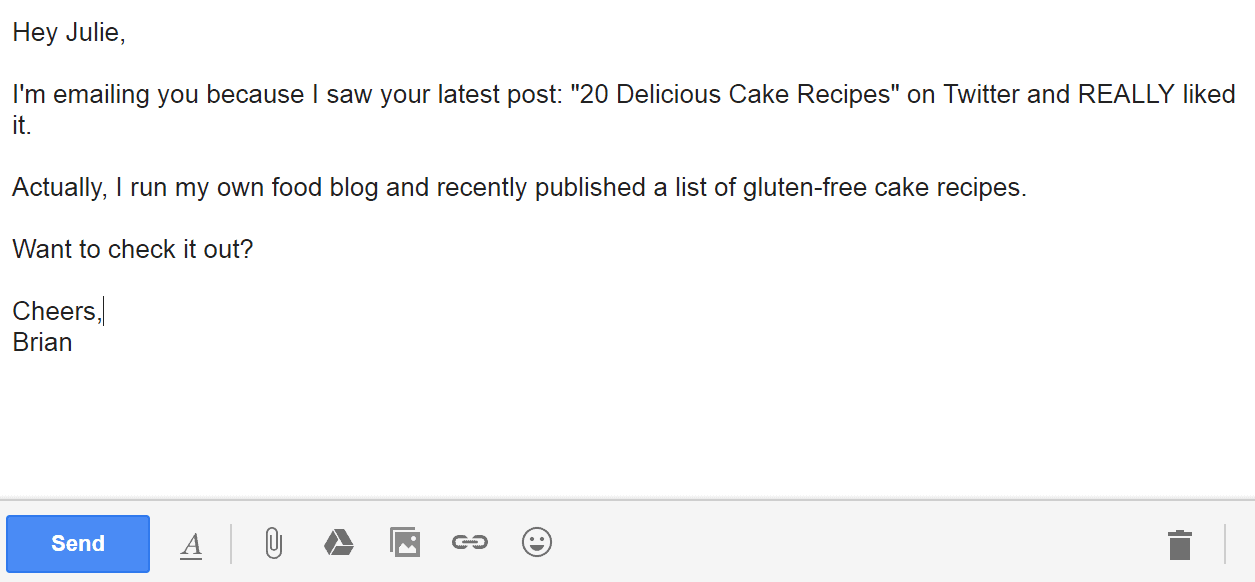
The person receiving that message knows why I’m emailing them after two seconds of reading.
But more importantly, the word “because” cements my reason for reaching out as more legit.
11. Write Long YouTube Descriptions
According to Semrush Sensor, videos appear on over 10% of all SERPs.
And considering that Google owns the popular video site, it’s a trend that’s not likely to change anytime soon.
And if you want your video to rank in Google, I recommend writing long video descriptions.
Remember: Google can’t watch or listen to your video content.
Instead, they rely on your video’s text-based title and description to determine what your video is about.
And this extra text content can help you rank for your target keywords.
For example, I recently published this video that outlines a handful of DIY search engine optimization strategies:
And here’s the description for that video:
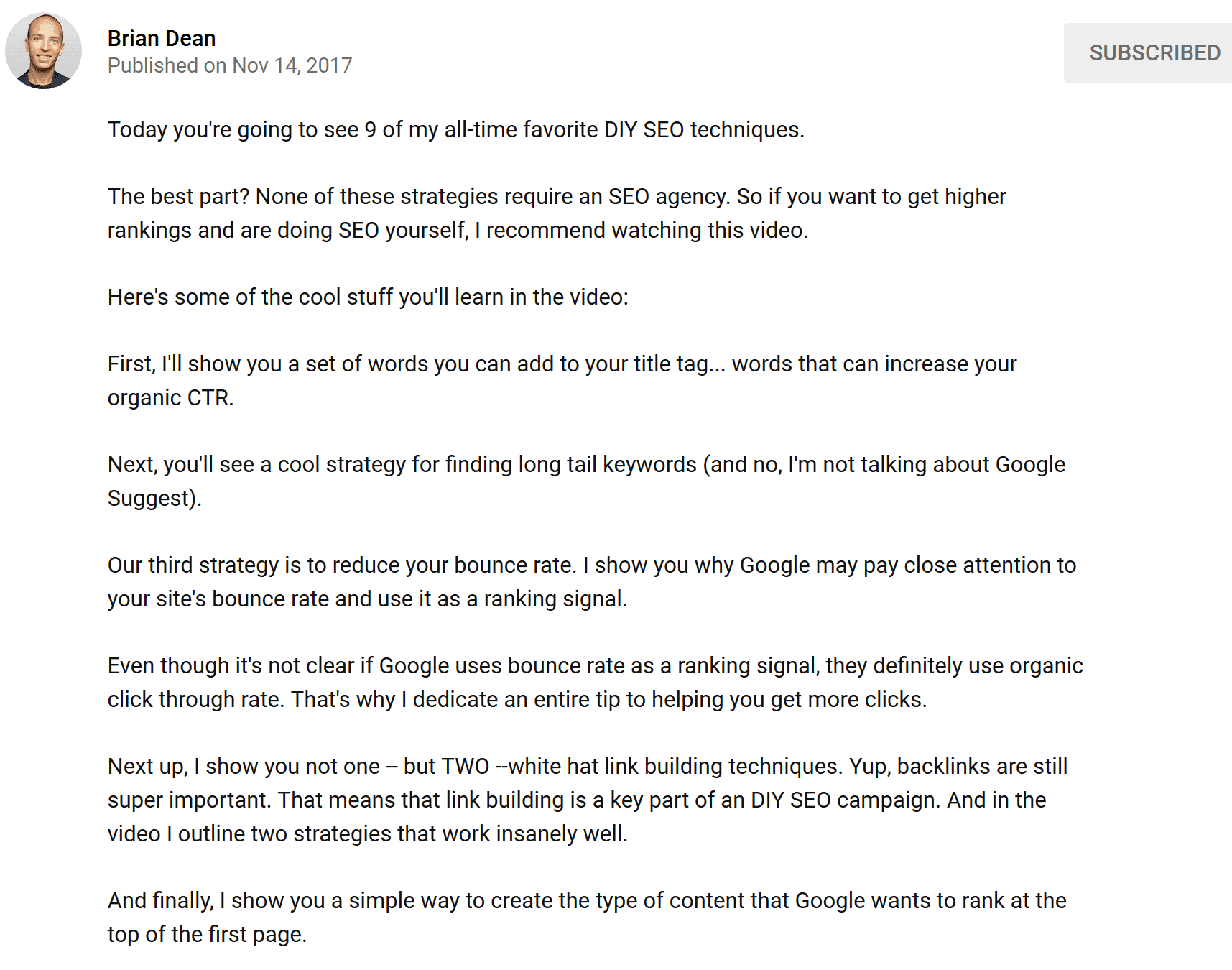
As you can see, that’s a high-quality, 200-word video description (you may have also noticed that it contains my target keyword, “DIY SEO”, several times).
And this description is one reason that my video rocketed to the first page of YouTube for my target keyword:

12. Optimize Content For Semantic SEO
A few years ago, Google rolled out a search algorithm called Hummingbird.
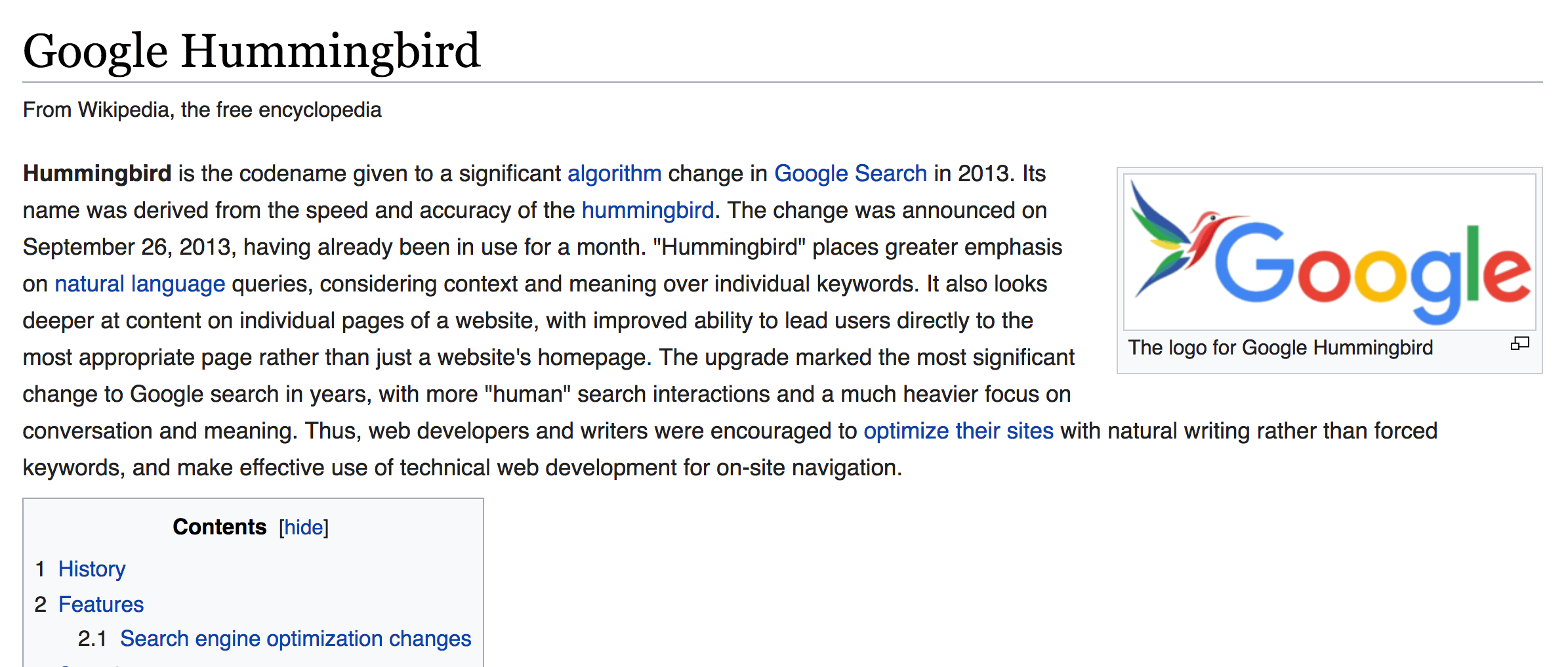
Before Hummingbird, basically, Google only analyzed the individual keywords on your page.

But thanks to this new algorithm, Google could now understand the topic of your page.
(By the way, the ability for search engines to understand topics is called: Semantic SEO.)
Here’s how to get started with semantic SEO:
First, optimize your page around your target keyword just like you normally would.
Then, cover subtopics related to your target keyword.
That way, Google can fully understand the topic of your page (not just your keyword).
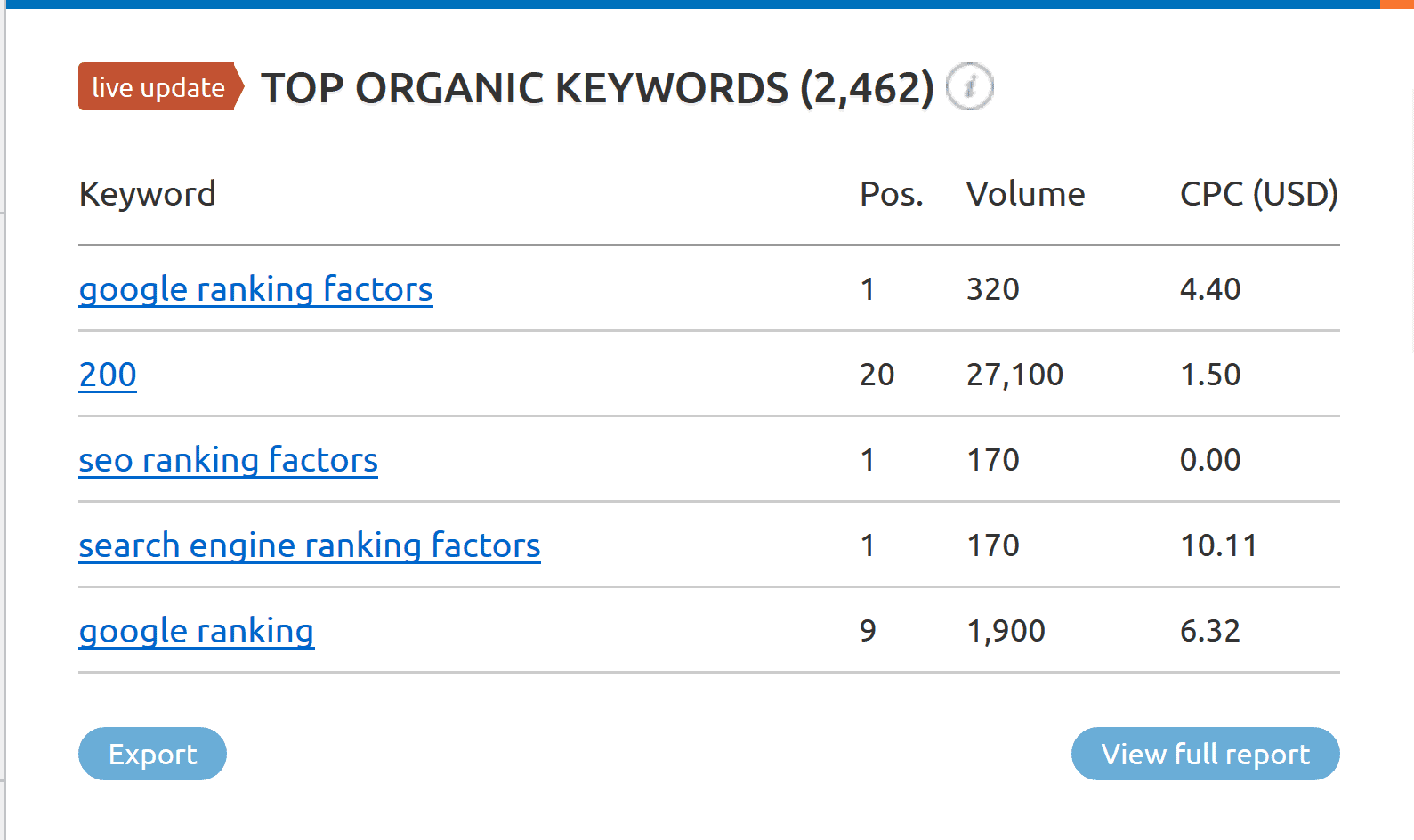
For example, this page on my site is a list of 200 Google ranking factors:

Because I cover subtopics (like Google penalties and site-level factors), Google knows what my content is about.
And because Google can fully understand my content’s topic, it ranks this single page for over 2,400 keywords (according to Semrush):
You can find related subtopics using a tool called LSIGraph:
This tool shows you subtopics (and terms) that are related to the keyword you typed into it.
13. Embed Long Tail Keywords In Title Tags
Here’s an example of this strategy in action:
I’ll explain: A while ago I published a post called “White Hat SEO Case Study: How To Get a #1 Ranking.”

My target keyword for that post was, “white hat SEO“.
So I included the keyword “white hat SEO” in the post’s title.
But I didn’t stop there…
I realized that the keyword “SEO case study” also got a decent amount of searches every month:
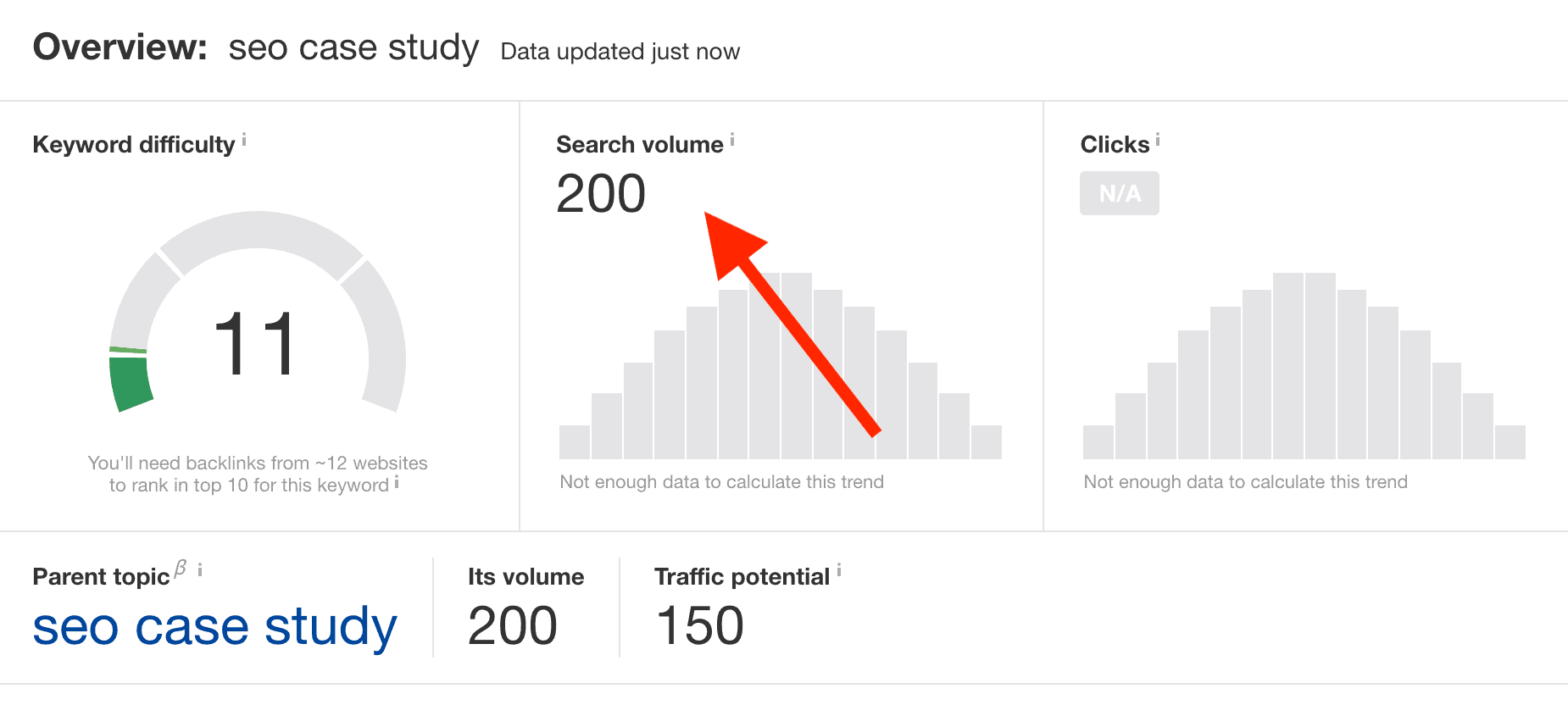
So I decided to embed that long-tail keyword into the blog post title:
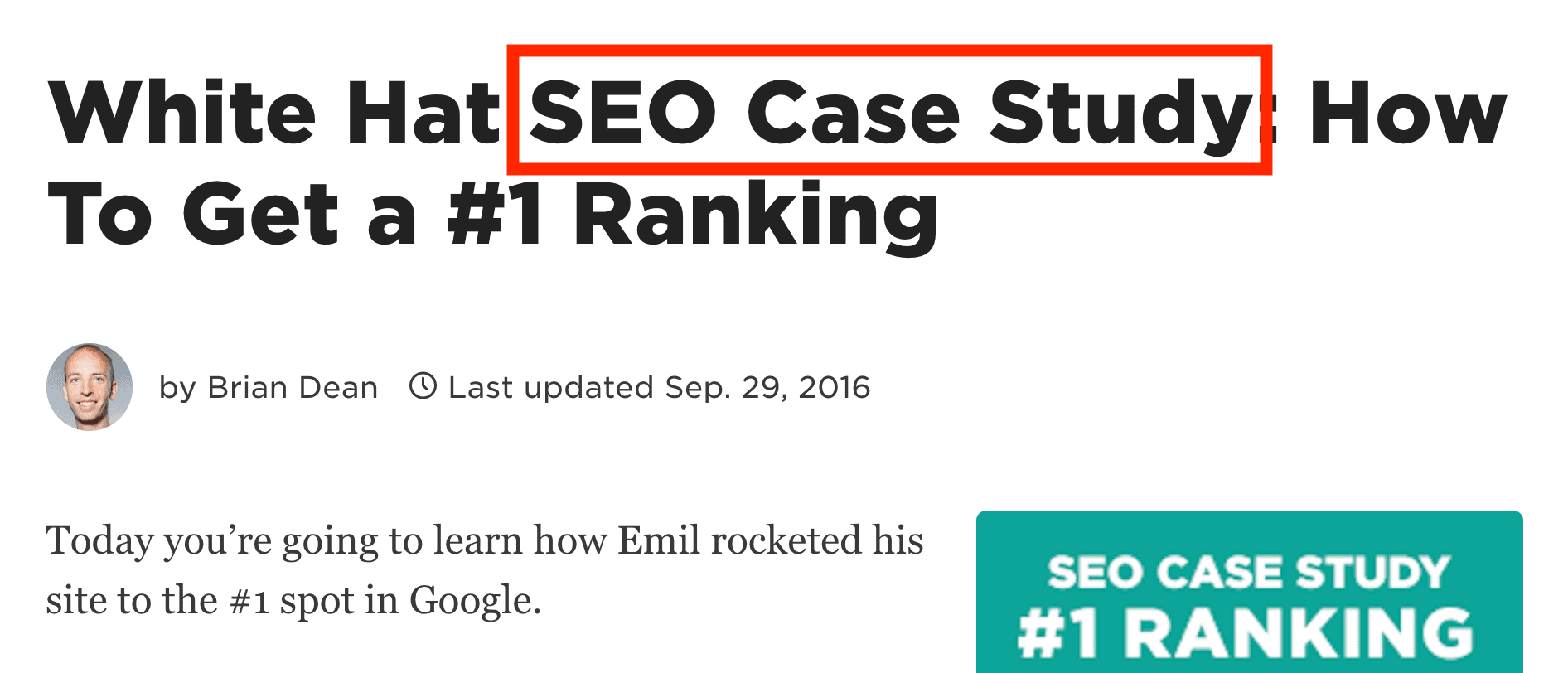
And it hit #5 spot for “SEO case study” in a few short weeks.
As you might expect, the keyword “SEO case study” is MUCH less competitive than “white hat SEO”.
Because of that, I got traffic from the keyword “SEO case study” within weeks.
And as that page has accumulated links, it made its way onto the first page for “white hat SEO”.
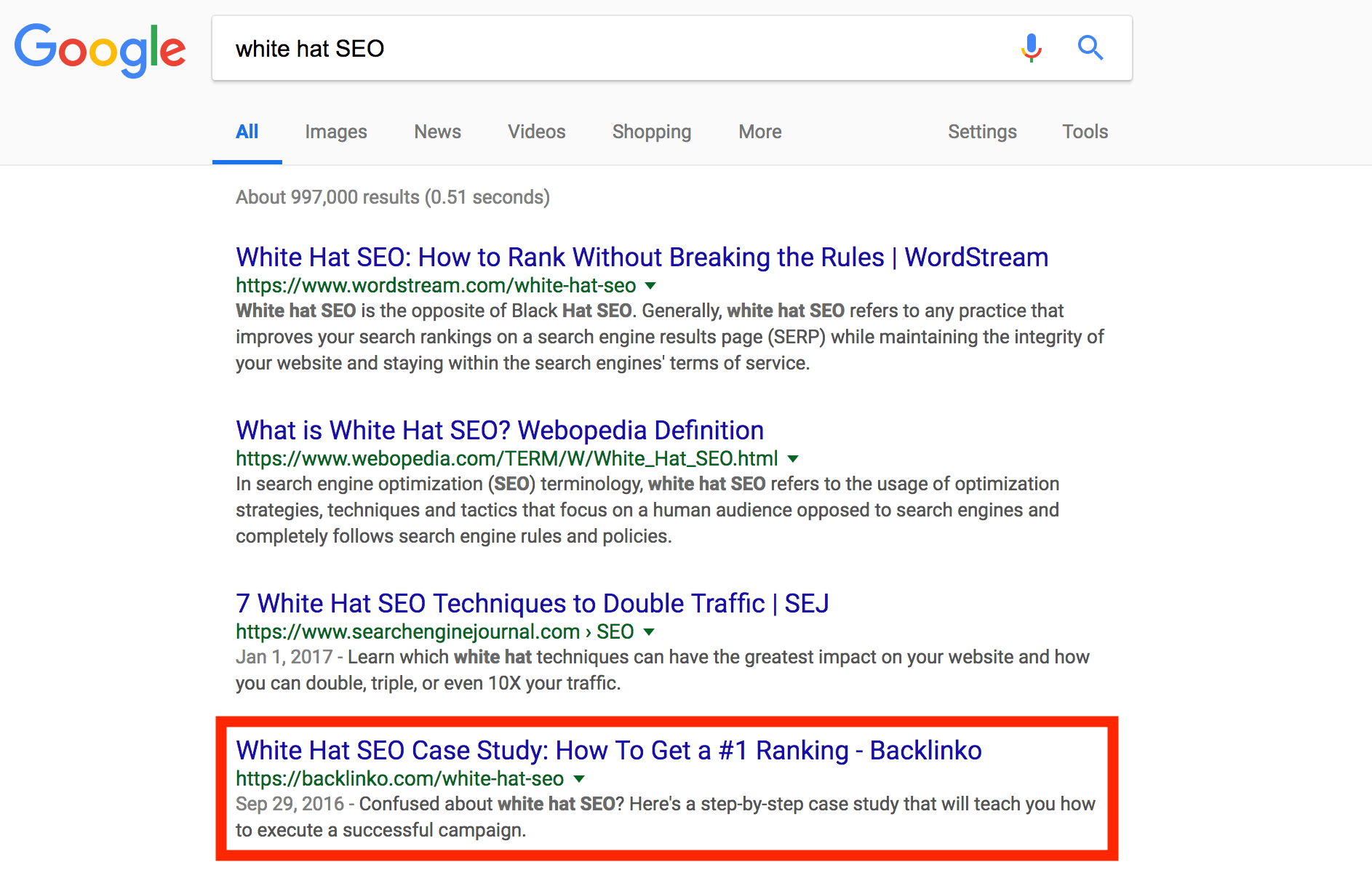
If I had only optimized for “white hat SEO”, I wouldn’t have received any organic traffic until I hit the first page for my target keyword.
Bottom line:
Find long-tail terms that you can embed into your titles.
You’ll get search engine traffic faster… and eventually, rank the page for more than one term.
14. Use Wikipedia for Keyword and Topic Ideas
Want to find untapped keywords that your competition doesn’t know about?
Try Wikipedia.
Why?
If you want to find keywords that are closely related to your seed keyword, you need a human mind.
Or better yet, the thousands of human minds that contribute to Wikipedia.
Here’s how:
Head over to Wikipedia and enter a keyword (I’m going to use the keyword “insurance” in this example):
Next, keep an eye out for sections on the Wikipedia entry that display closely related keywords and topics.
These sections are… The “Contents” box:

Callouts and sidebars:

Internal links:

And “See Also” sections:
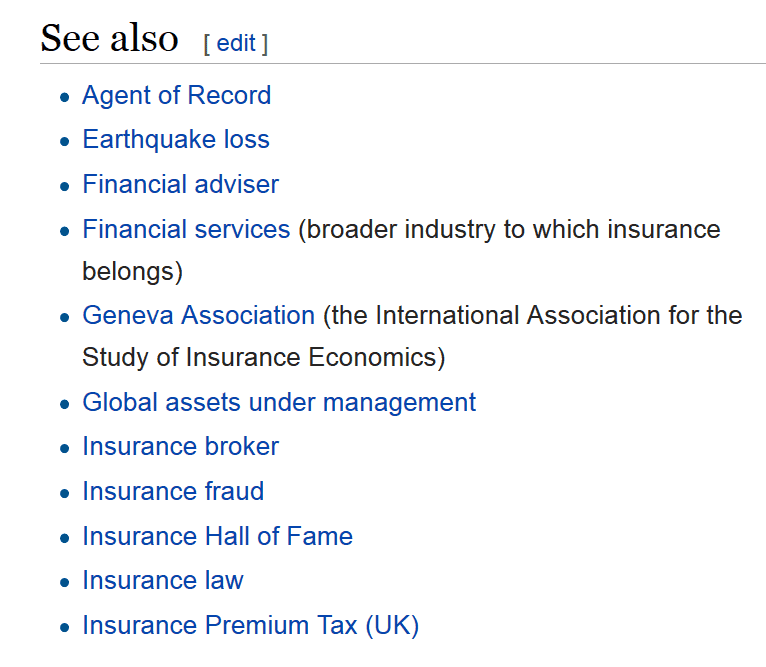
You’ll usually come away with fistfuls of keyword and topic ideas from a single Wikipedia entry.
If you want to find even more keyword ideas, click on an internal link.
Then simply follow the same process for that Wikipedia entry.
Rinse and repeat.
15. Find Link Building Opportunities From “Best of” Lists
If you do a lot of link building, you know that finding niche-relevant link prospects is not always easy.
What you may not realize is that bloggers in your niche create these lists for you in the form of “best of” blog posts.
“Best of” blog posts are simply hand-curated lists of the best blogs in a specific industry.
How can you find these “best of” blog posts?
Use these search strings:
- “[keyword] blogs to follow”
- “best [keyword] posts 2024”
- “top [keyword] blogs to follow” + “2024”
For example, I just did a quick search for “fitness blogs to follow”:
I found this list of 10 blogs in the fitness space:
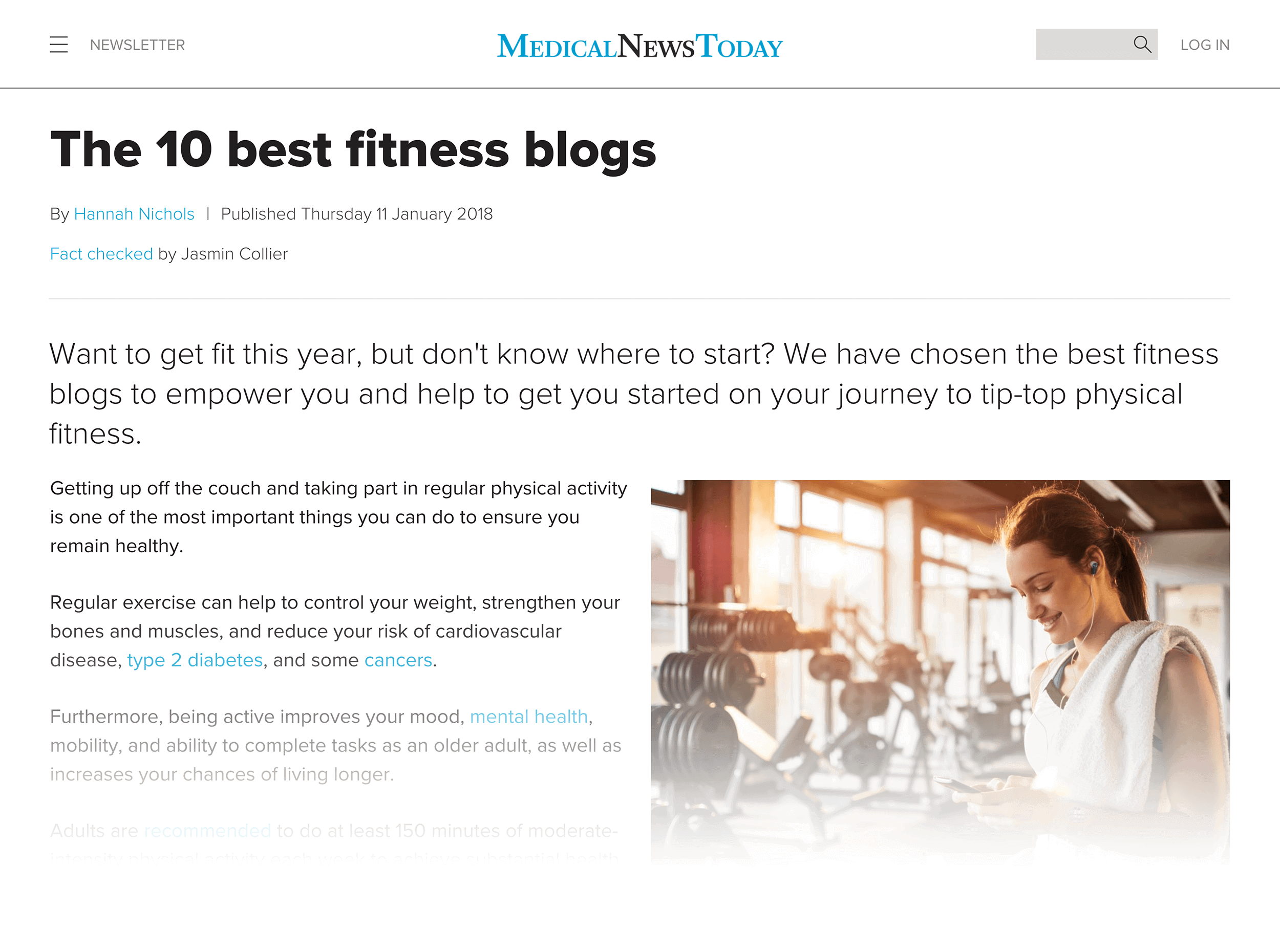
These 10 blogs are perfect places to reach out to the next time you want to promote a piece of content or build a long-term relationship.
16. Publish Content With At Least 1,447 Words
There’s no denying it: longer content CRUSHES short 300-word blog posts.
In fact, our study of 11.8 million Google search results found that the average word count of a first page Google results was 1,447 words.
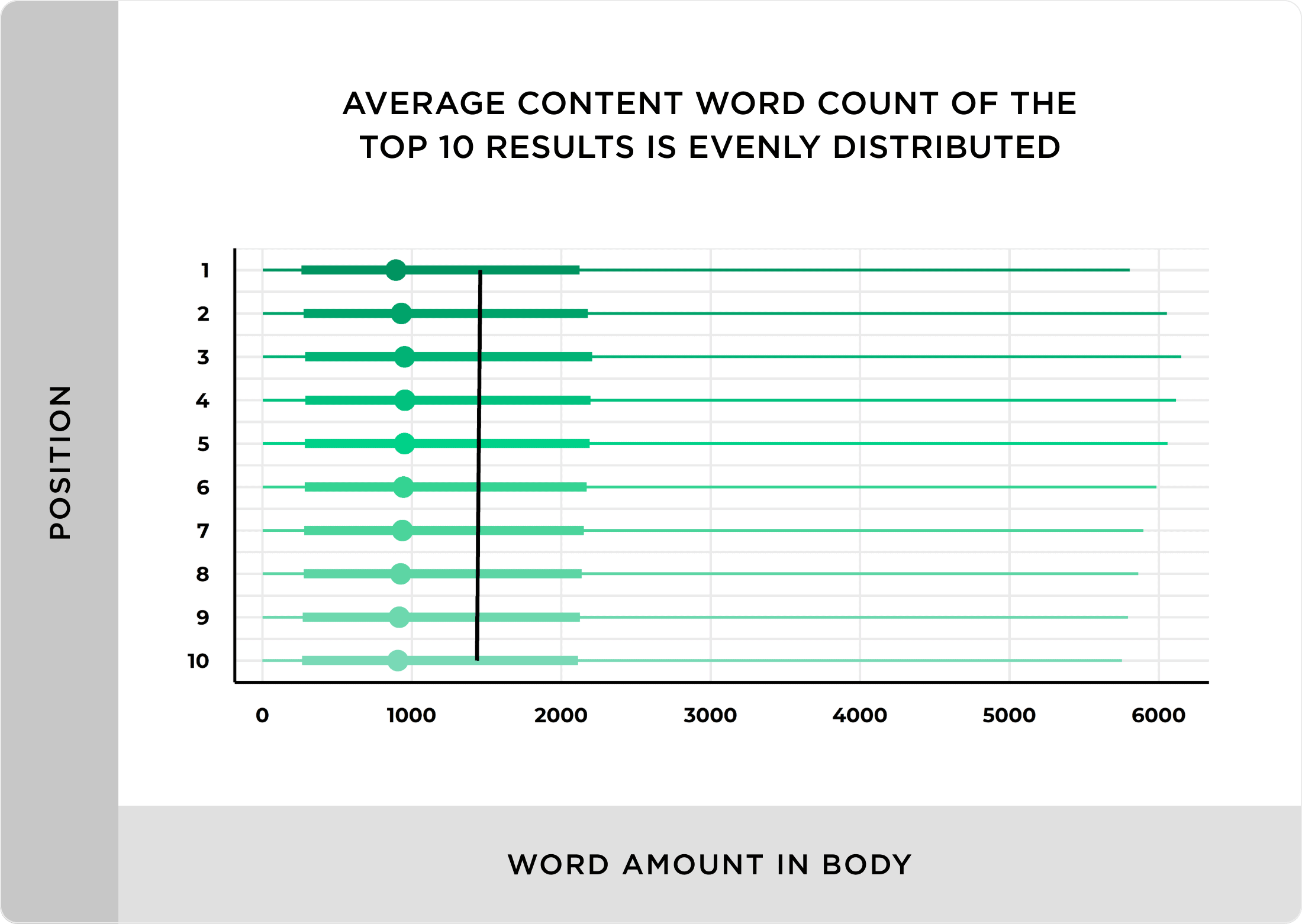
(Are long pieces of content mobile-friendly? According to our data, yes. Longer content also performed well for mobile searches)
Why do long posts work? First off, long posts show Google that you’re providing in-depth information for searchers.
Which is something that Google (obviously) wants to see.
17. Remember the “First Link Priority Rule”
Let’s say you have two links pointing to a page on your site… and both of those links are on the same page.
Which anchor text does Google pay attention to? The first one? The second one? Both?
According to the First Link Priority Rule, only the first link.
Why is this important?
Let’s say you have a navigation bar on your site, like this:

Because your navigation is at the top of the page, Google sees those links first.
Here’s where things get tricky:
Let’s say that you drop a link to your “Recipe Index” page in a blog post.
And that link has the anchor text: “healthy recipes”.
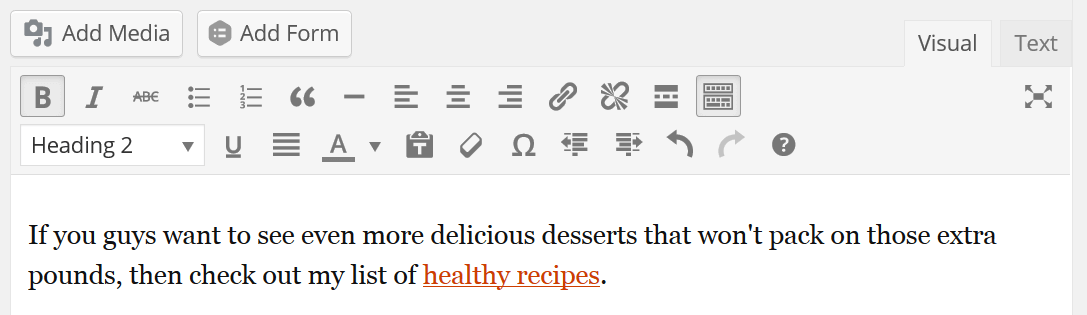
Unfortunately, the “healthy recipes” anchor text is ignored by Big G.
Google only counts the anchor text it saw first: “Recipe Index”.
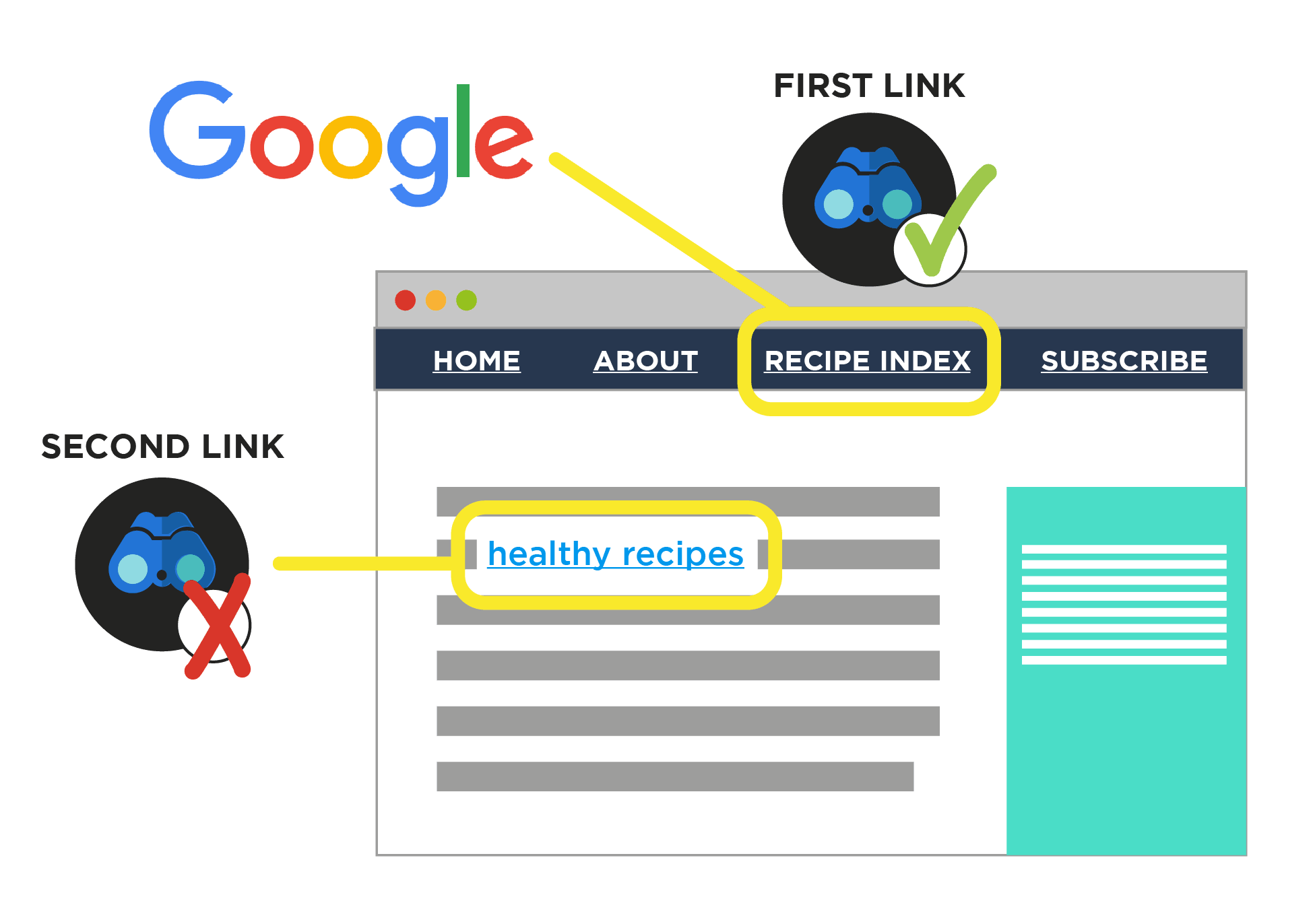
Bottom line Takeaway:
Use keyword-rich anchors in your site’s navigation.
As you just learned, the keyword-rich internal links below them don’t count.
18. Create Your Own Keywords
This is one of the best pieces of SEO advice I’ve ever learned:
You always rank #1 for keywords that you create.
When you create something truly original (like a brand, product, or a step-by-step system) you’re the only person optimizing for that term.
(After all, you made it up.)
And if your creation becomes popular, you’ll suddenly find yourself ranking #1 for a high-volume keyword.
Let me show you an example:
A while back I published a post called: Link Building Case Study: How I Increased My Search Traffic by 110% in 14 Days.
Now I could have optimized my post around a keyword like: “link building strategy”.
Instead, I decided to create my own keyword: “The Skyscraper Technique“.
Today, I get a steady stream of organic traffic from people searching for that keyword that I created.
How can you do the same thing?
The next time that you write about a technique that you created (whether it’s a diet tip, productivity hack or system for growing tomatoes) name it.
19. Use Creative Seed Keywords
If you’ve been in the SEO world for a while you know that a keyword tool is only as good as the seed keywords you put into it.
In other words:
If you use the same seed keywords as your competition, you’re going to see the same keywords they do.
Fortunately, there’s a little-known tool that helps you get around this problem: SeedKeywords.com.

Here’s how to use it:
First, head over to Seed Keywords and create a scenario.
(A scenario is what someone would use to find your business online.)
Hit “create my scenario” and you’ll get a special link.
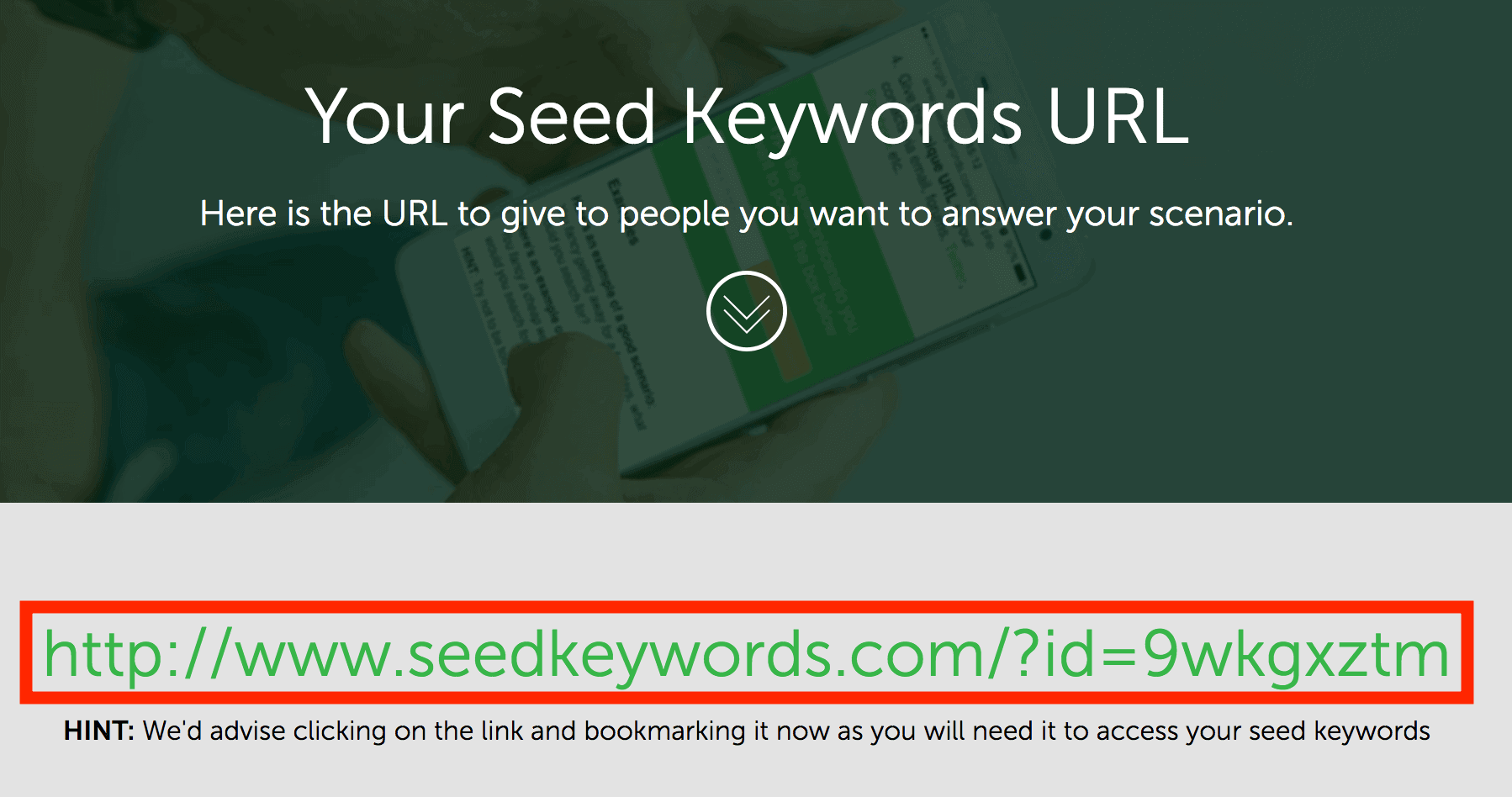
Send this link to friends, family and target customers to see what keywords they would use:
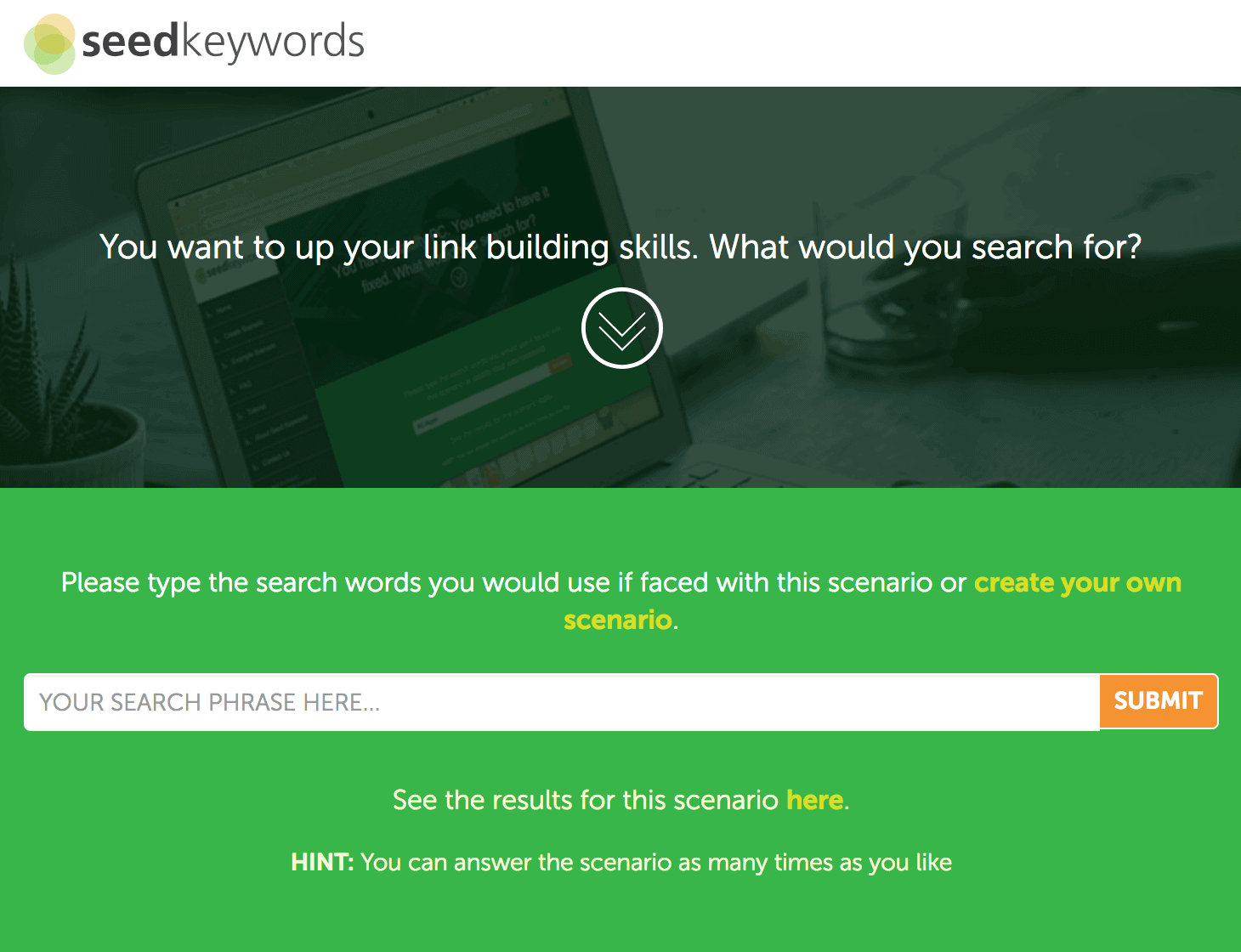
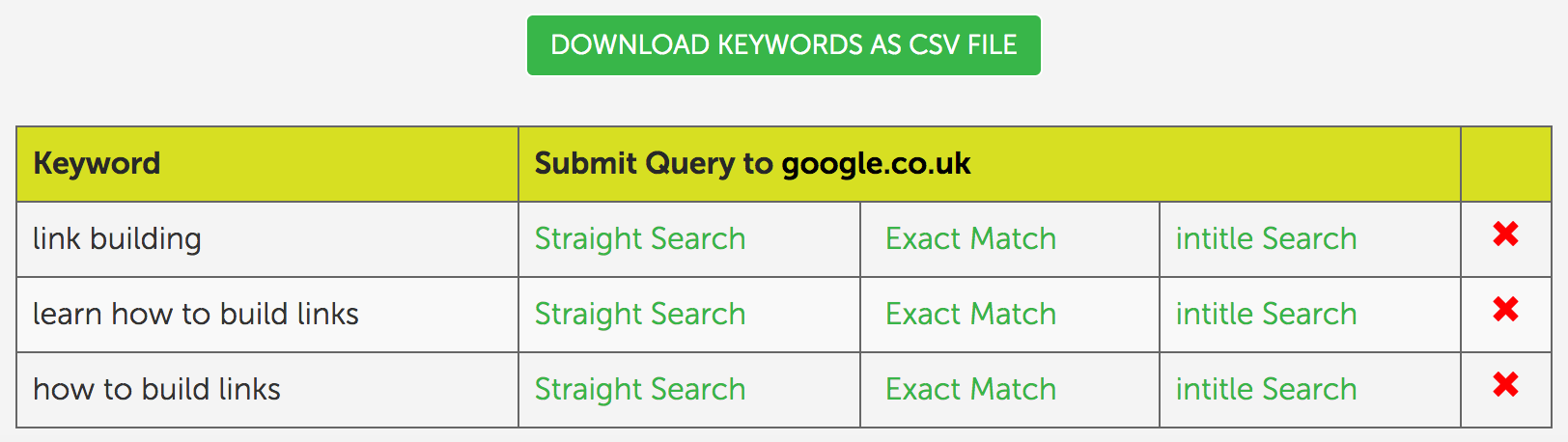
And you’ll get a list of outside-the-box seed keywords that you can pop into the Google Keyword Planner.
Wrapping Things Up
Backlinko is owned by Semrush. We’re still obsessed with bringing you world-class SEO insights, backed by hands-on experience. Unless otherwise noted, this content was written by either an employee or paid contractor of Semrush Inc.